
Squeezed coherent state
Encyclopedia
In physics
, a squeezed coherent state is any state of the quantum mechanical Hilbert space
such that the uncertainty principle
is saturated. That is, the product of the corresponding two operator
s takes on its minimum value:

The simplest such state is the ground state of the quantum harmonic oscillator
of the quantum harmonic oscillator
. The next simple class of states that satisfies this identity are the family of coherent state
s .
.
Often, the term squeezed state is used for any such state with in "natural oscillator units". The idea behind this is that the circle denoting a coherent state in a quadrature
in "natural oscillator units". The idea behind this is that the circle denoting a coherent state in a quadrature
diagram (see below) has been "squeezed" to an ellipse
of the same area.
 )
)

where are constants (a normalization constant, the center of the wavepacket, its width, and its average momentum
are constants (a normalization constant, the center of the wavepacket, its width, and its average momentum
). The new feature relative to a coherent state
is the free value of the width , which is the reason why the state is called "squeezed".
, which is the reason why the state is called "squeezed".
The squeezed state above is an eigenstate of a linear operator

and the corresponding eigenvalue equals . In this sense, it is a generalization of the ground state as well as the coherent state.
. In this sense, it is a generalization of the ground state as well as the coherent state.
is reduced, one can distinguish amplitude-squeezed and phase-squeezed states or general quadrature squeezed states. If no coherent excitation exists the state is called a squeezed vacuum. The figures below give a nice visual demonstration of the close connection between squeezed states and Heisenberg's uncertainty relation: Diminishing the quantum noise at a specific quadrature (phase) of the wave has as a direct consequence an enhancement of the noise of the complementary quadrature, that is, the field at the phase shifted by .
.
From the top:
As can be seen at once, in contrast to the coherent state
the quantum noise is not independent of the phase of the light wave anymore. A characteristic broadening and narrowing of the noise during one oscillation period can be observed. The wave packet
of a squeezed state is defined by the square of the wave function introduced in the last paragraph. They correspond to the probability distribution of the electric field strength of the light wave. The moving wave packets display an oscillatory motion combined with the widening and narrowing of their distribution: the "breathing" of the wave packet. For an amplitude-squeezed state, the most narrow distribution of the wave packet is reached at the field maximum, resulting in an amplitude that is defined more precisely than the one of a coherent state. For a phase-squeezed state, the most narrow distribution is reached at field zero, resulting in an average phase value that is better defined than the one of a coherent state.
In phase space, quantum mechanical uncertainties can be depicted by Wigner distribution Wigner quasi-probability distribution
. The intensity of the light wave, its coherent excitation, is given by the displacement of the Wigner distribution from the origin. A change in the phase of the squeezed quadrature results in a rotation of the distribution.
number distribution of the light wave and its phase
distribution as well.
For amplitude squeezed light the photon number distribution is usually narrower than the one of a coherent state of the same amplitude resulting in sub-Poissonian
light, whereas its phase distribution is wider. The opposite is true for the phase-squeezed light, which displays a large intensity (photon number) noise but a narrow phase distribution. Nevertheless the statistics of amplitude squeezed light was not observed directly with photon number resolving detector due to experimental difficulty.
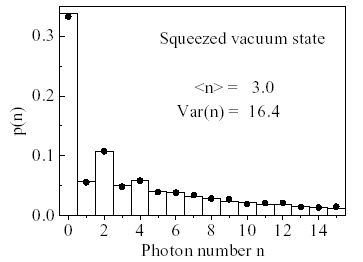 For the squeezed vacuum state the photon number distribution displays odd-even-oscillations. This can be explained by the mathematical form of the squeezing operator, that resembles the operator for two-photon generation
For the squeezed vacuum state the photon number distribution displays odd-even-oscillations. This can be explained by the mathematical form of the squeezing operator, that resembles the operator for two-photon generation
and annihilation processes. Photons in a squeezed vacuum state are more likely to appear in pairs.
s and non-linear optics (see optical parametric oscillator
). This is achieved by a simple process of four-wave mixing with a crystal; similarly traveling wave phase-sensitive amplifiers generate spatially-multimode quadrature-squeezed states of light when the
crystal; similarly traveling wave phase-sensitive amplifiers generate spatially-multimode quadrature-squeezed states of light when the  crystal is pumped in absence of any signal. Sub-poissonian current sources driving semiconductor laser diodes have led to amplitude squeezed light. Squeezed states have also been realized via motional states of an ion
crystal is pumped in absence of any signal. Sub-poissonian current sources driving semiconductor laser diodes have led to amplitude squeezed light. Squeezed states have also been realized via motional states of an ion
in a trap
, phonon
states in crystal lattices, or atom
ensembles. Even macroscopic oscillators were driven into classical motional states that were very similar to squeezed coherent states. Current state of the art in noise suppression, for laser radiation using squeezed light, amounts to 10 dB.
(see for example gravitational wave
s). Amplitude-squeezed light can improve the readout of very weak spectroscopic signals
.
Various squeezed coherent states, generalized to the case of many degrees of freedom
, are used in various calculations in quantum field theory
, for example Unruh effect
and Hawking radiation
, and generally, particle production in curved backgrounds and Bogoliubov transformation
).
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, a squeezed coherent state is any state of the quantum mechanical Hilbert space
Hilbert space
The mathematical concept of a Hilbert space, named after David Hilbert, generalizes the notion of Euclidean space. It extends the methods of vector algebra and calculus from the two-dimensional Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space to spaces with any finite or infinite number of dimensions...
such that the uncertainty principle
Uncertainty principle
In quantum mechanics, the Heisenberg uncertainty principle states a fundamental limit on the accuracy with which certain pairs of physical properties of a particle, such as position and momentum, can be simultaneously known...
is saturated. That is, the product of the corresponding two operator
Operator (physics)
In physics, an operator is a function acting on the space of physical states. As a resultof its application on a physical state, another physical state is obtained, very often along withsome extra relevant information....
s takes on its minimum value:

The simplest such state is the ground state
 of the quantum harmonic oscillator
of the quantum harmonic oscillatorQuantum harmonic oscillator
The quantum harmonic oscillator is the quantum-mechanical analog of the classical harmonic oscillator. Because an arbitrary potential can be approximated as a harmonic potential at the vicinity of a stable equilibrium point, it is one of the most important model systems in quantum mechanics...
. The next simple class of states that satisfies this identity are the family of coherent state
Coherent state
In quantum mechanics a coherent state is a specific kind of quantum state of the quantum harmonic oscillator whose dynamics most closely resembles the oscillating behaviour of a classical harmonic oscillator...
s
 .
.Often, the term squeezed state is used for any such state with
 in "natural oscillator units". The idea behind this is that the circle denoting a coherent state in a quadrature
in "natural oscillator units". The idea behind this is that the circle denoting a coherent state in a quadratureQuadrature
Quadrature may refer to:In signal processing:*Quadrature amplitude modulation , a modulation method of using both an carrier wave and a 'quadrature' carrier wave that is 90° out of phase with the main, or in-phase, carrier...
diagram (see below) has been "squeezed" to an ellipse
Ellipse
In geometry, an ellipse is a plane curve that results from the intersection of a cone by a plane in a way that produces a closed curve. Circles are special cases of ellipses, obtained when the cutting plane is orthogonal to the cone's axis...
of the same area.
Mathematical definition
The most general wave function that satisfies the identity above is the squeezed coherent state (we work in units with )
)
where
 are constants (a normalization constant, the center of the wavepacket, its width, and its average momentum
are constants (a normalization constant, the center of the wavepacket, its width, and its average momentumMomentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
). The new feature relative to a coherent state
Coherent state
In quantum mechanics a coherent state is a specific kind of quantum state of the quantum harmonic oscillator whose dynamics most closely resembles the oscillating behaviour of a classical harmonic oscillator...
is the free value of the width
 , which is the reason why the state is called "squeezed".
, which is the reason why the state is called "squeezed".The squeezed state above is an eigenstate of a linear operator

and the corresponding eigenvalue equals
 . In this sense, it is a generalization of the ground state as well as the coherent state.
. In this sense, it is a generalization of the ground state as well as the coherent state.Examples of squeezed coherent states
Depending on at which phase the state's quantum noiseQuantum noise
Quantum noise is uncertainty of some physical quantity due to its quantum origin.In the case of number of particles , the quantum noise is also called shot noise. Most optical communications use amplitude modulation...
is reduced, one can distinguish amplitude-squeezed and phase-squeezed states or general quadrature squeezed states. If no coherent excitation exists the state is called a squeezed vacuum. The figures below give a nice visual demonstration of the close connection between squeezed states and Heisenberg's uncertainty relation: Diminishing the quantum noise at a specific quadrature (phase) of the wave has as a direct consequence an enhancement of the noise of the complementary quadrature, that is, the field at the phase shifted by
 .
.  |
 |
 |
From the top:
- Vacuum state
- Squeezed vacuum state
- Phase-squeezed state
- arbitrary squeezed state
- Amplitude-squeezed state
As can be seen at once, in contrast to the coherent state
Coherent state
In quantum mechanics a coherent state is a specific kind of quantum state of the quantum harmonic oscillator whose dynamics most closely resembles the oscillating behaviour of a classical harmonic oscillator...
the quantum noise is not independent of the phase of the light wave anymore. A characteristic broadening and narrowing of the noise during one oscillation period can be observed. The wave packet
Wave packet
In physics, a wave packet is a short "burst" or "envelope" of wave action that travels as a unit. A wave packet can be analyzed into, or can be synthesized from, an infinite set of component sinusoidal waves of different wavenumbers, with phases and amplitudes such that they interfere...
of a squeezed state is defined by the square of the wave function introduced in the last paragraph. They correspond to the probability distribution of the electric field strength of the light wave. The moving wave packets display an oscillatory motion combined with the widening and narrowing of their distribution: the "breathing" of the wave packet. For an amplitude-squeezed state, the most narrow distribution of the wave packet is reached at the field maximum, resulting in an amplitude that is defined more precisely than the one of a coherent state. For a phase-squeezed state, the most narrow distribution is reached at field zero, resulting in an average phase value that is better defined than the one of a coherent state.
In phase space, quantum mechanical uncertainties can be depicted by Wigner distribution Wigner quasi-probability distribution
Wigner quasi-probability distribution
The Wigner quasi-probability distribution is a quasi-probability distribution. It was introduced by Eugene Wigner in 1932 to study quantum corrections to classical statistical mechanics...
. The intensity of the light wave, its coherent excitation, is given by the displacement of the Wigner distribution from the origin. A change in the phase of the squeezed quadrature results in a rotation of the distribution.
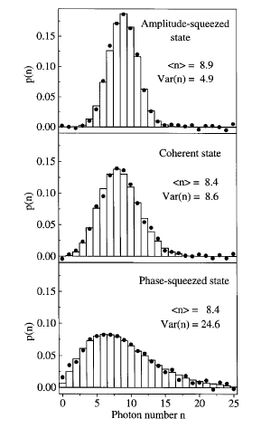
Photon number distributions and phase distributions of squeezed states
The squeezing angle, that is the phase with minimum quantum noise, has a large influence on the photonPhoton
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
number distribution of the light wave and its phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
distribution as well.
 |
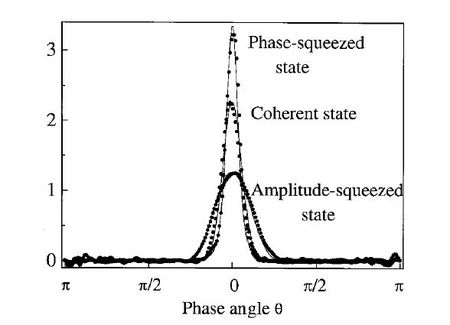 |
For amplitude squeezed light the photon number distribution is usually narrower than the one of a coherent state of the same amplitude resulting in sub-Poissonian
Poisson distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
light, whereas its phase distribution is wider. The opposite is true for the phase-squeezed light, which displays a large intensity (photon number) noise but a narrow phase distribution. Nevertheless the statistics of amplitude squeezed light was not observed directly with photon number resolving detector due to experimental difficulty.

Spontaneous parametric down conversion
Spontaneous parametric down-conversion is an important process in quantum optics, used especially as a source of entangled photon pairs, and of single photons.-Basic process:...
and annihilation processes. Photons in a squeezed vacuum state are more likely to appear in pairs.
Experimental realizations of squeezed coherent states
There has been a whole variety of successful demonstrations of squeezed states. The most prominent ones were experiments with light fields using laserLaser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
s and non-linear optics (see optical parametric oscillator
Optical parametric oscillator
An optical parametric oscillator is a parametric oscillator which oscillates at optical frequencies. It converts an input laser wave into two output waves of lower frequency by means of second order nonlinear optical interaction. The sum of the output waves frequencies is equal to the input wave...
). This is achieved by a simple process of four-wave mixing with a
 crystal; similarly traveling wave phase-sensitive amplifiers generate spatially-multimode quadrature-squeezed states of light when the
crystal; similarly traveling wave phase-sensitive amplifiers generate spatially-multimode quadrature-squeezed states of light when the  crystal is pumped in absence of any signal. Sub-poissonian current sources driving semiconductor laser diodes have led to amplitude squeezed light. Squeezed states have also been realized via motional states of an ion
crystal is pumped in absence of any signal. Sub-poissonian current sources driving semiconductor laser diodes have led to amplitude squeezed light. Squeezed states have also been realized via motional states of an ionIon
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
in a trap
Trap
A trap is a device or tactic intended to catch an intruder, enemy, error, or substance.Trap may also refer to:* Giovanni Trapattoni, Italian association football coach and former player known by this name* Bat and trap, an old game related to cricket...
, phonon
Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, such as solids and some liquids...
states in crystal lattices, or atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
ensembles. Even macroscopic oscillators were driven into classical motional states that were very similar to squeezed coherent states. Current state of the art in noise suppression, for laser radiation using squeezed light, amounts to 10 dB.
Applications
Squeezed states of the light field can be used to enhance precision measurements. For example phase-squeezed light can improve the phase read out of interferometric measurementsInterferometry
Interferometry refers to a family of techniques in which electromagnetic waves are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. An instrument used to interfere waves is called an interferometer. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy,...
(see for example gravitational wave
Gravitational wave
In physics, gravitational waves are theoretical ripples in the curvature of spacetime which propagates as a wave, traveling outward from the source. Predicted to exist by Albert Einstein in 1916 on the basis of his theory of general relativity, gravitational waves theoretically transport energy as...
s). Amplitude-squeezed light can improve the readout of very weak spectroscopic signals
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
.
Various squeezed coherent states, generalized to the case of many degrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom (physics and chemistry)
A degree of freedom is an independent physical parameter, often called a dimension, in the formal description of the state of a physical system...
, are used in various calculations in quantum field theory
Quantum field theory
Quantum field theory provides a theoretical framework for constructing quantum mechanical models of systems classically parametrized by an infinite number of dynamical degrees of freedom, that is, fields and many-body systems. It is the natural and quantitative language of particle physics and...
, for example Unruh effect
Unruh effect
The Unruh effect , was first described by Stephen Fulling in 1973, Paul Davies in 1975 and Bill Unruh in 1976. It is the prediction that an accelerating observer will observe black-body radiation where an inertial observer would observe none...
and Hawking radiation
Hawking radiation
Hawking radiation is a thermal radiation with a black body spectrum predicted to be emitted by black holes due to quantum effects. It is named after the physicist Stephen Hawking, who provided a theoretical argument for its existence in 1974, and sometimes also after the physicist Jacob Bekenstein...
, and generally, particle production in curved backgrounds and Bogoliubov transformation
Bogoliubov transformation
In theoretical physics, the Bogoliubov transformation, named after Nikolay Bogolyubov, is a unitary transformation from a unitary representation of some canonical commutation relation algebra or canonical anticommutation relation algebra into another unitary representation, induced by an...
).

