
Straight engine
Encyclopedia
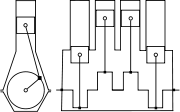
Cylinder (engine)
A cylinder is the central working part of a reciprocating engine or pump, the space in which a piston travels. Multiple cylinders are commonly arranged side by side in a bank, or engine block, which is typically cast from aluminum or cast iron before receiving precision machine work...
configurations, the straight engine, or inline engine is an internal-combustion engine with all cylinders
Cylinder (engine)
A cylinder is the central working part of a reciprocating engine or pump, the space in which a piston travels. Multiple cylinders are commonly arranged side by side in a bank, or engine block, which is typically cast from aluminum or cast iron before receiving precision machine work...
aligned in one row, with no offset. They have been used in automobile
Automobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
s, locomotive
Locomotive
A locomotive is a railway vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. The word originates from the Latin loco – "from a place", ablative of locus, "place" + Medieval Latin motivus, "causing motion", and is a shortened form of the term locomotive engine, first used in the early 19th...
s and aircraft
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
, although the term in-line has a broader meaning when applied to aircraft engines; see Inline engine (aviation)
Inline engine (aviation)
In aviation, an inline engine means any reciprocating engine with banks rather than rows of cylinders, including straight engines, flat engines, V engines and H engines, but excluding radial engines and rotary engines....
.
A straight engine is considerably easier to build than an otherwise equivalent horizontally opposed
Flat engine
A flat engine is an internal combustion engine with multiple pistons that move in a horizontal plane. Typically, the layout has cylinders arranged in two banks on either side of a single crankshaft and is sometimes known as the boxer, or horizontally opposed engine. The concept was patented in 1896...
or V engine
V engine
A V engine, or Vee engine is a common configuration for an internal combustion engine. The cylinders and pistons are aligned, in two separate planes or 'banks', so that they appear to be in a "V" when viewed along the axis of the crankshaft...
, because both the cylinder bank
Cylinder bank
Internal combustion piston engines are usually arranged so that the cylinders are in lines parallel to the crankshaft. Where they are in a single line, this is referred to as an inline or straight engine....
and crankshaft
Crankshaft
The crankshaft, sometimes casually abbreviated to crank, is the part of an engine which translates reciprocating linear piston motion into rotation...
can be milled from a single metal casting, and it requires fewer cylinder head
Cylinder head
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head sits above the cylinders on top of the cylinder block. It closes in the top of the cylinder, forming the combustion chamber. This joint is sealed by a head gasket...
s and camshaft
Camshaft
A camshaft is a shaft to which a cam is fastened or of which a cam forms an integral part.-History:An early cam was built into Hellenistic water-driven automata from the 3rd century BC. The camshaft was later described in Iraq by Al-Jazari in 1206. He employed it as part of his automata,...
s. In-line engines are also smaller in overall physical dimensions than designs such as the radial
Radial engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating type internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinders point outward from a central crankshaft like the spokes on a wheel...
, and can be mounted in any direction. Straight configurations are simpler than their V-shaped counterparts. They have a support bearing between each piston
Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from...
as compared to "flat and V" engines which have support bearings between every two pistons. Although six-cylinder engines are inherently balanced, the four-cylinder models are inherently off balance and rough, unlike 90-degree V fours and horizontally opposed 'boxer' 4 cylinders.
Automobile use
The inline-four engine is the most common four-cylinder configuration, whereas the straight-6Straight-6
The straight-six engine or inline-six engine is a six-cylinder internal combustion engine with all six cylinders mounted in a straight line along the crankcase...
has largely given way to the V6 engine
V6 engine
A V6 engine is a V engine with six cylinders mounted on the crankcase in two banks of three cylinders, usually set at either a right angle or an acute angle to each other, with all six pistons driving a common crankshaft...
, which although not as naturally smooth-running is smaller in both length and height and easier to fit into the engine bay of smaller modern cars. Some manufacturers, including Acura
Acura
Acura is the luxury vehicle division of Japanese automaker Honda Motor Company. The brand has been available in the United States and Canada since March 1986, marketing luxury, performance, and near-performance vehicles. It was introduced to Hong Kong in 1991, Mexico in 2004, and China in 2006...
, Audi
Audi
Audi AG is a German automobile manufacturer, from supermini to crossover SUVs in various body styles and price ranges that are marketed under the Audi brand , positioned as the premium brand within the Volkswagen Group....
, Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz is a German manufacturer of automobiles, buses, coaches, and trucks. Mercedes-Benz is a division of its parent company, Daimler AG...
, Toyota, Volkswagen
Volkswagen
Volkswagen is a German automobile manufacturer and is the original and biggest-selling marque of the Volkswagen Group, which now also owns the Audi, Bentley, Bugatti, Lamborghini, SEAT, and Škoda marques and the truck manufacturer Scania.Volkswagen means "people's car" in German, where it is...
and Volvo
Volvo Cars
Volvo Car Corporation, or Volvo Personvagnar AB, is a Swedish automobile manufacturer founded in 1927, in Gothenburg, Sweden. It is owned by Zhejiang Geely Holding Group. Volvo was originally formed as a subsidiary company to the ball bearing maker SKF. When Volvo AB was introduced on the Swedish...
, have also used straight-5
Straight-5
The straight-five engine or inline-five engine is an internal combustion engine with five cylinders aligned in one row or plane, sharing a single engine block and crankcase...
configurations. The General Motors Atlas
GM Atlas engine
Atlas is a name for a family of modern inline piston engines for trucks from General Motors. The series debuted in 2002 with the Oldsmobile Bravada, and is also used in the Chevrolet TrailBlazer and Colorado and their GMC twins, the Envoy and Canyon...
family includes straight-4, straight-5, and straight-6 engines.
Once, the straight-8 was the prestige engine arrangement; it could be made more cheaply than a V-engine by luxury car makers, who would focus on other specifics than the geometric ones, and even built engines more powerful than any V8 engine
V8 engine
A V8 engine is a V engine with eight cylinders mounted on the crankcase in two banks of four cylinders, in most cases set at a right angle to each other but sometimes at a narrower angle, with all eight pistons driving a common crankshaft....
. In the 1930s, Duesenberg
Duesenberg
Duesenberg was an Auburn, Indiana based American luxury automobile company active in various forms from 1913 to 1937, most famous for its high-quality passenger cars and record-breaking racing cars.-History:...
used an aluminium alloy
Aluminium alloy
Aluminium alloys are alloys in which aluminium is the predominant metal. The typical alloying elements are copper, magnesium, manganese, silicon and zinc. There are two principal classifications, namely casting alloys and wrought alloys, both of which are further subdivided into the categories...
cylinder block
Cylinder block
A cylinder block is an integrated structure comprising the cylinder of a reciprocating engine and often some or all of their associated surrounding structures...
with four valves
Multi-valve
In automotive engineering a multi-valve or multivalve engine is one where each cylinder has more than two valves. A multi-valve engine has better breathing and can operate at higher revolutions per minute than a two-valve engine, delivering more power.- Multi-valve rationale :A multi-valve design...
per cylinder and hemispherical heads to produce the most powerful engine on the market. It was thus a selling point for Pontiac
Pontiac
Pontiac was an automobile brand that was established in 1926 as a companion make for General Motors' Oakland. Quickly overtaking its parent in popularity, it supplanted the Oakland brand entirely by 1933 and, for most of its life, became a companion make for Chevrolet. Pontiac was sold in the...
to introduce the cheapest straight-8
Pontiac Straight-8 engine
The straight-8 was an eight-cylinder, in-line automobile engine that was used in production Pontiacs from 1933 to 1954. Introduced in the fall of 1932 for the 1933 models, it was Pontiac's most powerful engine at the time and was the least expensive eight-cylinder engine built by an American...
in 1933. However, following World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, the straight-8 was supplanted by the lighter and more compact V8 engine, which allowed shorter engine bays to be used in the design.
When a straight engine is mounted at an angle from the vertical it is called a slant engine. Chrysler's Slant 6 was used in many models in the 1960s and 1970s. Honda
Honda
is a Japanese public multinational corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles.Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than...
also often mounts its straight-4 and straight-5 engines at a slant, as on the Honda S2000
Honda S2000
The Honda S2000 is a roadster that was manufactured by the Japanese automaker Honda Motor Company. It was launched in April 1999 and was created to celebrate the company's 50th anniversary. The car was first shown as a concept at the Tokyo Motor Show in 1995, following which it was launched in...
and Acura Vigor
Acura Vigor
The Honda Vigor is a compact sedan sold in Japan from 1981 to 1995. It was sold in North America from 1992 to 1994 as the Acura Vigor, a mid-size luxury car. It was replaced in North America with the Acura TL and in Japan with the Honda Saber...
. SAAB
Saab
Saab AB is a Swedish aerospace and defence company, founded in 1937. From 1947 to 1990 it was the parent company of automobile manufacturer Saab Automobile, and between 1968 and 1995 the company was in a merger with commercial vehicle manufacturer Scania, known as Saab-Scania.-History:"Svenska...
first used an inline-4 tilted at 45 degrees for the Saab 99
Saab 99
- Development :On April 2, 1965, Gudmund's day in Sweden, after several years of planning, the Saab board started Project Gudmund. This was a project to develop a new and larger car to take the manufacturer beyond the market for the smaller Saab 96...
, but later versions of the engine were less tilted.
Two main factors have led to the recent decline of the straight-6 in automotive applications. First, Lanchester balance shafts, an old idea reintroduced by Mitsubishi in the 1980s to overcome the natural imbalance of the straight-4 engine and rapidly adopted by many other manufacturers, have made both straight-4 and V6 engine
V6 engine
A V6 engine is a V engine with six cylinders mounted on the crankcase in two banks of three cylinders, usually set at either a right angle or an acute angle to each other, with all six pistons driving a common crankshaft...
s smoother-running; the greater smoothness of the straight-6 layout is no longer such an advantage. Second, fuel consumption became more important, as cars became smaller and more space-efficient. The engine bay of a modern small or medium car, typically designed for a straight-4, often does not have room for a straight-6, but can fit a V6 with only minor modifications.
Some manufacturers (originally Lancia
Lancia
Lancia Automobiles S.p.A. is an Italian automobile manufacturer founded in 1906 by Vincenzo Lancia and which became part of the Fiat Group in 1969. The company has a long history of producing distinctive cars and also has a strong rally heritage. Some modern Lancias are seen as presenting a more...
, and more recently Volkswagen
Volkswagen
Volkswagen is a German automobile manufacturer and is the original and biggest-selling marque of the Volkswagen Group, which now also owns the Audi, Bentley, Bugatti, Lamborghini, SEAT, and Škoda marques and the truck manufacturer Scania.Volkswagen means "people's car" in German, where it is...
with the VR6 engine
VR6 engine
The VR6 engine is an internal combustion engine configuration, consisting of six cylinders. It was developed by the Volkswagen Group in the late 1980s, and evolutions of the original variant are still produced by them....
) have attempted to combine advantages of the straight- and V configurations by producing a narrow-angle V; this is more compact than either configuration, but is less smooth (without balancing) than either.
Straight-6 engines are used in some models from BMW
BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
, Ford Australia
Ford Australia
Ford Australia is the Australian subsidiary of Ford Motor Company and was founded in Geelong, Victoria, in 1925 as an outpost of Ford Motor Company of Canada, Limited. At that time, Ford Canada was a separate company from Ford USA...
, Chevrolet
Chevrolet
Chevrolet , also known as Chevy , is a brand of vehicle produced by General Motors Company . Founded by Louis Chevrolet and ousted GM founder William C. Durant on November 3, 1911, General Motors acquired Chevrolet in 1918...
, GMC, Toyota
Toyota Land Cruiser
The is a series of four-wheel drive vehicles produced by the Japanese car maker Toyota Motor Corporation. It is not related to the Studebaker Land Cruiser car produced in the US from 1934-1954....
, Suzuki
Suzuki
is a Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Hamamatsu, Japan that specializes in manufacturing compact automobiles and 4x4 vehicles, a full range of motorcycles, all-terrain vehicles , outboard marine engines, wheelchairs and a variety of other small internal combustion engines...
and Volvo Cars
Volvo Cars
Volvo Car Corporation, or Volvo Personvagnar AB, is a Swedish automobile manufacturer founded in 1927, in Gothenburg, Sweden. It is owned by Zhejiang Geely Holding Group. Volvo was originally formed as a subsidiary company to the ball bearing maker SKF. When Volvo AB was introduced on the Swedish...
.
Aviation use
In aviation, the term "inline engine" is used more broadly, for any non-radialRadial engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating type internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinders point outward from a central crankshaft like the spokes on a wheel...
, reciprocating, cylinder engine.
Some straight engines, in the strict sense, have been produced for aircraft. Renault produced a straight-6
Straight-6
The straight-six engine or inline-six engine is a six-cylinder internal combustion engine with all six cylinders mounted in a straight line along the crankcase...
inverted air-cooled motor, which was used on the Stampe
Stampe
Stampe et Vertongen was a Belgian aircraft manufacturer formed in 1922 and based at Antwerp. The company specialised in design and construction of primary trainers/tourers and advanced trainers...
. A similar design was the de Havilland Gipsy
De Havilland Gipsy
The de Havilland Gipsy is a British air-cooled 4-cylinder in-line aircraft engine designed by Frank Halford in 1927 to replace the ADC Cirrus in the de Havilland D.H.60 Moth light biplane....
series of engines, used on the Tiger Moth
Tiger moth
Tiger moths are moths of the family Arctiidae.Tiger moth may also refer to:*de Havilland Tiger Moth, an aircraft; an aerobatic and trainer tailwheel biplane*de Havilland DH.71 Tiger Moth, an earlier monoplane produced by de Havilland...
and other aircraft. Advantages include improved visibility for the pilot in single-engined craft, and lower center of gravity.
Engines of this type in some bus
Bus
A bus is a road vehicle designed to carry passengers. Buses can have a capacity as high as 300 passengers. The most common type of bus is the single-decker bus, with larger loads carried by double-decker buses and articulated buses, and smaller loads carried by midibuses and minibuses; coaches are...
es and train
Train
A train is a connected series of vehicles for rail transport that move along a track to transport cargo or passengers from one place to another place. The track usually consists of two rails, but might also be a monorail or maglev guideway.Propulsion for the train is provided by a separate...
s have been built in a horizontal form. This differs from a flat engine
Flat engine
A flat engine is an internal combustion engine with multiple pistons that move in a horizontal plane. Typically, the layout has cylinders arranged in two banks on either side of a single crankshaft and is sometimes known as the boxer, or horizontally opposed engine. The concept was patented in 1896...
because it is essentially an inline engine laid on its side. Underfloor engines for buses and diesel multiple unit
Diesel multiple unit
A diesel multiple unit or DMU is a multiple unit train consisting of multiple carriages powered by one or more on-board diesel engines. They may also be referred to as a railcar or railmotor, depending on country.-Design:...
s (DMUs) are commonly seen in this design. Such engines may be based on a conventional upright engine with alterations to make it suitable for horizontal mounting.
Automotive, aircraft and marine use
- Parallel twin
- Straight-3Straight-3A straight-three engine, also known as inline-three engine, or a triple, is a reciprocating piston internal combustion engine with three cylinders arranged in a straight line or plane, side by side....
- Straight-4Straight-4The inline-four engine or straight-four engine is an internal combustion engine with all four cylinders mounted in a straight line, or plane along the crankcase. The single bank of cylinders may be oriented in either a vertical or an inclined plane with all the pistons driving a common crankshaft....
- Straight-5Straight-5The straight-five engine or inline-five engine is an internal combustion engine with five cylinders aligned in one row or plane, sharing a single engine block and crankcase...
- Straight-6Straight-6The straight-six engine or inline-six engine is a six-cylinder internal combustion engine with all six cylinders mounted in a straight line along the crankcase...
- Straight-7
- Straight-8Straight-8The straight-eight engine or inline-eight engine is an eight-cylinder internal combustion engine with all eight cylinders mounted in a straight line along the crankcase...
- Straight-9Straight-9A straight-nine engine or inline-nine engine is a straight engine with nine cylinders. Straight-nine engines are usually diesel engines used for ship propulsion...
- Straight-10Straight-10A straight-10 engine or inline-10 engine is a ten-cylinder internal combustion engine with all ten cylinders mounted in a straight line along the crankcase. A straight-10 is a very long engine, and therefore straight-10 engines are not common in automobiles.-Marine use:Large ten-cylinder engines...
- Straight-12Straight-12A straight-12 engine or inline-12 engine is a twelve-cylinder internal combustion engine with all twelve cylinders mounted in a straight line along the crankcase. A straight-12 is a very long engine, and therefore straight-12 engines are not common in automobiles, but it has been used for large...
- Straight-14Straight-14A straight-14 engine or inline-14 engine is a fourteen-cylinder internal combustion engine with all fourteen cylinders mounted in a straight line along the crankcase...
- Straight-24

