
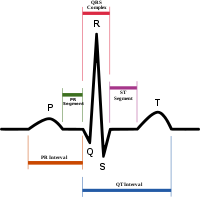
T wave
Encyclopedia
Repolarization
In neuroscience, repolarization refers to the change in membrane potential that returns the membrane potential to a negative value after the depolarization phase of an action potential has just previously changed the membrane potential to a positive value. Repolarization results from the movement...
(or recovery) of the ventricle
Ventricle
Ventricle may refer to:* Ventricle , the pumping chambers of the heart* Ventricular system in the brain* Ventricle of the larynx, a structure in the larynx* Stomach of the gastrointestinal tract...
s. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex
QRS complex
The QRS complex is a name for the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram . It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles of the human heart...
to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the absolute refractory period
Refractory period
In physiology, a refractory period is a period of time during which an organ or cell is incapable of repeating a particular action, or the amount of time it takes for an excitable membrane to be ready for a second stimulus once it returns to its resting state following an excitation...
. The last half of the T wave is referred to as the relative refractory period
Refractory period
In physiology, a refractory period is a period of time during which an organ or cell is incapable of repeating a particular action, or the amount of time it takes for an excitable membrane to be ready for a second stimulus once it returns to its resting state following an excitation...
(or vulnerable period). The T wave contains more information than the QT interval
QT interval
In cardiology, the QT interval is a measure of the time between the start of the Q wave and the end of the T wave in the heart's electrical cycle. In general, the QT interval represents electrical depolarization and repolarization of the left and right ventricles...
. The T wave can be described by its symmetry, skewness, slope of ascending and descending limbs, amplitude and subintervals like the TpeakTend interval
In most leads, the T wave is positive. However, a negative T wave is normal in lead aVR. Lead V1 may have a positive, negative, or biphasic (positive followed by negative, or vice versa) T wave. In addition, it is not uncommon to have an isolated negative T wave in lead III, aVL, or aVF.
Clinical significance
- T-wave inversion (negative T waves) can be a sign of coronary ischemia, Wellens' syndrome, left ventricular hypertrophyLeft ventricular hypertrophyLeft ventricular hypertrophy is the thickening of the myocardium of the left ventricle of the heart.-Causes:While ventricular hypertrophy occurs naturally as a reaction to aerobic exercise and strength training, it is most frequently referred to as a pathological reaction to cardiovascular...
, or CNSCentral nervous systemThe central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
disorder. - A periodic beat-to-beat variation in the amplitude or shape of the T wave may be termed T wave alternansT wave alternansT wave alternans is a periodic beat-to-beat variation in the amplitude or shape of the T wave in an electrocardiogram .TWA was first described in 1908. At that time, only large variations could be detected...
. - Tall and narrow ("peaked" or "tented") symmetrical T waves may indicate hyperkalemiaHyperkalemiaHyperkalemia refers to the condition in which the concentration of the electrolyte potassium in the blood is elevated...
.

Repolarization
In neuroscience, repolarization refers to the change in membrane potential that returns the membrane potential to a negative value after the depolarization phase of an action potential has just previously changed the membrane potential to a positive value. Repolarization results from the movement...
(or recovery) of the ventricle
Ventricle
Ventricle may refer to:* Ventricle , the pumping chambers of the heart* Ventricular system in the brain* Ventricle of the larynx, a structure in the larynx* Stomach of the gastrointestinal tract...
s. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex
QRS complex
The QRS complex is a name for the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram . It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles of the human heart...
to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the absolute refractory period
Refractory period
In physiology, a refractory period is a period of time during which an organ or cell is incapable of repeating a particular action, or the amount of time it takes for an excitable membrane to be ready for a second stimulus once it returns to its resting state following an excitation...
. The last half of the T wave is referred to as the relative refractory period
Refractory period
In physiology, a refractory period is a period of time during which an organ or cell is incapable of repeating a particular action, or the amount of time it takes for an excitable membrane to be ready for a second stimulus once it returns to its resting state following an excitation...
(or vulnerable period). The T wave contains more information than the QT interval
QT interval
In cardiology, the QT interval is a measure of the time between the start of the Q wave and the end of the T wave in the heart's electrical cycle. In general, the QT interval represents electrical depolarization and repolarization of the left and right ventricles...
. The T wave can be described by its symmetry, skewness, slope of ascending and descending limbs, amplitude and subintervals like the TpeakTend interval
In most leads, the T wave is positive. However, a negative T wave is normal in lead aVR. Lead V1 may have a positive, negative, or biphasic (positive followed by negative, or vice versa) T wave. In addition, it is not uncommon to have an isolated negative T wave in lead III, aVL, or aVF.
Clinical significance
- T-wave inversion (negative T waves) can be a sign of coronary ischemia, Wellens' syndrome, left ventricular hypertrophyLeft ventricular hypertrophyLeft ventricular hypertrophy is the thickening of the myocardium of the left ventricle of the heart.-Causes:While ventricular hypertrophy occurs naturally as a reaction to aerobic exercise and strength training, it is most frequently referred to as a pathological reaction to cardiovascular...
, or CNSCentral nervous systemThe central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
disorder. - A periodic beat-to-beat variation in the amplitude or shape of the T wave may be termed T wave alternansT wave alternansT wave alternans is a periodic beat-to-beat variation in the amplitude or shape of the T wave in an electrocardiogram .TWA was first described in 1908. At that time, only large variations could be detected...
. - Tall and narrow ("peaked" or "tented") symmetrical T waves may indicate hyperkalemiaHyperkalemiaHyperkalemia refers to the condition in which the concentration of the electrolyte potassium in the blood is elevated...
.

Repolarization
In neuroscience, repolarization refers to the change in membrane potential that returns the membrane potential to a negative value after the depolarization phase of an action potential has just previously changed the membrane potential to a positive value. Repolarization results from the movement...
(or recovery) of the ventricle
Ventricle
Ventricle may refer to:* Ventricle , the pumping chambers of the heart* Ventricular system in the brain* Ventricle of the larynx, a structure in the larynx* Stomach of the gastrointestinal tract...
s. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex
QRS complex
The QRS complex is a name for the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram . It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles of the human heart...
to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the absolute refractory period
Refractory period
In physiology, a refractory period is a period of time during which an organ or cell is incapable of repeating a particular action, or the amount of time it takes for an excitable membrane to be ready for a second stimulus once it returns to its resting state following an excitation...
. The last half of the T wave is referred to as the relative refractory period
Refractory period
In physiology, a refractory period is a period of time during which an organ or cell is incapable of repeating a particular action, or the amount of time it takes for an excitable membrane to be ready for a second stimulus once it returns to its resting state following an excitation...
(or vulnerable period). The T wave contains more information than the QT interval
QT interval
In cardiology, the QT interval is a measure of the time between the start of the Q wave and the end of the T wave in the heart's electrical cycle. In general, the QT interval represents electrical depolarization and repolarization of the left and right ventricles...
. The T wave can be described by its symmetry, skewness, slope of ascending and descending limbs, amplitude and subintervals like the TpeakTend interval
In most leads, the T wave is positive. However, a negative T wave is normal in lead aVR. Lead V1 may have a positive, negative, or biphasic (positive followed by negative, or vice versa) T wave. In addition, it is not uncommon to have an isolated negative T wave in lead III, aVL, or aVF.
Clinical significance
- T-wave inversion (negative T waves) can be a sign of coronary ischemia, Wellens' syndrome, left ventricular hypertrophyLeft ventricular hypertrophyLeft ventricular hypertrophy is the thickening of the myocardium of the left ventricle of the heart.-Causes:While ventricular hypertrophy occurs naturally as a reaction to aerobic exercise and strength training, it is most frequently referred to as a pathological reaction to cardiovascular...
, or CNSCentral nervous systemThe central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
disorder. - A periodic beat-to-beat variation in the amplitude or shape of the T wave may be termed T wave alternansT wave alternansT wave alternans is a periodic beat-to-beat variation in the amplitude or shape of the T wave in an electrocardiogram .TWA was first described in 1908. At that time, only large variations could be detected...
. - Tall and narrow ("peaked" or "tented") symmetrical T waves may indicate hyperkalemiaHyperkalemiaHyperkalemia refers to the condition in which the concentration of the electrolyte potassium in the blood is elevated...
.http://www.uhmc.sunysb.edu/internalmed/nephro/webpages/Part_D.htm - Flat T waves (less than 1 mV in the limb leads and less than 2 mV in the precordial leads) may indicate coronary ischemiaCoronary ischemiaCoronary ischemia is a medical term for not having enough blood through the coronary arteries. Coronary ischemia is linked to heart disease as well as heart attacks.It is also known as cardiac ischemia.-Causes:...
or hypokalemiaHypokalemiaHypokalemia or hypokalaemia , also hypopotassemia or hypopotassaemia , refers to the condition in which the concentration of potassium in the blood is low... - The earliest electrocardiographic finding of ST-elevation MI (STEMI) acute myocardial infarctionElectrocardiography in myocardial infarctionElectrocardiography in suspected myocardial infarction has the main purpose of detecting ischemia or acute coronary injury in emergency department populations coming for symptoms of myocardial infarction . Also, it can distinguish clinically different types of myocardial infarction.-Technical...
is sometimes the hyperacute T wave, which can be distinguished from hyperkalemiaHyperkalemiaHyperkalemia refers to the condition in which the concentration of the electrolyte potassium in the blood is elevated...
by the broad base and slight asymmetry. This may also be seen in Prinzmetal angina. - When left bundle branch blockLeft bundle branch blockLeft bundle branch block is a cardiac conduction abnormality seen on the electrocardiogram . In this condition, activation of the left ventricle is delayed, which results in the left ventricle contracting later than the right ventricle....
is present, the T wave should be deflected opposite the terminal deflection of the QRS complex. This is known as appropriate T wave discordance.
Frequency of inverted T-waves in precordial leads (lead V1 to V6) according to gender and age
Numbers from Lepeschkin E in| Age (ethnicity) | n | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | ||||||||
| 1 week - 1 y | 210 | 92% | 74% | 27% | 20% | 0.5% | 0% | |
| 1 y - 2 y | 154 | 96% | 85% | 39% | 10% | 0.7% | 0% | |
| 2 y - 5 y | 202 | 98% | 50% | 22% | 7% | 1% | 0% | |
| 5 y - 8 y | 94 | 91% | 25% | 14% | 5% | 1% | 1% | |
| 8 y - 16 y | 90 | 62% | 7% | 2% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| Males | ||||||||
| 12 y - 13 y | 209 | 47% | 7% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| 13 y - 14 y | 260 | 35% | 4.6% | 0.8% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| 16 y - 19 y (whites) | 50 | 32% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| 16 y - 19 y (blacks) | 310 | 46% | 7% | 2.9% | 1.3% | 0% | 0% | |
| 20 - 30 y (whites) | 285 | 41% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| 20 - 30 y (blacks) | 295 | 37% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| Females | ||||||||
| 12 y - 13 y | 174 | 69% | 11% | 1.2% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| 13 y - 14 y | 154 | 52% | 8.4% | 1.4% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| 16 y - 19 y (whites) | 50 | 66% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| 16 - 19 y (blacks) | 310 | 73% | 9% | 1.3% | 0.6% | 0% | 0% | |
| 20 - 30 y (whites) | 280 | 55% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| 20 - 30 y (blacks) | 330 | 55% | 2.4% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |

