Statistical interference
Encyclopedia
When two probability distribution
s overlap, statistical interference exists. Knowledge of the distributions can be used to determine the likelihood that one parameter exceeds another, and by how much.
This technique can be used for dimensioning of mechanical parts, determining when an applied load exceeds the strength of a structure, and in many other situations. This type of analysis can also be used to estimate the probability of failure or the frequency of failure.
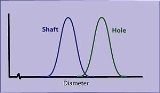
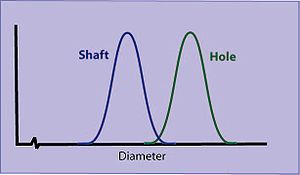 Mechanical parts are usually designed to fit precisely together. For example, if a shaft is designed to have a "sliding fit" in a hole, the shaft must be a little smaller than the hole. (Traditional tolerances
Mechanical parts are usually designed to fit precisely together. For example, if a shaft is designed to have a "sliding fit" in a hole, the shaft must be a little smaller than the hole. (Traditional tolerances
may suggest that all dimensions fall within those intended tolerances. A process capability
study of actual production, however, may reveal normal distributions with long tails.) Both the shaft and hole sizes will usually form normal distributions with some average (arithmetic mean
) and standard deviation
.
With two such normal distributions, a distribution of interference can be calculated. The derived distribution will also be normal, and its average will be equal to the difference between the means of the two base distributions. The variance
of the derived distribution will be the sum of the variances of the two base distributions.
This derived distribution can be used to determine how often the difference in dimensions will be less than zero (i.e., the shaft cannot fit in the hole), how often the difference will be less than the required sliding gap (the shaft fits, but too tightly), and how often the difference will be greater than the maximum acceptable gap (the shaft fits, but not tightly enough).
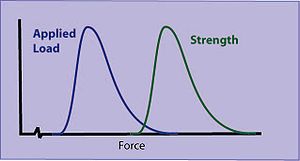 Physical properties and the conditions of use are also inherently variable. For example, the applied load (stress) on a mechanical part may vary. The measured strength of that part (tensile strength, etc) may also be variable. The part will break when the stress exceeds the strength.
Physical properties and the conditions of use are also inherently variable. For example, the applied load (stress) on a mechanical part may vary. The measured strength of that part (tensile strength, etc) may also be variable. The part will break when the stress exceeds the strength.
With two normal distributions, the statistical interference may be calculated as above. (This problem is also workable for transformed units such as the log-normal distribution). With other distributions, or combinations of different distributions, a Monte Carlo method
or simulation is often the most practical way to quantify the effects of statistical interference.
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
s overlap, statistical interference exists. Knowledge of the distributions can be used to determine the likelihood that one parameter exceeds another, and by how much.
This technique can be used for dimensioning of mechanical parts, determining when an applied load exceeds the strength of a structure, and in many other situations. This type of analysis can also be used to estimate the probability of failure or the frequency of failure.
Dimensional interference

Tolerance (engineering)
Engineering tolerance is the permissible limit or limits of variation in# a physical dimension,# a measured value or physical property of a material, manufactured object, system, or service,# other measured values ....
may suggest that all dimensions fall within those intended tolerances. A process capability
Process capability
A process is a unique combination of tools, materials, methods, and people engaged in producing a measurable output; for example a manufacturing line for machine parts...
study of actual production, however, may reveal normal distributions with long tails.) Both the shaft and hole sizes will usually form normal distributions with some average (arithmetic mean
Arithmetic mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean, often referred to as simply the mean or average when the context is clear, is a method to derive the central tendency of a sample space...
) and standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
.
With two such normal distributions, a distribution of interference can be calculated. The derived distribution will also be normal, and its average will be equal to the difference between the means of the two base distributions. The variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
of the derived distribution will be the sum of the variances of the two base distributions.
This derived distribution can be used to determine how often the difference in dimensions will be less than zero (i.e., the shaft cannot fit in the hole), how often the difference will be less than the required sliding gap (the shaft fits, but too tightly), and how often the difference will be greater than the maximum acceptable gap (the shaft fits, but not tightly enough).
Physical property interference

With two normal distributions, the statistical interference may be calculated as above. (This problem is also workable for transformed units such as the log-normal distribution). With other distributions, or combinations of different distributions, a Monte Carlo method
Monte Carlo method
Monte Carlo methods are a class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to compute their results. Monte Carlo methods are often used in computer simulations of physical and mathematical systems...
or simulation is often the most practical way to quantify the effects of statistical interference.
See also
- Tolerance (engineering)Tolerance (engineering)Engineering tolerance is the permissible limit or limits of variation in# a physical dimension,# a measured value or physical property of a material, manufactured object, system, or service,# other measured values ....
- Specification
- Process capabilityProcess capabilityA process is a unique combination of tools, materials, methods, and people engaged in producing a measurable output; for example a manufacturing line for machine parts...
- Probabilistic designProbabilistic designProbabilistic design is a discipline within engineering design. It deals primarily with the consideration of the effects of random variability upon the performance of an engineering system during the design phase. Typically, these effects are related to quality and reliability...
- Reliability engineeringReliability engineeringReliability engineering is an engineering field, that deals with the study, evaluation, and life-cycle management of reliability: the ability of a system or component to perform its required functions under stated conditions for a specified period of time. It is often measured as a probability of...
- Joint probability distribution
- Interference fitInterference fitAn interference fit, also known as a press fit or friction fit, is a fastening between two parts which is achieved by friction after the parts are pushed together, rather than by any other means of fastening...

