
System M
Encyclopedia
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
since July 1, 1941, and also in most of the Americas and Caribbean
Caribbean
The Caribbean is a crescent-shaped group of islands more than 2,000 miles long separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the west and south, from the Atlantic Ocean, to the east and north...
, South Korea
South Korea
The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south...
, and Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
. In addition, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
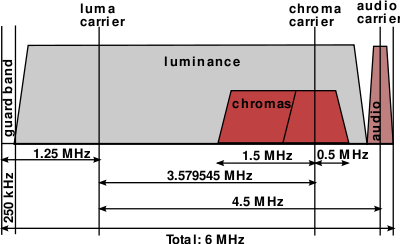
uses System J, which is nearly identical to System M. The systems were given their letter designations in the ITU identification scheme adopted in Stockholm in 1961. Both System M and System J display 525 lines of video at 30 frames per second using 6 MHz spacing between channel numbers, and is used for both VHF and UHF channels.
Specifications
| System | Lines | Frame rate | Channel b/w | Visual b/w | Sound offset | Vestigial sideband | Vision mod. | Sound mod. | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | 525 | 30 (29.97 NTSC) |
6 | 4.2 | +4.5 | 0.75 | neg. | FM | Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... (NTSC-J) |
| M | 525 | 30 (29.97 NTSC) |
6 | 4.2 | +4.5 | 0.75 | neg. | FM | Most of the Americas Americas The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily... and Caribbean Caribbean The Caribbean is a crescent-shaped group of islands more than 2,000 miles long separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the west and south, from the Atlantic Ocean, to the east and north... ; Philippines Philippines The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam... , South Korea South Korea The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south... , Taiwan Republic of China The Republic of China , commonly known as Taiwan , is a unitary sovereign state located in East Asia. Originally based in mainland China, the Republic of China currently governs the island of Taiwan , which forms over 99% of its current territory, as well as Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu and other minor... (all NTSC-M) Brazil Brazil Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people... (PAL-M) |
Color standards
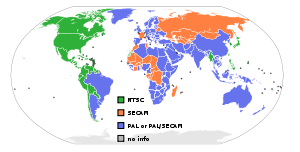
NTSC-M and NTSC-J
Strictly speaking, System M does not designate how color is transmitted. However, in nearly every System M country, NTSCNTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
is used for color television
Color television
Color television is part of the history of television, the technology of television and practices associated with television's transmission of moving images in color video....
, a combination called NTSC-M, but usually referred to more recently as simply "NTSC" because of the relative lack of importance of black-and-white television. In NTSC-M and Japan's NTSC-J
NTSC-J
NTSC-J is an analog television system and video display standard for the region of Japan.While NTSC-M is an official standard, "J" is more a colloquial indicator as used in Marketing definition but not an official term.-Technical definition:...
, the frame rate is offset slightly, becoming 30000/1001 frames per second, usually labeled as the rounded number 29.97.
PAL
The main exception to NTSC is BrazilBrazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, where PAL
PAL
PAL, short for Phase Alternating Line, is an analogue television colour encoding system used in broadcast television systems in many countries. Other common analogue television systems are NTSC and SECAM. This page primarily discusses the PAL colour encoding system...
color is used instead, resulting in the PAL-M combination unique to that country, which is monochrome-compatible with other System M countries, but not compatible with other PAL countries, which use different basic systems as their base. PAL-M signals are at 30 frames per second instead of slowing down to 29.97 like NTSC.
See also
- NTSCNTSCNTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
— dominant color system used with System M, so much so that System M is often referred to as "NTSC". Much of the information in the NTSC article is actually about System M. - Broadcast television systems — explains other types of television system standards
- Multichannel television soundMultichannel television soundMultichannel television sound, better known as MTS , is the method of encoding three additional channels of audio into an NTSC-format audio carrier.- History :...
— usual method for adding stereoSTEREOSTEREO is a solar observation mission. Two nearly identical spacecraft were launched into orbits that cause them to respectively pull farther ahead of and fall gradually behind the Earth...
to System M audio

