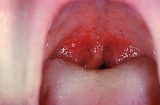
Strep throat
Encyclopedia
Streptococcal pharyngitis, streptococcal tonsillitis, or streptococcal sore throat (known colloquially as strep throat) is a type of pharyngitis
caused by a group A streptococcal infection
. It affects the pharynx
including the tonsils and possibly the larynx
. Common symptoms include fever
, sore throat
, and enlarged lymph nodes. It is the cause of 37% of sore throats among children.
Strep throat is a contagious infection, spread through close contact with an infected individual. A definitive diagnosis is made based on the results of a throat culture
. However, this is not always needed as treatment may be decided based on symptoms. In highly likely or confirmed cases, antibiotics are useful to both prevent complications and speed recovery.
, fever
of greater than 38 °C (100.4 °F), tonsillar exudates (pus
on the tonsils), and large cervical lymph nodes
.
Other symptoms include:
The incubation period
and thus the start of symptoms for strep throat is between one to three days post contact.
may also cause pharyngitis
. It is spread by direct, close contact with an infected person and thus crowding as may be found in the military and schools increases the rate of transmission. It has been found that dried bacteria in dust are not infectious, although moist bacteria on toothbrushes or similar items can persist for up to fifteen days. Rarely, contaminated food can result in outbreaks. Of children with no signs or symptoms 12% carry GAS in their pharynx.
The modified Centor score is used to determine the management of people with pharyngitis. Based on 5 clinical criteria, it indicates the probability of a streptococcal infection.
One point is given for each of the criteria:
is the gold standard
for the diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis with a sensitivity of 90–95%. A rapid strep test
(also called rapid antigen detection testing or RADT) may also be used. While the rapid strep test is quicker, it has a lower sensitivity (70%) and statistically equal specificity (98%) as throat culture.
A positive throat culture or RADT in association with symptoms establishes a positive diagnosis in those in which the diagnosis is in doubt. Asymptomatic individuals should not be routinely tested with a throat culture or RADT because a certain percentage of the population persistently "carries" the streptococcal bacteria in their throat without any harmful results.
, and red, irritated eyes
in addition to fever and sore throat are more indicative of a viral sore throat than of strep throat.
The presence of marked lymph node enlargement along with sore throat, fever and tonsillar enlargement may also occur in infectious mononucleosis
.
may be a reasonable preventative measure in those with frequent throat infections. Three or more a year was seen as sufficient in 2003. Watchful waiting is also appropriate.
and retropharyngeal abscess
es and they are effective if given within 9 days of the onset of symptoms.
s (NSAIDs) and paracetamol
(acetaminophen) help significantly in the management of pain associated with strep throat. Steroids are also useful in this respect as is viscous lidocaine
. Aspirin may be used in adults but is not recommended in children due to the risk of Reye's syndrome
.
due to safety, cost, and effectiveness. Amoxicillin
is preferred in Europe. In India, where the risk of rheumatic fever is higher, intramuscular benzathine penicillin G is the first choice for treatment. Appropriate antibiotics decrease the average 3–5 day duration of symptoms by about one day, and also reduce contagiousness. They are primarily prescribed out of a motivation to reduce rare complications such as acute rheumatic fever and peritonsillar abscess
. The arguments in favour of antibiotic treatment should be balanced by the consideration of possible side effects, and it is reasonable to suggest that no antimicrobial treatment be given to healthy adults who have adverse reactions to medication. Antibiotics are prescribed for strep throat at a higher rate than would be expected from its prevalence. Erythromycin
and other macrolides are recommended for people with severe penicillin allergies. First, general cephalosporins may be used in those with less severe allergies. Streptococcal infections may also lead to acute glomerulonephritis, however the incidence of this side effect is not reduced by the use of antibiotics.
Complications arising from streptococcal throat infections include:
, the broader category into which Streptococcal pharyngitis falls, is diagnosed in 11 million people annually in the United States. Although most cases are viral, group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus is the cause in 15–30% of the pharyngitis cases in children and 5–20% in adults. Cases usually occur in late winter and early spring.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the throat or pharynx. In most cases it is quite painful, and is the most common cause of a sore throat.Like many types of inflammation, pharyngitis can be acute – characterized by a rapid onset and typically a relatively short course – or chronic....
caused by a group A streptococcal infection
Group A streptococcal infection
The group A streptococcus bacterium is a form of β-hemolytic Streptococcus bacteria responsible for most cases of streptococcal illness. Other types may also cause infection...
. It affects the pharynx
Pharynx
The human pharynx is the part of the throat situated immediately posterior to the mouth and nasal cavity, and anterior to the esophagus and larynx. The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx , the oropharynx , and the laryngopharynx...
including the tonsils and possibly the larynx
Larynx
The larynx , commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the neck of amphibians, reptiles and mammals involved in breathing, sound production, and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. It manipulates pitch and volume...
. Common symptoms include fever
Fever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
, sore throat
Sore throat
A sore throat or throat pain is a common physical symptom usually caused by acute pharyngitis, or throat inflammation, though it also occurs in a number of other situations, such as post trauma and in diphtheria. It can cause mild to extreme pain....
, and enlarged lymph nodes. It is the cause of 37% of sore throats among children.
Strep throat is a contagious infection, spread through close contact with an infected individual. A definitive diagnosis is made based on the results of a throat culture
Throat culture
A throat culture is a laboratory diagnostic test to find a bacterial or fungal infection in the throat. Sampling is performed by throat swab, and the sample is put in a special cup that allows infections to grow. If an infection grows, the culture is positive. The type of infection is found using...
. However, this is not always needed as treatment may be decided based on symptoms. In highly likely or confirmed cases, antibiotics are useful to both prevent complications and speed recovery.
Signs and symptoms
The typical symptoms of streptococcal pharyngitis are a sore throatSore throat
A sore throat or throat pain is a common physical symptom usually caused by acute pharyngitis, or throat inflammation, though it also occurs in a number of other situations, such as post trauma and in diphtheria. It can cause mild to extreme pain....
, fever
Fever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
of greater than 38 °C (100.4 °F), tonsillar exudates (pus
Pus
Pus is a viscous exudate, typically whitish-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammatory during infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection of pus within or beneath the epidermis is known as a pustule or...
on the tonsils), and large cervical lymph nodes
Cervical lymph nodes
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck.-Classification:There are approximately 300 lymph nodes in the neck, and they can be classified in many different ways.Henri Rouvière produced an influential classification in 1938...
.
Other symptoms include:
- HeadacheHeadacheA headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
- NauseaNauseaNausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
and vomitingVomitingVomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose... - Abdominal painAbdominal painAbdominal pain can be one of the symptoms associated with transient disorders or serious disease. Making a definitive diagnosis of the cause of abdominal pain can be difficult, because many diseases can result in this symptom. Abdominal pain is a common problem...
- MyalgiaMyalgiaMyalgia means "muscle pain" and is a symptom of many diseases and disorders. The most common causes are the overuse or over-stretching of a muscle or group of muscles. Myalgia without a traumatic history is often due to viral infections...
(muscle pain) - Scarlatiniform rash or palatal petechiae, the latter being a an uncommon but highly specificSensitivity and specificitySensitivity and specificity are statistical measures of the performance of a binary classification test, also known in statistics as classification function. Sensitivity measures the proportion of actual positives which are correctly identified as such Sensitivity and specificity are statistical...
finding
The incubation period
Incubation period
Incubation period is the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, a chemical or radiation, and when symptoms and signs are first apparent...
and thus the start of symptoms for strep throat is between one to three days post contact.
Cause
Strep throat is caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GAS). Other bacteria such as non–group A beta-hemolytic streptococci and fusobacteriumFusobacterium
Fusobacterium is a genus of filamentous, anaerobic, Gram-negative bacteria, similar to Bacteroides.Fusobacterium contribute to several human diseases, including periodontal diseases, Lemierre's syndrome, and topical skin ulcers...
may also cause pharyngitis
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the throat or pharynx. In most cases it is quite painful, and is the most common cause of a sore throat.Like many types of inflammation, pharyngitis can be acute – characterized by a rapid onset and typically a relatively short course – or chronic....
. It is spread by direct, close contact with an infected person and thus crowding as may be found in the military and schools increases the rate of transmission. It has been found that dried bacteria in dust are not infectious, although moist bacteria on toothbrushes or similar items can persist for up to fifteen days. Rarely, contaminated food can result in outbreaks. Of children with no signs or symptoms 12% carry GAS in their pharynx.
Diagnosis
| Points | Probability of Strep | Management |
|---|---|---|
| 1 or less | <10% | No antibiotic or culture needed |
| 2 | 11–17% | Antibiotic based on culture or RADT |
| 3 | 28–35% | |
| 4 or 5 | 52% | Empiric antibiotics |
The modified Centor score is used to determine the management of people with pharyngitis. Based on 5 clinical criteria, it indicates the probability of a streptococcal infection.
One point is given for each of the criteria:
- Absence of a cough
- Swollen and tender cervical lymph nodes
- Temperature >38 °C (100.4 °F)
- Tonsillar exudate or swelling
- Age less than 15 (a point is subtracted if age >44)
Laboratory testing
A throat cultureThroat culture
A throat culture is a laboratory diagnostic test to find a bacterial or fungal infection in the throat. Sampling is performed by throat swab, and the sample is put in a special cup that allows infections to grow. If an infection grows, the culture is positive. The type of infection is found using...
is the gold standard
Gold standard (test)
In medicine and statistics, gold standard test refers to a diagnostic test or benchmark that is the best available under reasonable conditions. It does not have to be necessarily the best possible test for the condition in absolute terms...
for the diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis with a sensitivity of 90–95%. A rapid strep test
Rapid Strep Test
The Rapid Strep Test , or rapid antigen detection test , is an in-office test done by a clinician in order to determine whether or not a patient has streptococcal pharyngitis , which is a group A streptococcal infection of the pharynx and possibly other parts of the body.Streptococcal pharyngitis...
(also called rapid antigen detection testing or RADT) may also be used. While the rapid strep test is quicker, it has a lower sensitivity (70%) and statistically equal specificity (98%) as throat culture.
A positive throat culture or RADT in association with symptoms establishes a positive diagnosis in those in which the diagnosis is in doubt. Asymptomatic individuals should not be routinely tested with a throat culture or RADT because a certain percentage of the population persistently "carries" the streptococcal bacteria in their throat without any harmful results.
Differential diagnosis
As the symptoms of streptococcal pharyngitis overlap with other conditions it can be difficult to make the diagnosis clinically. Coughing, nasal discharge, diarrheaDiarrhea
Diarrhea , also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having three or more loose or liquid bowel movements per day. It is a common cause of death in developing countries and the second most common cause of infant deaths worldwide. The loss of fluids through diarrhea can cause dehydration and...
, and red, irritated eyes
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis refers to inflammation of the conjunctiva...
in addition to fever and sore throat are more indicative of a viral sore throat than of strep throat.
The presence of marked lymph node enlargement along with sore throat, fever and tonsillar enlargement may also occur in infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis is an infectious, widespread viral...
.
Prevention
TonsillectomyTonsillectomy
A tonsillectomy is a 3,000-year-old surgical procedure in which the tonsils are removed from either side of the throat. The procedure is performed in response to cases of repeated occurrence of acute tonsillitis or adenoiditis, obstructive sleep apnea, nasal airway obstruction, snoring, or...
may be a reasonable preventative measure in those with frequent throat infections. Three or more a year was seen as sufficient in 2003. Watchful waiting is also appropriate.
Treatment
Untreated streptococcal pharyngitis usually resolves within a few days. Treatment with antibiotics shortens the duration of the acute illness by about 16 hours. The primary reason for treatment with antibiotics is to reduce the risk of complications such as rheumatic feverRheumatic fever
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that occurs following a Streptococcus pyogenes infection, such as strep throat or scarlet fever. Believed to be caused by antibody cross-reactivity that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain, the illness typically develops two to three weeks after...
and retropharyngeal abscess
Retropharyngeal abscess
Most commonly seen in infants and young children, retropharyngeal abscess is an abscess located in the tissues in the back of the throat behind the posterior pharyngeal wall . Because RPA's typically occur in deep tissue, they are difficult to diagnose by physical examination alone...
es and they are effective if given within 9 days of the onset of symptoms.
Analgesics
Analgesics such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugNon-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, usually abbreviated to NSAIDs or NAIDs, but also referred to as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents/analgesics or nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory medicines , are drugs with analgesic and antipyretic effects and which have, in higher doses, anti-inflammatory...
s (NSAIDs) and paracetamol
Paracetamol
Paracetamol INN , or acetaminophen USAN , is a widely used over-the-counter analgesic and antipyretic . It is commonly used for the relief of headaches and other minor aches and pains and is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu remedies...
(acetaminophen) help significantly in the management of pain associated with strep throat. Steroids are also useful in this respect as is viscous lidocaine
Lidocaine
Lidocaine , Xylocaine, or lignocaine is a common local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug. Lidocaine is used topically to relieve itching, burning and pain from skin inflammations, injected as a dental anesthetic or as a local anesthetic for minor surgery.- History :Lidocaine, the first amino...
. Aspirin may be used in adults but is not recommended in children due to the risk of Reye's syndrome
Reye's syndrome
Reye's syndrome is a potentially fatal disease that causes numerous detrimental effects to many organs, especially the brain and liver, as well as causing a lower than usual level of blood sugar . The classic features are liver damage, aspirin use and a viral infection...
.
Antibiotics
The antibiotic of choice in the United States for streptococcal pharyngitis is penicillin VPhenoxymethylpenicillin
Phenoxymethylpenicillin, commonly known as penicillin V, is a penicillin antibiotic that is orally active. It is less active than benzylpenicillin against Gram-negative bacteria. Phenoxymethylpenicillin is more acid-stable than benzylpenicillin, which allows it to be given orally...
due to safety, cost, and effectiveness. Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin , formerly amoxycillin , and abbreviated amox, is a moderate-spectrum, bacteriolytic, β-lactam antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections caused by susceptible microorganisms. It is usually the drug of choice within the class because it is better absorbed, following oral...
is preferred in Europe. In India, where the risk of rheumatic fever is higher, intramuscular benzathine penicillin G is the first choice for treatment. Appropriate antibiotics decrease the average 3–5 day duration of symptoms by about one day, and also reduce contagiousness. They are primarily prescribed out of a motivation to reduce rare complications such as acute rheumatic fever and peritonsillar abscess
Peritonsillar abscess
Peritonsillar abscess , also called a quinsy or abbreviated as PTA is a recognised complication of tonsillitis and consists of a collection of pus beside the tonsil .-Symptoms and signs:...
. The arguments in favour of antibiotic treatment should be balanced by the consideration of possible side effects, and it is reasonable to suggest that no antimicrobial treatment be given to healthy adults who have adverse reactions to medication. Antibiotics are prescribed for strep throat at a higher rate than would be expected from its prevalence. Erythromycin
Erythromycin
Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic that has an antimicrobial spectrum similar to or slightly wider than that of penicillin, and is often used for people who have an allergy to penicillins. For respiratory tract infections, it has better coverage of atypical organisms, including mycoplasma and...
and other macrolides are recommended for people with severe penicillin allergies. First, general cephalosporins may be used in those with less severe allergies. Streptococcal infections may also lead to acute glomerulonephritis, however the incidence of this side effect is not reduced by the use of antibiotics.
Prognosis
The symptoms of strep throat usually improve irrespective of treatment within three to five days. Treatment with antibiotics reduces the risk of complications and transmission; children may return to school 24 hours after antibiotics are administered.Complications arising from streptococcal throat infections include:
- Acute rheumatic feverRheumatic feverRheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that occurs following a Streptococcus pyogenes infection, such as strep throat or scarlet fever. Believed to be caused by antibody cross-reactivity that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain, the illness typically develops two to three weeks after...
- Scarlet feverScarlet feverScarlet fever is a disease caused by exotoxin released by Streptococcus pyogenes. Once a major cause of death, it is now effectively treated with antibiotics...
- Streptococcal toxic shock syndromeToxic shock syndromeToxic shock syndrome is a potentially fatal illness caused by a bacterial toxin. Different bacterial toxins may cause toxic shock syndrome, depending on the situation. The causative bacteria include Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes...
- GlomerulonephritisGlomerulonephritisGlomerulonephritis, also known as glomerular nephritis, abbreviated GN, is a renal disease characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli, or small blood vessels in the kidneys...
- PANDAS syndrome
Epidemiology
PharyngitisPharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the throat or pharynx. In most cases it is quite painful, and is the most common cause of a sore throat.Like many types of inflammation, pharyngitis can be acute – characterized by a rapid onset and typically a relatively short course – or chronic....
, the broader category into which Streptococcal pharyngitis falls, is diagnosed in 11 million people annually in the United States. Although most cases are viral, group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus is the cause in 15–30% of the pharyngitis cases in children and 5–20% in adults. Cases usually occur in late winter and early spring.

