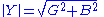Susceptance
Encyclopedia
In electrical engineering
, susceptance (B) is the imaginary part of admittance
. The inverse of admittance is impedance
and the real part of admittance is conductance. In SI
units, susceptance is measured in siemens
. Oliver Heaviside
first defined this property, which he called permittance, in June 1887.
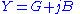
where
Rearranging yields
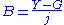 .
.
But since
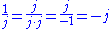 ,
,
we obtain
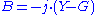 .
.
The admittance (Y) is the inverse of the impedance (Z)
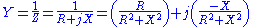
or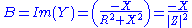
where
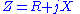
Note: The susceptance is the imaginary part of the admittance.
The magnitude of admittance is given by:
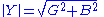
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
, susceptance (B) is the imaginary part of admittance
Admittance
In electrical engineering, the admittance is a measure of how easily a circuit or device will allow a current to flow. It is defined as the inverse of the impedance . The SI unit of admittance is the siemens...
. The inverse of admittance is impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
and the real part of admittance is conductance. In SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
units, susceptance is measured in siemens
Siemens (unit)
The siemens is the SI derived unit of electric conductance and electric admittance. Conductance and admittance are the reciprocals of resistance and impedance respectively, hence one siemens is equal to the reciprocal of one ohm, and is sometimes referred to as the mho. In English, the term...
. Oliver Heaviside
Oliver Heaviside
Oliver Heaviside was a self-taught English electrical engineer, mathematician, and physicist who adapted complex numbers to the study of electrical circuits, invented mathematical techniques to the solution of differential equations , reformulated Maxwell's field equations in terms of electric and...
first defined this property, which he called permittance, in June 1887.
Formula
The general equation defining admittance is given by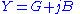
where
- Y is the admittanceAdmittanceIn electrical engineering, the admittance is a measure of how easily a circuit or device will allow a current to flow. It is defined as the inverse of the impedance . The SI unit of admittance is the siemens...
, measured in siemens (a.k.a. mho, the inverse of ohm). - G is the conductance, measured in siemens.
- j is the imaginary unitImaginary unitIn mathematics, the imaginary unit allows the real number system ℝ to be extended to the complex number system ℂ, which in turn provides at least one root for every polynomial . The imaginary unit is denoted by , , or the Greek...
, and - B is the susceptance, measured in siemens.
Rearranging yields
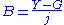 .
.But since
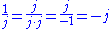 ,
,we obtain
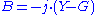 .
.The admittance (Y) is the inverse of the impedance (Z)
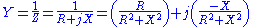
or
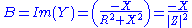
where
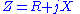
- Z is the impedanceElectrical impedanceElectrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
, measured in ohms - R is the resistanceElectrical resistanceThe electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
, measured in ohms - X is the reactance, measured in ohms.
Note: The susceptance is the imaginary part of the admittance.
The magnitude of admittance is given by: