Taxus canadensis
Encyclopedia
| Synonyms Synonym (taxonomy) In scientific nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that is or was used for a taxon of organisms that also goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name to the Norway spruce, which he called Pinus abies... |
|---|
| Taxus baccata var. minor |
| Michx. 1803 |
| Taxus procumbens |
| Lodd. ex Loudon 1836 |
| Taxus baccata var. procumbens |
| Loudon 1842 |
| Taxus baccata var. adpressa |
| Carrière 1855 |
| Taxus baccata var. canadensis |
| (Marshall) A.Gray 1856 |
| Taxus minor |
| (Michx.) Britton 1893 |
| Taxus baccata subsp. canadensis |
| (Marshall) Pilg. 1903 |
| Taxus canadensis var. adpressa |
| (Carrière) Spjut 2007 |
| Taxus canadensis var. minor |
| (Michx.) Spjut 2007 |
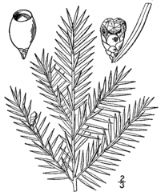
Taxus canadensis (Canadian Yew) is a conifer
Pinophyta
The conifers, division Pinophyta, also known as division Coniferophyta or Coniferae, are one of 13 or 14 division level taxa within the Kingdom Plantae. Pinophytes are gymnosperms. They are cone-bearing seed plants with vascular tissue; all extant conifers are woody plants, the great majority being...
native to central and eastern North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, thriving in swampy woods, ravines, riverbanks and on lake shores. Locally called simply "Yew", this species is also referred to as American Yew or Ground-hemlock.
Most of its range is well north of the Ohio River
Ohio River
The Ohio River is the largest tributary, by volume, of the Mississippi River. At the confluence, the Ohio is even bigger than the Mississippi and, thus, is hydrologically the main stream of the whole river system, including the Allegheny River further upstream...
. It is, however, found as a rare ice age relict
Relict
A relict is a surviving remnant of a natural phenomenon.* In biology a relict is an organism that at an earlier time was abundant in a large area but now occurs at only one or a few small areas....
in some coves of the Appalachian Mountains. The southernmost colonies are known from Ashe
Ashe County, North Carolina
- History :Historical evidence shows that Ashe county was inhabited by Native Americans, which included the Cherokee, Creek, and Shawnee tribes. Pieces of broken pottery, arrowheads, and other Native American artifacts have been found, indicating their presence...
and Watauga County, North Carolina
Watauga County, North Carolina
-Demographics:As of the census of 2000, there were 42,695 people, 16,540 households, and 9,411 families residing in the county. The population density was 137 people per square mile . There were 23,155 housing units at an average density of 74 per square mile...
.
It is usually a sprawling shrub
Shrub
A shrub or bush is distinguished from a tree by its multiple stems and shorter height, usually under 5–6 m tall. A large number of plants may become either shrubs or trees, depending on the growing conditions they experience...
, rarely exceeding 2.5 m tall. It sometimes forms strong upright central leaders, but these cannot be formed from spreading branches, only from the original leader of the seedling plant. The shrub has thin scaly brown bark
Bark
Bark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside of the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner...
. The leaves
Leaf
A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant, as defined in botanical terms, and in particular in plant morphology. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves as a feature of plants....
are lanceolate, flat, dark green, 1–2.5 cm long and 1.5 mm broad, arranged in two flat rows either side of the branch.
The seed cones
Conifer cone
A cone is an organ on plants in the division Pinophyta that contains the reproductive structures. The familiar woody cone is the female cone, which produces seeds. The male cones, which produce pollen, are usually herbaceous and much less conspicuous even at full maturity...
are highly modified, each cone containing a single seed
Seed
A seed is a small embryonic plant enclosed in a covering called the seed coat, usually with some stored food. It is the product of the ripened ovule of gymnosperm and angiosperm plants which occurs after fertilization and some growth within the mother plant...
partly surrounded by a modified scale which develops into a soft, bright red berry
Berry
The botanical definition of a berry is a fleshy fruit produced from a single ovary. Grapes are an example. The berry is the most common type of fleshy fruit in which the entire ovary wall ripens into an edible pericarp. They may have one or more carpels with a thin covering and fleshy interiors....
-like structure called an aril
Aril
An aril is any specialized outgrowth from the funiculus that covers or is attached to the seed. It is sometimes applied to any appendage or thickening of the seed coat in flowering plants, such as the edible parts of the mangosteen and pomegranate fruit, the mace of the nutmeg seed, or the...
, open at the end. The seeds are eaten by thrushes
Thrush (bird)
The thrushes, family Turdidae, are a group of passerine birds that occur worldwide.-Characteristics:Thrushes are plump, soft-plumaged, small to medium-sized birds, inhabiting wooded areas, and often feed on the ground or eat small fruit. The smallest thrush may be the Forest Rock-thrush, at and...
, waxwing
Waxwing
The waxwings form the genus Bombycilla of passerine birds. According to most authorities, this is the only genus placed in the family Bombycillidae.-Description:Waxwings are characterised by soft silky plumage...
s and other bird
Bird
Birds are feathered, winged, bipedal, endothermic , egg-laying, vertebrate animals. Around 10,000 living species and 188 families makes them the most speciose class of tetrapod vertebrates. They inhabit ecosystems across the globe, from the Arctic to the Antarctic. Extant birds range in size from...
s, which disperse the hard seeds undamaged in their droppings. The male cones are globose, 3 mm diameter. It is a monoecious
Plant sexuality
Plant sexuality covers the wide variety of sexual reproduction systems found across the plant kingdom. This article describes morphological aspects of sexual reproduction of plants....
plant — one of the few in the genus.
Uses and traditions

Taxus baccata
Taxus baccata is a conifer native to western, central and southern Europe, northwest Africa, northern Iran and southwest Asia. It is the tree originally known as yew, though with other related trees becoming known, it may be now known as the English yew, or European yew.-Description:It is a small-...
. All parts of the plant, save the aril, should be considered toxic.
Tribes in its native range used small quantities of yew leaf tea topically or internally for a variety of ailments – notably rheumatism
Rheumatism
Rheumatism or rheumatic disorder is a non-specific term for medical problems affecting the joints and connective tissue. The study of, and therapeutic interventions in, such disorders is called rheumatology.-Terminology:...
. Tribes are also been said to have used yew twigs in steam baths to help alleviate rheumatism
Rheumatism
Rheumatism or rheumatic disorder is a non-specific term for medical problems affecting the joints and connective tissue. The study of, and therapeutic interventions in, such disorders is called rheumatology.-Terminology:...
. Again, the plant is quite toxic and modern herbalists
Herbalism
Herbalism is a traditional medicinal or folk medicine practice based on the use of plants and plant extracts. Herbalism is also known as botanical medicine, medical herbalism, herbal medicine, herbology, herblore, and phytotherapy...
prefer safer, more effective herbs.
Taxus canadensis is also being harvested in northern Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
, Québec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
and Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada is the region of Canada comprising the four provinces located on the Atlantic coast, excluding Quebec: the three Maritime provinces – New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and Nova Scotia – and Newfoundland and Labrador...
as the plant is a source of the class of poisonous chemicals known as taxane
Taxane
The taxanes are diterpenes produced by the plants of the genus Taxus . As their name suggests, they were first derived from natural sources, but some have been synthesized artificially. Taxanes include paclitaxel and docetaxel . Paclitaxel was originally derived from the Pacific yew tree.Taxanes...
s, which have been a focus for cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
research. T. canadensis is much more abundant than the near-threatened Taxus brevifolia
Taxus brevifolia
Taxus brevifolia is a conifer native to the Pacific Northwest of North America. It ranges from southernmost Alaska south to central California, mostly in the Pacific Coast Ranges, but with an isolated disjunct population in southeast British Columbia, most notably occurring on Zuckerberg Island...
(Pacific Yew), and the "greens" (new growth) can be harvested sustainably
Sustainable yield
The sustainable yield of natural capital is the ecological yield that can be extracted without reducing the base of capital itself, i.e. the surplus required to maintain ecosystem services at the same or increasing level over time. This yield usually varies over time with the needs of the...
every five years, instead of stripping the bark and killing the plant.
The most abundant taxane in T. canadensis is 9-dihydro-13-acetylbaccatin III, which can be effectively converted to 10-deacetylbaccatin III, used in the production of paclitaxel
Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel is a mitotic inhibitor used in cancer chemotherapy. It was discovered in a U.S. National Cancer Institute program at the Research Triangle Institute in 1967 when Monroe E. Wall and Mansukh C. Wani isolated it from the bark of the Pacific yew tree, Taxus brevifolia and named it taxol...
. Recently, two new taxanes have been identified from T. canadensis, including 7β,10β,13α-triacetoxy-5α-(3'-dimethylamino-3'-phenylpropanoyl)oxy-2α-hydroxy-2(3→20)abeotaxa-4(20),11-dien-9-one and 2α,10β-diacetoxy-9α-hydroxy-5α-(3'-dimethylamino-3'-phenylpropanoyl)oxy-3,11-cyclotax-4(20)-en-13-one.

