Stress relaxation
Encyclopedia
Stress relaxation describes how polymers relieve stress under constant strain. Because they are viscoelastic, polymers behave in a nonlinear, non-Hookean
fashion. This nonlinearity is described by both stress relaxation and a phenomenon known as creep
, which describes how polymers strain under constant stress.
Viscoelastic
materials have the properties of both viscous and elastic materials and can be modeled by combining elements that represent these characteristics. One viscoelastic model, called the Maxwell model
predicts behavior akin to a spring (elastic element) being in series with a dashpot (viscous element), while the Voigt model
places these elements in parallel. Although the Maxwell model is good at predicting stress relaxation, it is fairly poor at predicting creep. On the other hand, the Voigt model is good at predicting creep but rather poor at predicting stress relaxation. The most accurate of the viscoelastic models is the Standard Linear Solid model
, which combines the characteristics of both the Maxwell and Voigt models to display both creep and stress relaxation (See Viscoelasticity
).
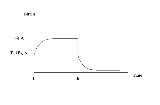
The following image shows the response of a Standard Linear Solid material to a constant stress, , over time from
, over time from  to a later time
to a later time  . For times greater than
. For times greater than 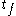 the load is removed. The curvature of the model represent the effects of both creep and stress relaxation.
the load is removed. The curvature of the model represent the effects of both creep and stress relaxation.
Stress relaxation calculations can differ for different materials:
To generalize, Obukhov uses power dependencies: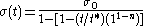
where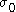 is the maximum stress at the time the loading was removed (t*), and n is a material parameter.
is the maximum stress at the time the loading was removed (t*), and n is a material parameter.
Vegener et al. use a power series to describe stress relaxation in polyamides:

To model stress relaxation in glass materials Dowvalter uses the following:
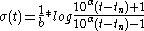
where is a material constant and b and
is a material constant and b and  depend on processing conditions.
depend on processing conditions.
The following non-material parameters all affect stress relaxation in polymers :
Hooke's law
In mechanics, and physics, Hooke's law of elasticity is an approximation that states that the extension of a spring is in direct proportion with the load applied to it. Many materials obey this law as long as the load does not exceed the material's elastic limit. Materials for which Hooke's law...
fashion. This nonlinearity is described by both stress relaxation and a phenomenon known as creep
Creep (deformation)
In materials science, creep is the tendency of a solid material to slowly move or deform permanently under the influence of stresses. It occurs as a result of long term exposure to high levels of stress that are below the yield strength of the material....
, which describes how polymers strain under constant stress.
Viscoelastic
Viscoelasticity
Viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like honey, resist shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Elastic materials strain instantaneously when stretched and just...
materials have the properties of both viscous and elastic materials and can be modeled by combining elements that represent these characteristics. One viscoelastic model, called the Maxwell model
Maxwell material
A Maxwell material is a viscoelastic material having the properties both of elasticity and viscosity. It is named for James Clerk Maxwell who proposed the model in 1867. It is also known as a Maxwell fluid.- Definition :...
predicts behavior akin to a spring (elastic element) being in series with a dashpot (viscous element), while the Voigt model
Kelvin-Voigt material
A Kelvin–Voigt material, also called a Voigt material, is a viscoelastic material having the properties both of elasticity and viscosity. It is named after the British physicist and engineer William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin and after German physicist Woldemar Voigt.- Definition :The Kelvin–Voigt...
places these elements in parallel. Although the Maxwell model is good at predicting stress relaxation, it is fairly poor at predicting creep. On the other hand, the Voigt model is good at predicting creep but rather poor at predicting stress relaxation. The most accurate of the viscoelastic models is the Standard Linear Solid model
Standard Linear Solid model
The standard linear solid model, also known as the Zener model, is a method of modeling the behavior of a viscoelastic material using a linear combination of springs and dashpots to represent elastic and viscous components, respectively. Often more similar Maxwell model and the Kelvin–Voigt model...
, which combines the characteristics of both the Maxwell and Voigt models to display both creep and stress relaxation (See Viscoelasticity
Viscoelasticity
Viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like honey, resist shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Elastic materials strain instantaneously when stretched and just...
).
The following image shows the response of a Standard Linear Solid material to a constant stress,
 , over time from
, over time from  to a later time
to a later time  . For times greater than
. For times greater than  the load is removed. The curvature of the model represent the effects of both creep and stress relaxation.
the load is removed. The curvature of the model represent the effects of both creep and stress relaxation.Stress relaxation calculations can differ for different materials:
To generalize, Obukhov uses power dependencies:
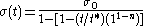
where
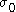 is the maximum stress at the time the loading was removed (t*), and n is a material parameter.
is the maximum stress at the time the loading was removed (t*), and n is a material parameter.Vegener et al. use a power series to describe stress relaxation in polyamides:

To model stress relaxation in glass materials Dowvalter uses the following:
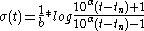
where
 is a material constant and b and
is a material constant and b and  depend on processing conditions.
depend on processing conditions.The following non-material parameters all affect stress relaxation in polymers :
- Magnitude of initial loading
- Speed of loading
- Temperature (isothermal vs non-isothermal conditions)
- Loading medium
- Friction and wear
- Long-term storage
See also
- CreepCreep (deformation)In materials science, creep is the tendency of a solid material to slowly move or deform permanently under the influence of stresses. It occurs as a result of long term exposure to high levels of stress that are below the yield strength of the material....
- ViscoelasticityViscoelasticityViscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like honey, resist shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Elastic materials strain instantaneously when stretched and just...
- Standard Linear Solid ModelStandard Linear Solid modelThe standard linear solid model, also known as the Zener model, is a method of modeling the behavior of a viscoelastic material using a linear combination of springs and dashpots to represent elastic and viscous components, respectively. Often more similar Maxwell model and the Kelvin–Voigt model...
- Maxwell materialMaxwell materialA Maxwell material is a viscoelastic material having the properties both of elasticity and viscosity. It is named for James Clerk Maxwell who proposed the model in 1867. It is also known as a Maxwell fluid.- Definition :...
- Kelvin-Voigt materialKelvin-Voigt materialA Kelvin–Voigt material, also called a Voigt material, is a viscoelastic material having the properties both of elasticity and viscosity. It is named after the British physicist and engineer William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin and after German physicist Woldemar Voigt.- Definition :The Kelvin–Voigt...

