Star position
Encyclopedia
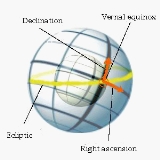
Star position in the sky is defined by a pair of angle
s. These two angles - which refer to the celestial equator
- are called declination
(abbrev. δ or Dec) and right ascension
(α or RA).
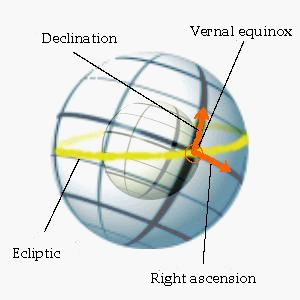 While δ is given in degrees
While δ is given in degrees
(kkfrom +90° at the celestial north pole
to -90° at the south pole), α is usually given in hour
s (0 ... 24h). This is due to the observation technique of star transit
s, which cross the eyepiece of telescopes because of the Earth's rotation. The observation techniques are topics of position astronomy and of astrogeodesy.
Ideally the two-dimensional coordinate system
α, δ refers to an inertial frame of reference
; the 3rd coordinate is the star distance
which normally is used as an attribute of the individual star.
Star positions are changing in time, caused by
The effects 1 and 2 are considered by so called mean places of stars, contrary to their apparent places
as seen from the moving Earth. Usually the mean places refer to a special epoch
, e.g. 1950.0 or 2000.0. The 3rd effect has to be handled individually.
The star positions α, δ are compiled in several star catalogue
s of different volume and accuracy. Absolute and very precise coordinates of 1000-3000 stars are collected in Fundamental catalogues, starting with the FK (Berlin ~1890) up to the modern FK6.
Relative coordinates of numerous stars are collected in catalogues like the Bonner Durchmusterung (Germany 1852-1862, 200.000 rough positions), the SAO
catalogue (USA 1966, 250.000 astrometric stars) or the Hipparcos
and Tycho catalogue (110.000 and 2 million stars by space astrometry).
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
s. These two angles - which refer to the celestial equator
Celestial equator
The celestial equator is a great circle on the imaginary celestial sphere, in the same plane as the Earth's equator. In other words, it is a projection of the terrestrial equator out into space...
- are called declination
Declination
In astronomy, declination is one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and...
(abbrev. δ or Dec) and right ascension
Right ascension
Right ascension is the astronomical term for one of the two coordinates of a point on the celestial sphere when using the equatorial coordinate system. The other coordinate is the declination.-Explanation:...
(α or RA).

Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
(kkfrom +90° at the celestial north pole
North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface...
to -90° at the south pole), α is usually given in hour
Hour
The hour is a unit of measurement of time. In modern usage, an hour comprises 60 minutes, or 3,600 seconds...
s (0 ... 24h). This is due to the observation technique of star transit
Star transit
A Star transit is the passage of a star through the eyepiece of an telescope.The precise observation of star transits is the basis of many methods in Astronomy and in Geodesy...
s, which cross the eyepiece of telescopes because of the Earth's rotation. The observation techniques are topics of position astronomy and of astrogeodesy.
Ideally the two-dimensional coordinate system
Coordinate system
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system which uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of a point or other geometric element. The order of the coordinates is significant and they are sometimes identified by their position in an ordered tuple and sometimes by...
α, δ refers to an inertial frame of reference
Inertial frame of reference
In physics, an inertial frame of reference is a frame of reference that describes time homogeneously and space homogeneously, isotropically, and in a time-independent manner.All inertial frames are in a state of constant, rectilinear motion with respect to one another; they are not...
; the 3rd coordinate is the star distance
Distance
Distance is a numerical description of how far apart objects are. In physics or everyday discussion, distance may refer to a physical length, or an estimation based on other criteria . In mathematics, a distance function or metric is a generalization of the concept of physical distance...
which normally is used as an attribute of the individual star.
Star positions are changing in time, caused by
- precessionPrecessionPrecession is a change in the orientation of the rotation axis of a rotating body. It can be defined as a change in direction of the rotation axis in which the second Euler angle is constant...
and nutationNutationNutation is a rocking, swaying, or nodding motion in the axis of rotation of a largely axially symmetric object, such as a gyroscope, planet, or bullet in flight, or as an intended behavior of a mechanism...
- slow tilts of the Earth's axis with rates of 50" resp. 2" per year - aberrationAberration of lightThe aberration of light is an astronomical phenomenon which produces an apparent motion of celestial objects about their real locations...
and parallaxParallaxParallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight, and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. The term is derived from the Greek παράλλαξις , meaning "alteration"...
- effects of the Earth's orbit around the sun - proper motionProper motionThe proper motion of a star is its angular change in position over time as seen from the center of mass of the solar system. It is measured in seconds of arc per year, arcsec/yr, where 3600 arcseconds equal one degree. This contrasts with radial velocity, which is the time rate of change in...
of the individual stars.
The effects 1 and 2 are considered by so called mean places of stars, contrary to their apparent places
Apparent places
The wrong place of an object is the position in space as seen by the observer. Because of physical and/or geometrical effects it has a deviation from the "true position"....
as seen from the moving Earth. Usually the mean places refer to a special epoch
Epoch (astronomy)
In astronomy, an epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity, such as celestial coordinates, or elliptical orbital elements of a celestial body, where these are subject to perturbations and vary with time...
, e.g. 1950.0 or 2000.0. The 3rd effect has to be handled individually.
The star positions α, δ are compiled in several star catalogue
Star catalogue
A star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some...
s of different volume and accuracy. Absolute and very precise coordinates of 1000-3000 stars are collected in Fundamental catalogues, starting with the FK (Berlin ~1890) up to the modern FK6.
Relative coordinates of numerous stars are collected in catalogues like the Bonner Durchmusterung (Germany 1852-1862, 200.000 rough positions), the SAO
Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory Star Catalog
The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory Star Catalog is an astrometric star catalogue. It was published by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory in 1966 and contains 258,997 stars. The catalogue was...
catalogue (USA 1966, 250.000 astrometric stars) or the Hipparcos
Hipparcos
Hipparcos was a scientific mission of the European Space Agency , launched in 1989 and operated between 1989 and 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky...
and Tycho catalogue (110.000 and 2 million stars by space astrometry).
See also
- Star catalogueStar catalogueA star catalogue, or star catalog, is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years, and this article covers only some...
, FK4, FK6 - Equatorial coordinates, Ecliptic coordinates
- Vernal equinox, YearbookYearbookA yearbook, also known as an annual, is a book to record, highlight, and commemorate the past year of a school or a book published annually. Virtually all American, Australian and Canadian high schools, most colleges and many elementary and middle schools publish yearbooks...
- annual aberration, improper motion
- Geodetic astronomyGeodetic astronomyGeodetic astronomy is the application of astronomical methods into networks and technical projects of geodesy.The most important topics are:* Establishment of geodetic datum systems Geodetic astronomy is the application of astronomical methods into networks and technical projects of geodesy.The...
, transit instrumentTransit instrumentIn astronomy, transit instruments are used for the precise observation of star positions. The instruments can be divided into three groups:- Meridian instruments :for observation of star transits in the exact direction of South or North:...
s

