
Table of muscles of the human body: Neck
Encyclopedia
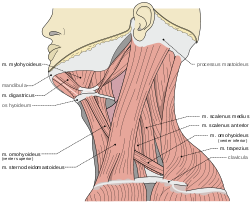
Cervical
| Muscle | |Origin | | Insertion | | Artery | | Nerve | | Action | |Antagonist |-valign="top" | platysma Platysma muscle The platysma is a superficial muscle that overlaps the sternocleidomastoid.It is a broad sheet arising from the fascia covering the upper parts of the pectoralis major and deltoid; its fibers cross the clavicle, and proceed obliquely upward and medially along the side of the neck.The anterior... |
inferior clavicle Clavicle In human anatomy, the clavicle or collar bone is a long bone of short length that serves as a strut between the scapula and the sternum. It is the only long bone in body that lies horizontally... and fascia of chest |
mandible | cervical branch of the facial nerve Cervical branch of the facial nerve The cervical branch of the facial nerve runs forward beneath the Platysma, and forms a series of arches across the side of the neck over the suprahyoid region.... (CN VII) |
Draws the corners of the mouth Mouth The mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food andsaliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth.... inferiorly and widens it (as in expressions of sadness and fright). Also draws the skin Skin -Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat... of the neck Neck The neck is the part of the body, on many terrestrial or secondarily aquatic vertebrates, that distinguishes the head from the torso or trunk. The adjective signifying "of the neck" is cervical .-Boner anatomy: The cervical spine:The cervical portion of the human spine comprises seven boney... superiorly Anatomical terms of location Standard anatomical terms of location are designations employed in science that deal with the anatomy of animals to avoid ambiguities that might otherwise arise. They are not language-specific, and thus require no translation... when teeth are clenched |
Masseter Masseter muscle In human anatomy, the masseter is one of the muscles of mastication.In the animal kingdom, it is particularly powerful in herbivores to facilitate chewing of plant matter.-Origin and insertion of the two heads:... , Temporalis Temporalis muscle The temporal muscle is one of the muscles of mastication.-Structure:It arises from the temporal fossa and the deep part of temporal fascia... >-valign="top" | sternocleidomastoid Sternocleidomastoid muscle In human anatomy, the sternocleidomastoid muscle , also known as sternomastoid and commonly abbreviated as SCM, is a paired muscle in the superficial layers of the anterior portion of the neck... |
manubrium sterni, medial portion of the clavicle Clavicle In human anatomy, the clavicle or collar bone is a long bone of short length that serves as a strut between the scapula and the sternum. It is the only long bone in body that lies horizontally... |
mastoid process of the temporal bone, superior nuchal line | occipital artery Occipital artery The occipital artery arises from the external carotid artery opposite the facial artery, its path is below the posterior belly of digastric to the occipital region. This artery supplies blood to the back of the scalp and sterno-mastoid muscles... and the superior thyroid artery Superior thyroid artery The superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery just below the level of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and ends in the thyroid gland.-Relations:... |
motor: accessory nerve Accessory nerve In anatomy, the accessory nerve is a nerve that controls specific muscles of the shoulder and neck. As part of it was formerly believed to originate in the brain, it is considered a cranial nerve... sensory: cervical plexus Cervical plexus The cervical plexus is a plexus of the ventral rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which are located from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral from lateral side... |
Acting alone, tilts head to its own side and rotates it so the face is turned towards the opposite side. Acting together, flexes the neck, raises the sternum and assists in forced inspiration. |
>-valign="top" |
|---|
SuprahyoidSuprahyoid musclesThe term suprahyoid refers to the region above the hyoid bone in the neck. The suprahyoid muscles include digastric, stylohyoid, geniohyoid, and mylohyoid...
| Muscle | |Origin | | Insertion | | Artery | | Nerve | | Action | |Antagonist |-valign="top" | digastric Digastric muscle The digastric muscle is a small muscle located under the jaw. so digastric muscles are muscle fibers in ligament of treitz ,omohyoid , occipitofrontalis.... |
anterior belly - digastric fossa (mandible); posterior belly - mastoid process Mastoid process The mastoid process is a conical prominence projecting from the undersurface of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone. It is located just behind the external acoustic meatus, and lateral to the styloid process... of temporal bone Temporal bone The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebrum.The temporal bone supports that part of the face known as the temple.-Parts:The temporal bone consists of four parts:* Squama temporalis... |
Intermediate tendon (hyoid bone Hyoid bone The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies at the level of the base of the mandible in the front and the third cervical vertebra behind.Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly... ) |
anterior belly - mandibular division of the trigeminal (CN V) via the mylohyoid nerve Mylohyoid nerve The mylohyoid nerve is a nerve that innervates the mylohyoid muscle and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle.-Structure:... ; posterior belly - facial nerve Facial nerve The facial nerve is the seventh of twelve paired cranial nerves. It emerges from the brainstem between the pons and the medulla, and controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue and oral cavity... (CN VII) |
Opens the jaw when the masseter and the temporalis are relaxed. | >-valign="top" | styloid process (temporal) Styloid process (temporal) The styloid process is a pointed piece of bone that extends down from the human skull, just below the ear.-Structure:The styloid process is a slender pointed piece of bone just below the ear... |
greater cornu Greater cornu The greater cornua of the hyoid bone project backward from the lateral borders of the body; they are flattened from above downward and diminish in size from before backward; each ends in a tubercle to which is fixed the lateral hyothyroid ligament.The upper surface is rough close to its lateral... of hyoid bone Hyoid bone The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies at the level of the base of the mandible in the front and the third cervical vertebra behind.Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly... |
facial nerve Facial nerve The facial nerve is the seventh of twelve paired cranial nerves. It emerges from the brainstem between the pons and the medulla, and controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue and oral cavity... (CN VII) |
Elevate the hyoid during swallowing | >-valign="top" | mylohyoid line Mylohyoid line Extending upward and backward on either side from the lower part of the symphysis of the mandible is the mylohyoid line, which is the origin of the mylohyoid muscle; the posterior part of this line, near the alveolar margin, gives attachment to a small part of the Constrictor pharyngis superior,... (mandible) |
median raphé Pharyngeal raphe The Pharyngeal raphe is a raphe that serves as the origin and insertion for several of the pharyngeal constrictors .-External links:*... |
mylohyoid branch of inferior alveolar artery Mylohyoid branch of inferior alveolar artery As the inferior alveolar artery enters the mandibular foramen, it gives off a mylohyoid branch which runs in the mylohyoid groove, and supplies the mylohyoid muscle.... |
mylohyoid nerve Mylohyoid nerve The mylohyoid nerve is a nerve that innervates the mylohyoid muscle and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle.-Structure:... , from inferior alveolar branch of mandibular nerve [V3 Inferior alveolar nerve The inferior alveolar nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve, which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve .-Path:... ] |
Raises oral cavity floor, elevates hyoid, depresses Depression (kinesiology) Depression, in kinesiology, is the anatomical term of motion for movement in an inferior direction.It is the opposite of elevation.This term is often applied to the shoulders Depression, in kinesiology, is the anatomical term of motion for movement in an inferior direction.It is the opposite of... mandible |
>-valign="top" | symphysis menti Symphysis menti The external surface of the mandible is marked in the median line by a faint ridge, indicating the symphysis menti, mandibular symphysis, or line of junction of the two pieces of which the bone is composed at an early period of life.... |
hyoid bone Hyoid bone The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies at the level of the base of the mandible in the front and the third cervical vertebra behind.Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly... |
C1 Cervical spinal nerve 1 The cervical spinal nerve 1 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 1 .Muscles innervated by this nerve are:*Geniohyoid muscle- through Hypoglossal nerve... via hypoglossal nerve Hypoglossal nerve The hypoglossal nerve is the twelfth cranial nerve , leading to the tongue. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus and emerges from the medulla oblongata in the preolivary sulcus separating the olive and the pyramid. It then passes through the hypoglossal canal... |
carry hyoid bone and the tongue upward during deglutition Swallowing Swallowing, known scientifically as deglutition, is the process in the human or animal body that makes something pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. If this fails and the object goes through the trachea, then choking or pulmonary aspiration... |
>-valign="top" |
|---|
Infrahyoid/Strap
| Muscle | |Origin | | Insertion | | Artery | | Nerve | | Action | |Antagonist |-valign="top" | sternohyoid Sternohyoid muscle The sternohyoid muscle is a thin, narrow muscle attaching the hyoid bone to the sternum, one of the paired strap muscles of the infrahyoid muscles serving to depress the hyoid bone... |
manubrium Manubrium The manubrium or manubrium sterni is the broad, upper part of the sternum. Located ventrally with a quadrangular shape, wider superiorly and narrower inferiorly, it articulates with the clavicles and the first two ribs.-Borders:The superior border is the thickest and presents at its center the... of sternum |
hyoid bone Hyoid bone The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies at the level of the base of the mandible in the front and the third cervical vertebra behind.Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly... |
ansa cervicalis Ansa cervicalis The ansa cervicalis is a loop of nerves that are part of the cervical plexus. It lies superficial to the internal jugular vein in the carotid sheath.... |
depress Depression (kinesiology) Depression, in kinesiology, is the anatomical term of motion for movement in an inferior direction.It is the opposite of elevation.This term is often applied to the shoulders Depression, in kinesiology, is the anatomical term of motion for movement in an inferior direction.It is the opposite of... hyoid bone |
>-valign="top" | manubrium Manubrium The manubrium or manubrium sterni is the broad, upper part of the sternum. Located ventrally with a quadrangular shape, wider superiorly and narrower inferiorly, it articulates with the clavicles and the first two ribs.-Borders:The superior border is the thickest and presents at its center the... |
thyroid cartilage Thyroid cartilage The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the laryngeal skeleton, the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx.... |
ansa cervicalis Ansa cervicalis The ansa cervicalis is a loop of nerves that are part of the cervical plexus. It lies superficial to the internal jugular vein in the carotid sheath.... |
Elevates larynx, may slightly depress hyoid bone | >-valign="top" | thyroid cartilage Thyroid cartilage The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the laryngeal skeleton, the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx.... |
hyoid bone Hyoid bone The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies at the level of the base of the mandible in the front and the third cervical vertebra behind.Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly... |
first cervical nerve Cervical nerves The cervical nerves are the spinal nerves from the cervical vertebrae.Although there are seven cervical vertebrae , there are eight cervical nerves . All nerves except C8 emerge above their corresponding vertebrae, while the C8 nerve emerges below the C7 vertebra... |
depress Depression (kinesiology) Depression, in kinesiology, is the anatomical term of motion for movement in an inferior direction.It is the opposite of elevation.This term is often applied to the shoulders Depression, in kinesiology, is the anatomical term of motion for movement in an inferior direction.It is the opposite of... hyoid bone |
>-valign="top" | upper border of the scapula | hyoid bone Hyoid bone The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies at the level of the base of the mandible in the front and the third cervical vertebra behind.Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly... |
ansa cervicalis Ansa cervicalis The ansa cervicalis is a loop of nerves that are part of the cervical plexus. It lies superficial to the internal jugular vein in the carotid sheath.... |
Depresses the larynx and hyoid bone. Carries hyoid bone backward and to the side | >-valign="top" |
|---|
Anterior
| Muscle | |Origin | | Insertion | | Artery | | Nerve | | Action | |Antagonist |-valign="top" | longus colli Longus colli muscle The Longus colli muscle is a muscle of the human body.The Longus colli is situated on the anterior surface of the vertebral column, between the atlas and the third thoracic vertebra.... |
Transverse processes of C-3 - C-6 | Inferior surface of the occipital bone Occipital bone The occipital bone, a saucer-shaped membrane bone situated at the back and lower part of the cranium, is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself... |
C2 Cervical spinal nerve 2 The cervical spinal nerve 2 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 2 .... , C3 Cervical spinal nerve 3 The cervical spinal nerve 3 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 3 .... , C4 Cervical spinal nerve 4 The cervical spinal nerve 4 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 4 .Its control of the thoracic diaphragm has inspired a medical mnemonic: "Cut C4, breathe no more."... , C5 Cervical spinal nerve 5 The cervical spinal nerve 5 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 5 .... , C6 Cervical spinal nerve 6 The cervical spinal nerve 6 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 6 .... |
Flexes the neck and head | >-valign="top" | anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebrae Cervical vertebrae In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also... |
basilar Basilar artery In human anatomy, the basilar artery is one of the arteries that supplies the brain with oxygen-rich blood.The two vertebral arteries and the basilar artery are sometimes together called the vertebrobasilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior part of circle of Willis and anastomoses with... part of the occipital bone Occipital bone The occipital bone, a saucer-shaped membrane bone situated at the back and lower part of the cranium, is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself... |
C1 Cervical spinal nerve 1 The cervical spinal nerve 1 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 1 .Muscles innervated by this nerve are:*Geniohyoid muscle- through Hypoglossal nerve... , C2 Cervical spinal nerve 2 The cervical spinal nerve 2 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 2 .... , C3 Cervical spinal nerve 3 The cervical spinal nerve 3 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 3 .... /C4 Cervical spinal nerve 4 The cervical spinal nerve 4 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 4 .Its control of the thoracic diaphragm has inspired a medical mnemonic: "Cut C4, breathe no more."... |
flexion Flexion In anatomy, flexion is a position that is made possible by the joint angle decreasing. The skeletal and muscular systems work together to move the joint into a "flexed" position. For example the elbow is flexed when the hand is brought closer to the shoulder... of neck Neck The neck is the part of the body, on many terrestrial or secondarily aquatic vertebrates, that distinguishes the head from the torso or trunk. The adjective signifying "of the neck" is cervical .-Boner anatomy: The cervical spine:The cervical portion of the human spine comprises seven boney... at atlanto-occipital joint Atlanto-occipital joint The Atlanto-occipital joint consists of a pair of condyloid joints. The atlanto-occipital joint is a synovial joint.-Ligaments:The ligaments connecting the bones are:* Two Articular capsules... |
>-valign="top" | atlas Atlas (anatomy) In anatomy, the atlas is the most superior cervical vertebra of the spine.It is named for the Atlas of Greek mythology, because it supports the globe of the head.... |
occipital bone Occipital bone The occipital bone, a saucer-shaped membrane bone situated at the back and lower part of the cranium, is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself... |
C1 Cervical spinal nerve 1 The cervical spinal nerve 1 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 1 .Muscles innervated by this nerve are:*Geniohyoid muscle- through Hypoglossal nerve... |
flexion Flexion In anatomy, flexion is a position that is made possible by the joint angle decreasing. The skeletal and muscular systems work together to move the joint into a "flexed" position. For example the elbow is flexed when the hand is brought closer to the shoulder... of neck Neck The neck is the part of the body, on many terrestrial or secondarily aquatic vertebrates, that distinguishes the head from the torso or trunk. The adjective signifying "of the neck" is cervical .-Boner anatomy: The cervical spine:The cervical portion of the human spine comprises seven boney... at atlanto-occipital joint Atlanto-occipital joint The Atlanto-occipital joint consists of a pair of condyloid joints. The atlanto-occipital joint is a synovial joint.-Ligaments:The ligaments connecting the bones are:* Two Articular capsules... |
>-valign="top" | upper surface of the transverse process of the atlas Atlas (anatomy) In anatomy, the atlas is the most superior cervical vertebra of the spine.It is named for the Atlas of Greek mythology, because it supports the globe of the head.... |
under surface of the jugular process Jugular process In the lateral part of the occipital bone, extending lateralward from the posterior half of the condyle is a quadrilateral plate of bone, the jugular process, excavated in front by the jugular notch, which, in the articulated skull, forms the posterior part of the jugular foramen.It serves as the... of the occipital bone Occipital bone The occipital bone, a saucer-shaped membrane bone situated at the back and lower part of the cranium, is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself... |
C1 Cervical spinal nerve 1 The cervical spinal nerve 1 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 1 .Muscles innervated by this nerve are:*Geniohyoid muscle- through Hypoglossal nerve... |
>-valign="top" |
|---|
Lateral
| Muscle | |Origin | | Insertion | | Artery | | Nerve | | Action | |Antagonist |-valign="top" | scalene muscles Scalene muscles The scalene muscles are a group of three pairs of muscles in the lateral neck, namely the scalenus anterior, scalenus medius, and scalenus posterior.They are innervated by the spinal nerves C4-C6.... |
cervical vertebrae Cervical vertebrae In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also... (C2 Cervical vertebrae In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also... -C7 Cervical vertebrae In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also... ) |
first and second ribs | ascending cervical artery Ascending cervical artery The ascending cervical artery is a small branch which arises from the inferior thyroid artery as that vessel is passing behind the carotid sheath; it runs up on the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebræ in the interval between the Scalenus anterior and Longus... (branch of inferior thyroid artery Inferior thyroid artery The inferior thyroid artery arrises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and Longus colli, then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and also behind the sympathetic trunk, the middle cervical ganglion resting upon the... ) |
cervical nerves Cervical nerves The cervical nerves are the spinal nerves from the cervical vertebrae.Although there are seven cervical vertebrae , there are eight cervical nerves . All nerves except C8 emerge above their corresponding vertebrae, while the C8 nerve emerges below the C7 vertebra... (C3 Cervical spinal nerve 3 The cervical spinal nerve 3 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 3 .... , C4 Cervical spinal nerve 4 The cervical spinal nerve 4 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 4 .Its control of the thoracic diaphragm has inspired a medical mnemonic: "Cut C4, breathe no more."... , C5 Cervical spinal nerve 5 The cervical spinal nerve 5 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 5 .... , C6 Cervical spinal nerve 6 The cervical spinal nerve 6 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 6 .... , C7 Cervical spinal nerve 7 The cervical spinal nerve 7 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 7 .... |
elevation of ribs I&II | >-valign="top" | C3 Cervical vertebrae In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also... -C6 Cervical vertebrae In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also... |
first rib First rib The first rib is the most curved and usually the shortest of all the ribs; it is broad and flat, its surfaces looking upward and downward, and its borders inward and outward.... |
ascending cervical artery Ascending cervical artery The ascending cervical artery is a small branch which arises from the inferior thyroid artery as that vessel is passing behind the carotid sheath; it runs up on the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebræ in the interval between the Scalenus anterior and Longus... (branch of inferior thyroid artery Inferior thyroid artery The inferior thyroid artery arrises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and Longus colli, then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and also behind the sympathetic trunk, the middle cervical ganglion resting upon the... ) |
ventral ramus Ventral ramus The ventral ramus supply the antero-lateral parts of the trunk, and the limbs; they are for the most part larger than the posterior divisions.... of C5 Cervical spinal nerve 5 The cervical spinal nerve 5 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 5 .... , C6 Cervical spinal nerve 6 The cervical spinal nerve 6 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 6 .... |
When the neck is fixed, elevates the first rib to aid in breathing or when the rib is fixed, bends the neck forward and sideways and rotates it to the opposite side | >-valign="top" | C2 Cervical vertebrae In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also... -C6 Cervical vertebrae In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also... |
first rib First rib The first rib is the most curved and usually the shortest of all the ribs; it is broad and flat, its surfaces looking upward and downward, and its borders inward and outward.... |
ascending cervical artery Ascending cervical artery The ascending cervical artery is a small branch which arises from the inferior thyroid artery as that vessel is passing behind the carotid sheath; it runs up on the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebræ in the interval between the Scalenus anterior and Longus... (branch of inferior thyroid artery Inferior thyroid artery The inferior thyroid artery arrises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and Longus colli, then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and also behind the sympathetic trunk, the middle cervical ganglion resting upon the... ) |
ventral rami of the third to eighth cervical spinal nerves | Elevate 1st rib, rotate the neck to the opposite side | >-valign="top" | transverse processes of C4 Cervical vertebrae In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also... - C6 Cervical vertebrae In vertebrates, cervical vertebrae are those vertebrae immediately inferior to the skull.Thoracic vertebrae in all mammalian species are defined as those vertebrae that also carry a pair of ribs, and lie caudal to the cervical vertebrae. Further caudally follow the lumbar vertebrae, which also... |
2nd rib | ascending cervical artery Ascending cervical artery The ascending cervical artery is a small branch which arises from the inferior thyroid artery as that vessel is passing behind the carotid sheath; it runs up on the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebræ in the interval between the Scalenus anterior and Longus... , superficial cervical artery |
C6 Cervical spinal nerve 6 The cervical spinal nerve 6 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 6 .... , C7 Cervical spinal nerve 7 The cervical spinal nerve 7 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 7 .... , C8 Cervical spinal nerve 8 The cervical spinal nerve 8 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment.It originates from the spinal column from below the cervical vertebra 7 .- Innervation :... |
Elevate 2nd rib, tilt the neck to the same side |
|---|

