
Spin tensor
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
and mathematical physics
, the Euclidean group
of direct isometries is generated by translation
s and rotation
s. Its Lie algebra
is written
 .
.
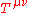 .
.
It satisfies the continuity equation
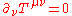 .
.
And
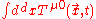
gives the energy-momentum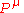 at time t, which is time-independent.
at time t, which is time-independent.
The Noether current for a rotation about the point y is given by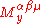 .
.
Because of the Lie algebra relations,
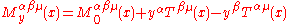 ,
,
where 0 is the origin
.
And
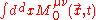
gives the angular momentum
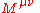 at time t.
at time t.
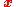 to be the value of the Noether current at
to be the value of the Noether current at 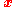 of a rotation about x,
of a rotation about x,
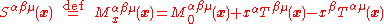
Because of the continuity equation
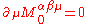 ,
,
we get
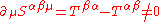
and therefore, the stress-energy tensor
isn't symmetric.
S gives the spin density and M gives the angular momentum density. The angular momentum is the sum of the orbital angular momentum and spin
.
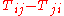 gives the torque
gives the torque
density showing the rate of conversion between the orbital angular momentum and spin.
and turbulent fluids. For molecular fluids, the individual molecules may be spinning. The electromagnetic field can have circularly polarized light. For turbulent fluids, we may arbitrarily make a distinction between long wavelength phenomena and short wavelength phenomena. A long wavelength vorticity may be converted via turbulence into tinier and tinier vortices transporting the angular momentum into smaller and smaller wavelengths while simultaneously reducing the vorticity. This can be approximated by the eddy viscosity.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
and mathematical physics
Mathematical physics
Mathematical physics refers to development of mathematical methods for application to problems in physics. The Journal of Mathematical Physics defines this area as: "the application of mathematics to problems in physics and the development of mathematical methods suitable for such applications and...
, the Euclidean group
Euclidean group
In mathematics, the Euclidean group E, sometimes called ISO or similar, is the symmetry group of n-dimensional Euclidean space...
- SE(d)
of direct isometries is generated by translation
Translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. Whereas interpreting undoubtedly antedates writing, translation began only after the appearance of written literature; there exist partial translations of the Sumerian Epic of...
s and rotation
Rotation
A rotation is a circular movement of an object around a center of rotation. A three-dimensional object rotates always around an imaginary line called a rotation axis. If the axis is within the body, and passes through its center of mass the body is said to rotate upon itself, or spin. A rotation...
s. Its Lie algebra
Lie algebra
In mathematics, a Lie algebra is an algebraic structure whose main use is in studying geometric objects such as Lie groups and differentiable manifolds. Lie algebras were introduced to study the concept of infinitesimal transformations. The term "Lie algebra" was introduced by Hermann Weyl in the...
is written
 .
.Noether currents
The Noether currents for the translations make up the stress-energy tensorStress-energy tensor
The stress–energy tensor is a tensor quantity in physics that describes the density and flux of energy and momentum in spacetime, generalizing the stress tensor of Newtonian physics. It is an attribute of matter, radiation, and non-gravitational force fields...
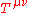 .
.It satisfies the continuity equation
Continuity equation
A continuity equation in physics is a differential equation that describes the transport of a conserved quantity. Since mass, energy, momentum, electric charge and other natural quantities are conserved under their respective appropriate conditions, a variety of physical phenomena may be described...
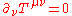 .
.And
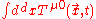
gives the energy-momentum
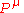 at time t, which is time-independent.
at time t, which is time-independent.The Noether current for a rotation about the point y is given by
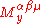 .
.Because of the Lie algebra relations,
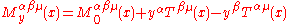 ,
,where 0 is the origin
Origin (mathematics)
In mathematics, the origin of a Euclidean space is a special point, usually denoted by the letter O, used as a fixed point of reference for the geometry of the surrounding space. In a Cartesian coordinate system, the origin is the point where the axes of the system intersect...
.
And
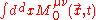
gives the angular momentum
Angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
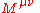 at time t.
at time t.Definition
Define the spin tensor at a point to be the value of the Noether current at
to be the value of the Noether current at  of a rotation about x,
of a rotation about x,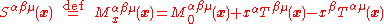
Because of the continuity equation
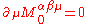 ,
,we get
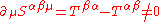
and therefore, the stress-energy tensor
Stress-energy tensor
The stress–energy tensor is a tensor quantity in physics that describes the density and flux of energy and momentum in spacetime, generalizing the stress tensor of Newtonian physics. It is an attribute of matter, radiation, and non-gravitational force fields...
isn't symmetric.
S gives the spin density and M gives the angular momentum density. The angular momentum is the sum of the orbital angular momentum and spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
.
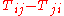 gives the torque
gives the torqueTorque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
density showing the rate of conversion between the orbital angular momentum and spin.
Examples
Examples of materials with a nonzero spin density are molecular fluids, the electromagnetic fieldElectromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field is a physical field produced by moving electrically charged objects. It affects the behavior of charged objects in the vicinity of the field. The electromagnetic field extends indefinitely throughout space and describes the electromagnetic interaction...
and turbulent fluids. For molecular fluids, the individual molecules may be spinning. The electromagnetic field can have circularly polarized light. For turbulent fluids, we may arbitrarily make a distinction between long wavelength phenomena and short wavelength phenomena. A long wavelength vorticity may be converted via turbulence into tinier and tinier vortices transporting the angular momentum into smaller and smaller wavelengths while simultaneously reducing the vorticity. This can be approximated by the eddy viscosity.

