Surname
Encyclopedia
A surname is a name added to a given name
and is part of a personal name
. In many cases, a surname is a family name
. Many dictionaries define "surname" as a synonym
of "family name". In some Western countries, it is commonly called "last name", with the notable exception of Hungary
, where, just like in China
, Japan
and in many other East Asia
n countries, the family name is placed before a person's given name.
The western style of having both a family name (surname) and a given name (Christian name or forename) is far from universal. In many countries it is common for ordinary people to have only one name or Mononym.
, Andhra Pradesh
in South India
, Sri Lanka and countries in the Chinese cultural sphere including Japan
, Korea
, Vietnam
and China
.
In Japan and Hong Kong (China), when people of Japanese or Hong Kong Chinese origin, respectively, write their personal name in the Latin alphabet
, it is common to reverse the order of the given and family names for the convenience of Westerners. Hungarians do the same when interacting with other Europeans
. Reversing the order of names is also customary for the Baltic Fennic peoples
and the Hungarians, but other Uralic peoples
didn't need surnames, because of the clanic
structure of their societies. Surnames have been imposed by the dominant authorities: evangelists, then administrations. Thus, the Samis saw no change or a transformation of their name, for example: some Sire became Siri, Hætta Jáhkoš Ásslat became Aslak Jacobsen Hætta
— as it was the norm
until recently, when integration into the EU and accelerated international exchanges pushed many people to reverse the order of their full name to given name - surname, so that they are not called Ms. Rauha (a first name), just like Japanese, some Koreans, Chinese or some Vietnamese do, for the same reason.
In France
and Italy
, administrative usage is to put the surname before the first on official documents.
such as "Andersen
", a matronymic
such as "Beaton
", or a clan name such as "O'Brien
". Multiple surnames may be derived from a single given name: e.g. there are thought to be over 90 Italian surnames based on the given name "Giovanni
".
Occupational names include such simple examples as "Eisenhauer" (iron worker, later Anglicized in America as "Eisenhower
") or "Schneider
" (tailor) as well as more complicated names based on occupational titles. In England it was common for servants to take a modified version of their employer's occupation or first name as their last name, adding the letter "s" to the word, although this formation could also be a patronymic
. For instance, the surname "Vickers
" is thought to have arisen as an occupational name adopted by the servant of a vicar, while "Roberts
" could have been adopted by either the son or the servant of a man named Robert. A subset of occupational names in English are names thought to be derived from the medieval mystery plays. The participants would often play the same roles for life, passing the part down to their oldest sons. Names derived from this may include "King", "Lord", "Virgin", and "Death"; the last is often wrongly thought to be an Anglicization of the French name "D'Ath". It is now thought that the surname "D'Ath" arose well after the surname "Death" was first used.
". Although some surnames (such as "London" or "Bialystok") are derived from large cities, more people reflect the names of smaller communities, as in Ó Creachmhaoil
, derived from a village in County Galway
. This is thought to be due to the tendency in Europe during the Middle Ages for migration to chiefly be from smaller communities to the cities, and the need for new arrivals to choose a defining surname.
Many Japanese surnames
derive from geographical features; for example, Ishikawa (石川) means "stone river", Yamamoto (山本) means "the base of the mountain", and Inoue (井上) means "above the well".
Arabic name
s also contain surnames that denote the city of origin, for example, in cases of Saddam Hussein al Tikriti
, meaning Saddam Hussein of Tikrit
, a city in Iraq. This component of the name is called a nisbah.
" ("morning star"), "Safire" ("sapphire"), and "Reis" ("branch"). In some cases, such as Chinese Indonesians and Chinese Thais, certain ethnic groups are subject to political pressure to change their surnames, in which case surnames can lose their family-name meaning. For instance, Indonesian business tycoon Liem Swie Liong (林绍良) "indonesianised" his name to Sudono Salim
. In this case "Liem" (林) was rendered by "Salim", a name of Arabic origin, while "Sudono", a Javanese name with the honorific prefix "su-" of Sanskrit origin, was supposed to be a rendering of "Swie Liong".
", which has no known meaning. Other surnames may have arisen from more than one source: the name "De Luca", for instance, likely arose either in or near Lucania or in the family of someone named Lucas or Lucius; in some instances, however, the name may have arisen from Lucca, with the spelling and pronunciation changing over time and with emigration. The same name may appear in different cultures by coincidence or romanization; the surname Lee
is used in English culture, but is also a romanization of the Chinese surname Li
.
Surname origins have been the subject of much folk etymology, often by individuals intent on proving that their own surname is more noble or royal than the average name. The name "Ryan" mentioned above, for example, is often said to be derived from Gaelic words meaning "little king"; this etymology is commonly found on name origin websites and in less stringently edited books. Some folk etymologies also develop because a name is seen to be coarse or crude: the surname "Death" is explained away as being an Anglicization of "D'Ath" for this reason.
Surnames were uncommon prior to the 12th century, and still somewhat rare into the 13th; most European surnames were originally occupational or locational, and served to distinguish one person from another if they happened to live near one another (e.g., two different people named John could conceivably be identified as 'John Butcher' and 'John Chandler'). This still happens, in some communities where a surname is particularly common, for example on the Isle of Lewis in Scotland
, many residents have the family name MacLeod (son of Lewis) and so may still be known by a surname symbolising their occupation such as 'Kevin the post' and 'Kevin Handbag'
In French Canada
until the 19th century, several families adopted surnames that followed the family name in order to distinguish the various branches of a large family. Such a surname was preceded by the word "dit" ("said") and was known as a "nom-dit" ("said-name"). (Compare with some Roman naming conventions
.) While this tradition is no longer in use, in many cases the nom-dit has come to replace the original family name. Thus the Bourbeau family has split into Bourbeau dit Verville, Bourbeau dit Lacourse, and Bourbeau dit Beauchesne. In many cases Verville, Lacourse, or Beauchesne has become the new family name. Likewise, the Rivard family has split into the Rivard dit Lavigne, Rivard dit Loranger and Rivard dit Lanoie. The origin of the nom-dit can vary. Often it denoted a geographical trait of the area where that branch of the family lived: Verville lived towards the city, Beauchesne lived near an oak tree, Larivière near a river, etc. Some of the oldest noms-dits are derived from the war name of a settler who served in the army or militia: Tranchemontagne ("mountain slasher"), Jolicœur ("braveheart"). Others denote a personal trait: Lacourse might have been a fast runner, Legrand was probably tall, etc.
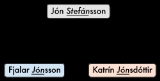
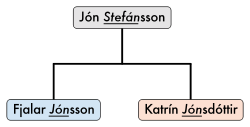 The Icelandic system, formerly used in much of Scandinavia, does not use family names. A person's surname indicates the first name of the person's father (patronymic
The Icelandic system, formerly used in much of Scandinavia, does not use family names. A person's surname indicates the first name of the person's father (patronymic
) or in some cases mother (matronymic
). Most family names in other Scandinavian countries are a result of this naming practice, such as Hansen
(son of Hans
), Johansen
(son of Johan
) and Olsen
(Son of Ole
/Ola
) the three most common surnames in Norway
.
Patronymic name conventions are similar in some other nations, including Malaysia (see Malaysian name
) and other Muslim countries, among most people of the Indian states of Tamil Nadu
and Kerala
(unlike another Indian state Andhra Pradesh
, where ancestral origin village names have become surnames for the people), in Mongolia and in the Scottish Gaelic personal naming system
. In Russia and Bulgaria
, both a patronym and a family name are obligatory parts of one's full name: e.g., if a Russian is called Ivan Andreyevich Sergeyev, that means that his father's name is Andrey and his family name is Sergeyev. A similar system is used in Greece. However, unlike the Icelandic case, only the family name is generally identified as a surname proper.
In Ethiopia and Eritrea
, a child adopts the given name of one of their parents, usually the father, as a pseudo-surname. For example, Abraham Mesfin's father's name would have been Mesfin, while a child would be called "Nestanet Abraham". Referring to Abraham Mesfin as "Mr. Mesfin" would be erroneous: The correct term would be "Mr. Abraham". Very rarely do children adopt their mother's given name, who in any case would retain their "pseudo-surname".
or ironsmith.
Approximately 70 percent of Canadians have surnames that are of English, Irish, French, or Scottish derivation.
Some estimates say that 85 percent of China's population shares 100 surnames. In China the names Wang, Zhang and Li are the most common.
Given name
A given name, in Western contexts often referred to as a first name, is a personal name that specifies and differentiates between members of a group of individuals, especially in a family, all of whose members usually share the same family name...
and is part of a personal name
Personal name
A personal name is the proper name identifying an individual person, and today usually comprises a given name bestowed at birth or at a young age plus a surname. It is nearly universal for a human to have a name; except in rare cases, for example feral children growing up in isolation, or infants...
. In many cases, a surname is a family name
Family name
A family name is a type of surname and part of a person's name indicating the family to which the person belongs. The use of family names is widespread in cultures around the world...
. Many dictionaries define "surname" as a synonym
Synonym
Synonyms are different words with almost identical or similar meanings. Words that are synonyms are said to be synonymous, and the state of being a synonym is called synonymy. The word comes from Ancient Greek syn and onoma . The words car and automobile are synonyms...
of "family name". In some Western countries, it is commonly called "last name", with the notable exception of Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
, where, just like in China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
and in many other East Asia
East Asia
East Asia or Eastern Asia is a subregion of Asia that can be defined in either geographical or cultural terms...
n countries, the family name is placed before a person's given name.
The western style of having both a family name (surname) and a given name (Christian name or forename) is far from universal. In many countries it is common for ordinary people to have only one name or Mononym.
Order of words
In some cultures, including those of most Western countries, the surname or family name ("last name") is placed after the personal or given name ("first name"). In other cultures the surname is placed first, followed by the given name or names; this is the case in HungaryHungarian name
Hungarian names invariably use the "Eastern name order", or family name followed by given name, except in foreign language text. Hungary is the only European and Western country to do so....
, Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh , is one of the 28 states of India, situated on the southeastern coast of India. It is India's fourth largest state by area and fifth largest by population. Its capital and largest city by population is Hyderabad.The total GDP of Andhra Pradesh is $100 billion and is ranked third...
in South India
South India
South India is the area encompassing India's states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Pondicherry, occupying 19.31% of India's area...
, Sri Lanka and countries in the Chinese cultural sphere including Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, Korea
Korea
Korea ) is an East Asian geographic region that is currently divided into two separate sovereign states — North Korea and South Korea. Located on the Korean Peninsula, Korea is bordered by the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and is separated from Japan to the...
, Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
.
In Japan and Hong Kong (China), when people of Japanese or Hong Kong Chinese origin, respectively, write their personal name in the Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
, it is common to reverse the order of the given and family names for the convenience of Westerners. Hungarians do the same when interacting with other Europeans
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. Reversing the order of names is also customary for the Baltic Fennic peoples
Baltic Finns
The Baltic Finns are a historical linguistic group of peoples of northern Europe whose modern descendants include the Finns proper, Karelians , Izhorians, Veps, Votes, Livonians and Estonians who speak Baltic-Finnic languages and have inhabited the Baltic Sea region for 3,000 years according to...
and the Hungarians, but other Uralic peoples
Uralic languages
The Uralic languages constitute a language family of some three dozen languages spoken by approximately 25 million people. The healthiest Uralic languages in terms of the number of native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, Estonian, Mari and Udmurt...
didn't need surnames, because of the clanic
Clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clan members may be organized around a founding member or apical ancestor. The kinship-based bonds may be symbolical, whereby the clan shares a "stipulated" common ancestor that is a...
structure of their societies. Surnames have been imposed by the dominant authorities: evangelists, then administrations. Thus, the Samis saw no change or a transformation of their name, for example: some Sire became Siri, Hætta Jáhkoš Ásslat became Aslak Jacobsen Hætta
Aslak Hætta
Aslak Jacobsen Hætta was one of the leaders of the Sami revolt in Guovdageaidnu in November 1852. During the riots, the merchant Carl Johan Ruth and the local government official Lars Johan Bucht were killed and the pastor Fredrik Waldemar Hvoslef was whipped...
— as it was the norm
Convention (norm)
A convention is a set of agreed, stipulated or generally accepted standards, norms, social norms or criteria, often taking the form of a custom....
until recently, when integration into the EU and accelerated international exchanges pushed many people to reverse the order of their full name to given name - surname, so that they are not called Ms. Rauha (a first name), just like Japanese, some Koreans, Chinese or some Vietnamese do, for the same reason.
In France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, administrative usage is to put the surname before the first on official documents.
Formation
Name etymologists classify European surnames under five categories, depending on their origin: given name, occupational name, location name, nickname, and ornamental name. This classification can be extended to surnames originating elsewhere.Passed down from generations.Given name
These may be a simple first name such as "Wilhelm", a patronymicPatronymic
A patronym, or patronymic, is a component of a personal name based on the name of one's father, grandfather or an even earlier male ancestor. A component of a name based on the name of one's mother or a female ancestor is a matronymic. Each is a means of conveying lineage.In many areas patronyms...
such as "Andersen
Andersen
Andersen is a Danish-Norwegian patronymic surname meaning "son of Anders"...
", a matronymic
Matronymic
A matronymic is a personal name based on the name of one's mother, grandmother, or any female ancestor. It is the female equivalent of a patronymic. In patriarchal societies, matronymic surnames are far less common than patronyms. In the past, matronymic last names were often given to children of...
such as "Beaton
Beaton (surname)
Beaton is a surname in the English language, which has multiple origins. One origin of the name is from the placename of Béthune, in Pas-de-Calais, France. Another derivation is from the mediaeval personal name Beaton, Beton, which is pet form of a short form of the names Bartholomew or Beatrice...
", or a clan name such as "O'Brien
O'Brien
The O'Brien dynasty are a royal and noble house founded in the 10th century by Brian Boru of the Dál gCais or Dalcassians. After becoming King of Munster, through conquest he established himself as High King of Ireland...
". Multiple surnames may be derived from a single given name: e.g. there are thought to be over 90 Italian surnames based on the given name "Giovanni
Giovanni (name)
Giovanni is a male Italian given name , the Italian equivalent of John. Giovanni is occasionally spelled Geovanni, Giovonnie or Giovannie; however, this deviates from the original Italian, and, in this manner, is made a unisex name...
".
Occupational name
Occupational names include such simple examples as "Eisenhauer" (iron worker, later Anglicized in America as "Eisenhower
Eisenhower (name)
Eisenhower is a surname of German or Dutch origin meaning "iron worker"Notable people who have borne the name are*Edgar N. Eisenhower , American lawyer, brother of President Dwight D. Eisenhower...
") or "Schneider
Schneider (surname)
Schneider is a very common family name in Germany. Alternate spellings include: Schnieder , Snyder, Snider, Sneider, Sneijder , Schnyder, Schnider , Sznajder and Znaider .-People:*Alexander Schneider, classical...
" (tailor) as well as more complicated names based on occupational titles. In England it was common for servants to take a modified version of their employer's occupation or first name as their last name, adding the letter "s" to the word, although this formation could also be a patronymic
Patronymic
A patronym, or patronymic, is a component of a personal name based on the name of one's father, grandfather or an even earlier male ancestor. A component of a name based on the name of one's mother or a female ancestor is a matronymic. Each is a means of conveying lineage.In many areas patronyms...
. For instance, the surname "Vickers
Vickers (disambiguation)
Vickers may refer to:*Vickers, a British engineering conglomerate founded in 1828.** Vickers Limited 1828-1927** Vickers-Armstrongs 1927-1977** Vickers plc 1977-1999...
" is thought to have arisen as an occupational name adopted by the servant of a vicar, while "Roberts
Roberts (surname)
Roberts is a surname of North Welsh origin, deriving from the Anglo Saxon/Norman given name Robert, meaning "bright fame" – from the Germanic elements "hrod" meaning fame and "beraht" meaning bright. Roberts may mean either "servant of Robert" or "son of Robert"; the latter is more common in...
" could have been adopted by either the son or the servant of a man named Robert. A subset of occupational names in English are names thought to be derived from the medieval mystery plays. The participants would often play the same roles for life, passing the part down to their oldest sons. Names derived from this may include "King", "Lord", "Virgin", and "Death"; the last is often wrongly thought to be an Anglicization of the French name "D'Ath". It is now thought that the surname "D'Ath" arose well after the surname "Death" was first used.
Location name
Location names, or habitation names, may be as generic as "Gorski" (Polish for "hill") or "Pitt" (English for "pit"), but may also refer to specific locations. "Washington", for instance, is thought to mean "the homestead of the family of Wassa", while "Lucci" likely means "resident of LuccaLucca
Lucca is a city and comune in Tuscany, central Italy, situated on the river Serchio in a fertile plainnear the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Lucca...
". Although some surnames (such as "London" or "Bialystok") are derived from large cities, more people reflect the names of smaller communities, as in Ó Creachmhaoil
Ó Creachmhaoil
Ó Creachmhaoil is an Irish surname. The name is often anglicised as Craughwell, and Crockwell. It was largely unknown outside of the south-east of County Galway, where the village of Creachmhaoil is also found, until the latter end of the 19th century when emigres established branches of the family...
, derived from a village in County Galway
County Galway
County Galway is a county in Ireland. It is located in the West Region and is also part of the province of Connacht. It is named after the city of Galway. Galway County Council is the local authority for the county. There are several strongly Irish-speaking areas in the west of the county...
. This is thought to be due to the tendency in Europe during the Middle Ages for migration to chiefly be from smaller communities to the cities, and the need for new arrivals to choose a defining surname.
Many Japanese surnames
Japanese name
in modern times usually consist of a family name , followed by a given name. "Middle names" are not generally used.Japanese names are usually written in kanji, which are characters of usually Chinese origin in Japanese pronunciation...
derive from geographical features; for example, Ishikawa (石川) means "stone river", Yamamoto (山本) means "the base of the mountain", and Inoue (井上) means "above the well".
Arabic name
Arabic name
Long ago, Arabic names were based on a long naming system; most Arabs did not simply have given/middle/family names, but a full chain of names. This system was in use throughout the Arab world. Today however, Arabic names are similar in structure to those of Modern and Western names...
s also contain surnames that denote the city of origin, for example, in cases of Saddam Hussein al Tikriti
Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein Abd al-Majid al-Tikriti was the fifth President of Iraq, serving in this capacity from 16 July 1979 until 9 April 2003...
, meaning Saddam Hussein of Tikrit
Tikrit
Tikrit is a town in Iraq, located 140 km northwest of Baghdad on the Tigris river . The town, with an estimated population in 2002 of about 260,000 is the administrative center of the Salah ad Din Governorate.-Ancient times:...
, a city in Iraq. This component of the name is called a nisbah.
Nicknames
These include names, also known as eke-names, based on appearance such as "Schwartzkopf", "Short", and probably "Caesar", and names based on temperament and personality such as "Daft", "Gutman", and "Maiden", which according to a number of sources was an English nickname meaning "effeminate". When Jewish families in Central Europe were forced to adopt surnames in the 18th and 19th century, those who failed to choose a surname were often given pejorative or even cruel nicknames (such as "Schweinmann" ("pig man") or "Schmutz" (a variant of "filthy")) by the local registrar. Many families later changed these names.Ornamental name
Ornamental names as surnames are more common in communities which adopted (or were forced to adopt) surnames in the 18th and 19th centuries, and are common among Jewish families and in Scandinavia. Examples include "MorgensternMorgenstern
Morgenstern is a Germanic surname meaning morning star.-Surname:* Barbara Morgenstern , German musician* Erin Morgenstern, American author* Joe Morgenstern, American film critic...
" ("morning star"), "Safire" ("sapphire"), and "Reis" ("branch"). In some cases, such as Chinese Indonesians and Chinese Thais, certain ethnic groups are subject to political pressure to change their surnames, in which case surnames can lose their family-name meaning. For instance, Indonesian business tycoon Liem Swie Liong (林绍良) "indonesianised" his name to Sudono Salim
Sudono Salim
Sudono Salim , also known as Liem Sioe Liong, is a Chinese Indonesian businessman of Hokchia origin. He was once considered the richest individual in Indonesia. He was the head of the conglomerate Salim Group before turning over its management to his youngest son Anthony in 1992.-Early life:Salim...
. In this case "Liem" (林) was rendered by "Salim", a name of Arabic origin, while "Sudono", a Javanese name with the honorific prefix "su-" of Sanskrit origin, was supposed to be a rendering of "Swie Liong".
Gender-specific versions of surname
Cultures like Greek and Russian tend to have surnames that change form depending on the gender of the person. For example in Greece, if a man called Papadopoulos has a daughter, she will likely be named Papadopoulou (if the couple have decided their offspring will take the father's surname), since that name has a female version.Other
The meanings of some names are unknown or unclear. The most common European name in this category may be the Irish name "RyanRyan (surname)
Ryan is a common Irish surname, as well as being a common given name.There are several possible origins for the surname. In certain cases it can be a simplified form of Mulryan...
", which has no known meaning. Other surnames may have arisen from more than one source: the name "De Luca", for instance, likely arose either in or near Lucania or in the family of someone named Lucas or Lucius; in some instances, however, the name may have arisen from Lucca, with the spelling and pronunciation changing over time and with emigration. The same name may appear in different cultures by coincidence or romanization; the surname Lee
Lee (English name)
Lee is a common surname in English-speaking countries. There are several distinct origins of the Lee surname. The most common surname of English origin is derived from Middle English lea, meaning "meadow, forest clearing" , and is therefore a name describing the bearer's place of residence...
is used in English culture, but is also a romanization of the Chinese surname Li
Li (surname)
Li is a common transliteration of several Chinese family names, including 李 , the most common Chinese family name, and the Korean family name Lee...
.
Surname origins have been the subject of much folk etymology, often by individuals intent on proving that their own surname is more noble or royal than the average name. The name "Ryan" mentioned above, for example, is often said to be derived from Gaelic words meaning "little king"; this etymology is commonly found on name origin websites and in less stringently edited books. Some folk etymologies also develop because a name is seen to be coarse or crude: the surname "Death" is explained away as being an Anglicization of "D'Ath" for this reason.
Surnames were uncommon prior to the 12th century, and still somewhat rare into the 13th; most European surnames were originally occupational or locational, and served to distinguish one person from another if they happened to live near one another (e.g., two different people named John could conceivably be identified as 'John Butcher' and 'John Chandler'). This still happens, in some communities where a surname is particularly common, for example on the Isle of Lewis in Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, many residents have the family name MacLeod (son of Lewis) and so may still be known by a surname symbolising their occupation such as 'Kevin the post' and 'Kevin Handbag'
In French Canada
French Canada
French Canada, also known as "Lower Canada", is a term to distinguish the French Canadian population of Canada from English Canada.-Definition:...
until the 19th century, several families adopted surnames that followed the family name in order to distinguish the various branches of a large family. Such a surname was preceded by the word "dit" ("said") and was known as a "nom-dit" ("said-name"). (Compare with some Roman naming conventions
Roman naming conventions
By the Republican era and throughout the Imperial era, a name in ancient Rome for a male citizen consisted of three parts : praenomen , nomen and cognomen...
.) While this tradition is no longer in use, in many cases the nom-dit has come to replace the original family name. Thus the Bourbeau family has split into Bourbeau dit Verville, Bourbeau dit Lacourse, and Bourbeau dit Beauchesne. In many cases Verville, Lacourse, or Beauchesne has become the new family name. Likewise, the Rivard family has split into the Rivard dit Lavigne, Rivard dit Loranger and Rivard dit Lanoie. The origin of the nom-dit can vary. Often it denoted a geographical trait of the area where that branch of the family lived: Verville lived towards the city, Beauchesne lived near an oak tree, Larivière near a river, etc. Some of the oldest noms-dits are derived from the war name of a settler who served in the army or militia: Tranchemontagne ("mountain slasher"), Jolicœur ("braveheart"). Others denote a personal trait: Lacourse might have been a fast runner, Legrand was probably tall, etc.
Surname formed from a parent's name

Patronymic
A patronym, or patronymic, is a component of a personal name based on the name of one's father, grandfather or an even earlier male ancestor. A component of a name based on the name of one's mother or a female ancestor is a matronymic. Each is a means of conveying lineage.In many areas patronyms...
) or in some cases mother (matronymic
Matronymic
A matronymic is a personal name based on the name of one's mother, grandmother, or any female ancestor. It is the female equivalent of a patronymic. In patriarchal societies, matronymic surnames are far less common than patronyms. In the past, matronymic last names were often given to children of...
). Most family names in other Scandinavian countries are a result of this naming practice, such as Hansen
Hansen
Hansen may refer to:People with the surname Hansen:* Hansen In places:* Hansen, Idaho, town in the United States* Hansen, Wisconsin, town in the United States* Hansen Township, Ontario, CanadaIn music:...
(son of Hans
Hans
Hans may refer to:*Hans, Marne, a commune in France*Hans, Magazine, a Hindi literary magazine in India*Hans Island, contested between Greenland and Canada* Hans , a given name...
), Johansen
Johansen
Johansen is a Scandinavian patronymic surname meaning "son of Johan". It is most common in Denmark and Norway. The Swedish variant is Johansson, while the most common spelling in the US is Johanson. There are still other spellings. Johansen is an uncommon given name...
(son of Johan
Johan
-Other uses:* Jo-Han, a manufacturer of plastic scale model kits* Johan and Peewit, Belgian comics series* Johan Frandsen, frontman for cult Swedish band, The Knockouts* Johan , a Dutch pop-group* Johan Cruijff-schaal, football trophy in the Netherlands...
) and Olsen
Olsen
Olsen may refer to:*Olsen , people with the surname Olsen*Fred. Olsen & Co., a large shipping company with worldwide headquarters based in Oslo, Norway-See also:...
(Son of Ole
Ole (name)
Ole is a Danish and Norwegian masculine given name, derived from the Old Norse name Óláfr, meaning "ancestor's descendant".-People named Ole:* Ole Anderson, former wrestler* Ole Barman, Norwegian novelist* Ole Barndorff-Nielsen, Danish mathematician...
/Ola
Ola
Ola may refer to:-Places:Panama*Olá, a townRussia*Ola, Russia, an urban-type settlement in Magadan Oblast, Russia*Ola River, a river near Ola, Russia in Magadan Oblast, RussiaUnited States*Ola, Arkansas, a city...
) the three most common surnames in Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
.
Patronymic name conventions are similar in some other nations, including Malaysia (see Malaysian name
Malaysian Name
Personal names in Malaysia are extremely useful in tracing a person's cultural and ethnic background as Malaysia comprises many ethnicities and cultures in which, each has its own distinct system of names. Personal names are to a certain degree, regulated by the national registration department,...
) and other Muslim countries, among most people of the Indian states of Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu is one of the 28 states of India. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu lies in the southernmost part of the Indian Peninsula and is bordered by the union territory of Pondicherry, and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh...
and Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
(unlike another Indian state Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh , is one of the 28 states of India, situated on the southeastern coast of India. It is India's fourth largest state by area and fifth largest by population. Its capital and largest city by population is Hyderabad.The total GDP of Andhra Pradesh is $100 billion and is ranked third...
, where ancestral origin village names have become surnames for the people), in Mongolia and in the Scottish Gaelic personal naming system
Scottish Gaelic personal naming system
-Forenames:Scottish Gaelic has a number of personal names, such as Ailean, Aonghas, Dòmhnall, Donnchadh, Coinneach, and Murchadh, for which there are traditional forms in English...
. In Russia and Bulgaria
Bulgarian name
Compared to other systems, the Bulgarian name system can be said to be rather simple. As a whole, it has considerable similarities with most other European name systems, and with those of other Slavic peoples in particular....
, both a patronym and a family name are obligatory parts of one's full name: e.g., if a Russian is called Ivan Andreyevich Sergeyev, that means that his father's name is Andrey and his family name is Sergeyev. A similar system is used in Greece. However, unlike the Icelandic case, only the family name is generally identified as a surname proper.
In Ethiopia and Eritrea
Habesha name
Habesha names are constructed in a fashion similar to Arabic name convention. In this convention, there are no family names. Instead, one is known through their lineage...
, a child adopts the given name of one of their parents, usually the father, as a pseudo-surname. For example, Abraham Mesfin's father's name would have been Mesfin, while a child would be called "Nestanet Abraham". Referring to Abraham Mesfin as "Mr. Mesfin" would be erroneous: The correct term would be "Mr. Abraham". Very rarely do children adopt their mother's given name, who in any case would retain their "pseudo-surname".
Culture and prevalence
In the United States, 1,712 surnames cover 50 percent of the population, and about 1 percent of the population has the surname Smith, which is also the most common English name and an occupational name ("metal worker"), a contraction of blacksmithBlacksmith
A blacksmith is a person who creates objects from wrought iron or steel by forging the metal; that is, by using tools to hammer, bend, and cut...
or ironsmith.
Approximately 70 percent of Canadians have surnames that are of English, Irish, French, or Scottish derivation.
Some estimates say that 85 percent of China's population shares 100 surnames. In China the names Wang, Zhang and Li are the most common.
See also
- Family nameFamily nameA family name is a type of surname and part of a person's name indicating the family to which the person belongs. The use of family names is widespread in cultures around the world...
- Family name (surname) in the Russian Empire, Soviet Union and CIS countries
- List of most common surnames
- MatrinameMatrinameMatrilineal surnames, or equivalently matrinames, are inherited or handed down from mother to daughter in matrilineal cultures, and this line of descent or "mother line" is called a matriline...
- One-name studyOne-name studyA one-name study is a project researching a specific surname, as opposed to a particular pedigree or descendancy...
- Scandinavian family name etymologyScandinavian family name etymologyHeritable family names were generally adopted rather late within Scandinavia. Nobility were the first to take names that would be passed on from one generation to the next. Later, clergy, artisans and merchants in cities took heritable names...
- Surname lawSurname lawSurname law can refer to any law controlling the use of surnames. Specifically, it may refer to:* Surname Law , adopted on June 21, 1934 which required the use of Western-style surnames....

