
Step-index profile
Encyclopedia
For an optical fiber
, a step-index profile is a refractive index
profile characterized by a uniform refractive index within the core and a sharp decrease in refractive index at the core-cladding
interface so that the cladding is of a lower refractive index. The step-index profile corresponds to a power-law index profile with the profile parameter approaching infinity. The step-index profile is used in most single-mode fibers and some multimode fibers.
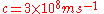
A step-index fiber is characterized by the core and cladding refractive indices n1 and n2 and the core and cladding radii a and b. Examples of standard core and cladding diameters 2a/2b are 8/125, 50/125, 62.5/125, 85/125, or 100/140 (units of µm). The fractional refractive-index change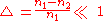 . The value of n1 is typically between 1.44 and 1.46, and
. The value of n1 is typically between 1.44 and 1.46, and  is typically between 0.001 and 0.02.
is typically between 0.001 and 0.02.
Step-index optical fiber is generally made by doping
high-purity fused silica glass (SiO2) with different concentrations of materials like titanium, germanium, or boron.
Pulse dispersion in a step index optical fiber is given by
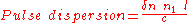
where
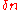 is the difference in refractive indices of core and cladding.
is the difference in refractive indices of core and cladding.
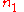 is the refractive index of core
is the refractive index of core
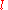 is the length of the optical fiber under observation
is the length of the optical fiber under observation
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
, a step-index profile is a refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
profile characterized by a uniform refractive index within the core and a sharp decrease in refractive index at the core-cladding
Cladding (fiber optics)
Cladding is one or more layers of material of lower refractive index, in intimate contact with a core material of higher refractive index. The cladding causes light to be confined to the core of the fiber by total internal reflection at the boundary between the two. Light propagation in the...
interface so that the cladding is of a lower refractive index. The step-index profile corresponds to a power-law index profile with the profile parameter approaching infinity. The step-index profile is used in most single-mode fibers and some multimode fibers.
A step-index fiber is characterized by the core and cladding refractive indices n1 and n2 and the core and cladding radii a and b. Examples of standard core and cladding diameters 2a/2b are 8/125, 50/125, 62.5/125, 85/125, or 100/140 (units of µm). The fractional refractive-index change
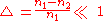 . The value of n1 is typically between 1.44 and 1.46, and
. The value of n1 is typically between 1.44 and 1.46, and  is typically between 0.001 and 0.02.
is typically between 0.001 and 0.02.Step-index optical fiber is generally made by doping
Doping (semiconductor)
In semiconductor production, doping intentionally introduces impurities into an extremely pure semiconductor for the purpose of modulating its electrical properties. The impurities are dependent upon the type of semiconductor. Lightly and moderately doped semiconductors are referred to as extrinsic...
high-purity fused silica glass (SiO2) with different concentrations of materials like titanium, germanium, or boron.
Pulse dispersion in a step index optical fiber is given by
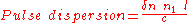
where
 is the difference in refractive indices of core and cladding.
is the difference in refractive indices of core and cladding.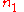 is the refractive index of core
is the refractive index of core is the length of the optical fiber under observation
is the length of the optical fiber under observation
See also
- Graded-index fiberGraded-index fiberIn fiber optics, a graded-index or gradient-index fiber is an optical fiber whose core has a refractive index that decreases with increasing radial distance from the fiber axis ....
- Critical Angle
- Numerical apertureNumerical apertureIn optics, the numerical aperture of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one...

