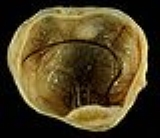
Teratoma
Encyclopedia
A teratoma is an encapsulated tumor
with tissue
or organ
components resembling normal derivatives of all three germ layer
s. There are rare occasions when not all three germ layers are identifiable. The tissues of a teratoma, although normal in themselves, may be quite different from surrounding tissues and may be highly disparate; teratomas have been reported to contain hair
, teeth, bone
and, very rarely, more complex organs such as eyes, torso
, and hands, feet
, or other limb
s.
Usually, however, a teratoma will contain no organs but rather one or more tissues normally found in organs such as the brain
, thyroid
, liver
, and lung
. Sometimes, the teratoma has within its capsule one or more fluid-filled cysts; when a large cyst occurs, there is a potential for the teratoma to produce a structure within the cyst that resembles a fetus. Because they are encapsulated, teratomas are usually benign, although several forms of malignant
teratoma are known and some of these are common forms of teratoma. A mature teratoma is typically benign and found more commonly in women, while an immature teratoma is typically malignant and is more often found in men.
Teratomas are thought to be present at birth (congenital), but small ones are often not discovered until much later in life.
Definitive medical diagnosis
of a teratoma is based on its histology
; this diagnosis is made by a pathologist
.
and means roughly "monstrous tumor".
There are some differences in terminology in the U.S. and U.K. The words "teratoma" (U.S. terminology) and "mature teratoma" (U.K. terminology) both may be used to refer to a benign growth, while the word "teratoma" (U.K. terminology) may refer to "immature teratoma", a cancerous growth. It is therefore important to specify whether one is using U.S. or U.K. terminology.
The term "malignant teratoma" has sometimes been used as a synonym for nonseminomatous germ cell tumor
.
(N.S.G.C.T.). All tumors of this class are the result of abnormal development of pluripotent cells: germ cell
s and embryonal cells
. Teratomas of embryonic origin are congenital
; teratomas of germ cell origin may or may not be congenital (this is not known). The kind of pluripotent cell appears to be unimportant, apart from constraining the location of the teratoma in the body.
in women. Teratomas derived from embryonic cells usually occur on the subject's midline: in the brain, elsewhere in the skull
, in the nose, in the tongue, under the tongue, and in the neck
(cervical teratoma), mediastinum
, retroperitoneum
, and attached to the coccyx
. However, teratomas may also occur elsewhere: very rarely in solid organs (most notably the heart and liver) and hollow organs (such as the stomach and bladder), and more commonly on the skull sutures
.
(see below) is not a teratoma at all but rather a parasitic twin
.
, muscle
, and bone
. Skin may surround a cyst and grow abundant hair
(see Dermoid cyst). Mature teratomas generally are benign; malignant mature teratomas are of several distinct types.
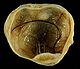 A dermoid cyst
A dermoid cyst
is a mature cystic teratoma containing hair (sometimes very abundant) and other structures characteristic of normal skin and other tissues derived from the ectoderm
. The term is most often applied to teratoma on the skull sutures and in the ovaries of females.
and fetiform teratoma are rare forms of mature teratoma that include one or more components resembling a malformed fetus. Both forms may contain or appear to contain complete organ systems, even major body parts such as torso or limbs. Fetus in fetu differs from fetiform teratoma in having an apparent spine
and bilateral symmetry.
Most authorities agree that fetiform teratomas are highly developed mature teratomas; the natural history of fetus in fetu, however, is controversial. There also may be a cultural difference, with fetiform teratoma being reported more often in ovarian teratomas (by gynecologists) and fetus in fetu being reported more often in retroperitoneal teratomas (by general surgeons). Fetus in fetu
has often been interpreted as a fetus
growing within its twin
. As such, this interpretation assumes a special complication of twin
ning, one of several grouped under the term parasitic twin
. In this regard, it is noteworthy that in many cases the fetus in fetu is reported to occupy a fluid-filled cyst within a mature teratoma. Cysts within mature teratoma may have partially developed organ systems, reports include cases of partial cranial bones, long bones and a rudimentary beating heart.
Regardless of whether fetus in fetu and fetiform teratoma are one entity or two, they are distinct from and not to be confused with ectopic pregnancy
.
of the ovary) is a rare form of mature teratoma that contains mostly thyroid
tissue.
system. This indicates whether chemotherapy
or radiation therapy
may be needed in addition to surgery. Teratomas commonly are classified using the Gonzalez-Crussi grading system: 0 or mature (benign
); 1 or immature, probably benign; 2 or immature, possibly malignant
(cancer
ous); and 3 or frankly malignant. If frankly malignant, the tumor is a cancer
for which additional cancer staging
applies.
Teratomas are also classified by their content: a solid teratoma contains only tissues (perhaps including more complex structures); a cystic teratoma contain only pockets of fluid or semi-fluid such as cerebrospinal fluid
, sebum, or fat; a mixed teratoma contains both solid and cystic parts. Cystic teratomas usually are grade 0 and, conversely, grade 0 teratomas usually are cystic.
Grade 0, 1 and 2 pure teratomas have the potential to become malignant (grade 3), and malignant pure teratomas have the potential to metastasize. These rare forms of teratoma with malignant transformation may contain elements of somatic (non germ cell) malignancy such as leukemia
, carcinoma
or sarcoma
.
A teratoma may contain elements of other germ cell tumors, in which case it is not a pure teratoma but rather is a mixed germ cell tumor
and is malignant. In infants and young children, these elements usually are endodermal sinus tumor
, followed by choriocarcinoma
. Finally, a teratoma can be pure and not malignant yet highly aggressive: this is exemplified by growing teratoma syndrome, in which chemotherapy eliminates the malignant elements of a mixed tumor, leaving pure teratoma which paradoxically begins to grow very rapidly.
has been reported in cases of formerly benign mature teratoma, even in fetiform teratoma and fetus in fetu. Squamous cell carcinoma
has been found in a mature cystic teratoma at the time of initial surgery.
A grade 1 immature teratoma that appears to be benign (e.g., because AFP is not elevated) has a much higher risk of malignancy, and requires adequate follow-up.
This grade of teratoma also may be difficult to diagnose correctly. It can be confused with other small round cell neoplasms such as neuroblastoma, small cell carcinoma of hypercalcemic type, primitive neuroectodermal tumor, Wilm's tumor, desmoplastic small round cell tumor, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
A teratoma with malignant transformation (TMT) is a very rare form of teratoma that may contain elements of somatic (non germ cell) malignant tumors such as leukemia
, carcinoma
or sarcoma
. Of 641 children with pure teratoma, nine developed TMT: five carcinoma
, two glioma
, and two embryonal carcinoma (here, these last are classified among germ cell tumors).
, usually considered to be a glioma
(a type of non-germ cell tumor), may be an unusual form of mature teratoma.
. Additional diagnostic methods may include prenatal MRI
. In rare circumstances, the tumor is so large that the fetus
may be damaged or die. In the case of large sacrococcygeal teratomas, a significant portion of the fetus' blood flow
is redirected toward the teratoma (a phenomenon called steal syndrome
), causing heart failure
, or hydrops
, of the fetus. In certain cases, fetal surgery
may be indicated.
Beyond the newborn period, symptoms of a teratoma depend on its location and organ of origin. Ovarian teratomas often present with abdominal or pelvic pain, caused by torsion
of the ovary
or irritation of its ligaments. A recently discovered condition where ovarian teratomas cause encephalitis associated with antibodies against the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) -often simply referred to as "Ovarian Teratoma Encephalitis", has identified a more serious complication from these tumours. Patients develop a multistage illness that progresses from psychosis, memory deficits, seizures, and language disintegration into a state of unresponsiveness with catatonic features often associated with abnormal movements, and autonomic and breathing instability. One such case has been described in popular literature as well. Testicular teratomas present as a palpable mass in the testis; mediastinal
teratomas often cause compression of the lungs or the airways and may present with chest pain
and/or respiratory symptoms.
Some teratomas contain yolk sac
elements, which secrete alpha-fetoprotein
(AFP). Detection of AFP may help to confirm the diagnosis and is often used as a marker for recurrence or treatment efficacy, but is rarely the method of initial diagnosis. (Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein
, or MSAFP, is a useful screening test
for other fetal conditions, including Down syndrome
, spina bifida
and abdominal wall
defects such as gastroschisis
).
, in fetuses.
The most commonly diagnosed fetal teratomas are sacrococcygeal teratoma
(Altman types I, II, and III) and cervical (neck) teratoma. Because these teratomas project from the fetal body into the surrounding amniotic fluid
, they can be seen during routine prenatal ultrasound exams. Teratomas within the fetal body are less easily seen with ultrasound; for these, MRI of the pregnant uterus is more informative.
or a large amount of blood flow through the tumor (known as vascular steal). The mass effect frequently consists of obstruction of normal passage of fluids from surrounding organs. The vascular steal can place a strain on the growing heart of the fetus, even resulting in heart failure, and thus must be monitored by fetal echocardiography
.
After surgery, there is a risk of regrowth in place, or in nearby organs.
Prevention of recurrence does not require en bloc resection of surrounding tissues.
Teratomas that are in surgically inaccessible locations, or are very complex, or are likely to be malignant (due to late discovery and/or treatment) sometimes are treated first with chemotherapy.
Depending on which tissue(s) it contains, a teratoma may secrete a variety of chemicals with systemic effects. Some teratomas secrete the "pregnancy hormone" human chorionic gonadotropin
(βhCG), which can be used in clinical practice to monitor the successful treatment or relapse in patients with a known HCG-secreting teratoma. This hormone is not recommended as a diagnostic marker, because most teratomas do not secrete it. Some teratomas secrete thyroxine
, in some cases to such a degree that it can lead to clinical hyperthyroidism
in the patient. Of special concern is the secretion of alpha-fetoprotein
(AFP); under some circumstances AFP can be used as a diagnostic marker specific for the presence of yolk sac
cells within the teratoma. These cells can develop into a frankly malignant tumor known as yolk sac tumor or endodermal sinus tumor
.
Adequate follow-up requires close observation, involving repeated physical examination, scanning (ultrasound, MRI, or CT), and measurement of AFP and/or βhCG.
is the single most common tumor found in newly born humans.
Of teratomas on the skull sutures, approximately 50% are found in or adjacent to the orbit
. Limbal dermoid is a choristoma, not a teratoma.
Teratoma qualifies as a rare disease
, but is not extremely rare. Sacrococcygeal teratoma alone is diagnosed at birth in one out of 40,000 humans. Given the current human population and birth-rate, this equals five per day or 1800 per year. Add to that number sacrococcygeal teratomas diagnosed later in life, and teratomas in other locales, and the incidence
approaches ten thousand new diagnoses of teratoma per year.
Obviously, teratomas also occur, rarely, in other species.
, teratomas are being looked at as an alternative source for research since they lack the potential to grow into functional human beings.
s and in canines.
Neoplasia
Neoplasm is an abnormal mass of tissue as a result of neoplasia. Neoplasia is the abnormal proliferation of cells. The growth of neoplastic cells exceeds and is not coordinated with that of the normal tissues around it. The growth persists in the same excessive manner even after cessation of the...
with tissue
Biological tissue
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
or organ
Organ (anatomy)
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in structural unit to serve a common function. Usually there is a main tissue and sporadic tissues . The main tissue is the one that is unique for the specific organ. For example, main tissue in the heart is the myocardium, while sporadic are...
components resembling normal derivatives of all three germ layer
Germ layer
A germ layer, occasionally referred to as a germinal epithelium, is a group of cells, formed during animal embryogenesis. Germ layers are particularly pronounced in the vertebrates; however, all animals more complex than sponges produce two or three primary tissue layers...
s. There are rare occasions when not all three germ layers are identifiable. The tissues of a teratoma, although normal in themselves, may be quite different from surrounding tissues and may be highly disparate; teratomas have been reported to contain hair
Hair
Hair is a filamentous biomaterial, that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Found exclusively in mammals, hair is one of the defining characteristics of the mammalian class....
, teeth, bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
and, very rarely, more complex organs such as eyes, torso
Torso
Trunk or torso is an anatomical term for the central part of the many animal bodies from which extend the neck and limbs. The trunk includes the thorax and abdomen.-Major organs:...
, and hands, feet
Foot
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws...
, or other limb
Limb (anatomy)
A limb is a jointed, or prehensile , appendage of the human or other animal body....
s.
Usually, however, a teratoma will contain no organs but rather one or more tissues normally found in organs such as the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
, thyroid
Thyroid
The thyroid gland or simply, the thyroid , in vertebrate anatomy, is one of the largest endocrine glands. The thyroid gland is found in the neck, below the thyroid cartilage...
, liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, and lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
. Sometimes, the teratoma has within its capsule one or more fluid-filled cysts; when a large cyst occurs, there is a potential for the teratoma to produce a structure within the cyst that resembles a fetus. Because they are encapsulated, teratomas are usually benign, although several forms of malignant
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
teratoma are known and some of these are common forms of teratoma. A mature teratoma is typically benign and found more commonly in women, while an immature teratoma is typically malignant and is more often found in men.
Teratomas are thought to be present at birth (congenital), but small ones are often not discovered until much later in life.
Definitive medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis refers both to the process of attempting to determine or identify a possible disease or disorder , and to the opinion reached by this process...
of a teratoma is based on its histology
Histology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining cells and tissues commonly by sectioning and staining; followed by examination under a light microscope or electron microscope...
; this diagnosis is made by a pathologist
Pathology
Pathology is the precise study and diagnosis of disease. The word pathology is from Ancient Greek , pathos, "feeling, suffering"; and , -logia, "the study of". Pathologization, to pathologize, refers to the process of defining a condition or behavior as pathological, e.g. pathological gambling....
.
Cause
The word teratoma comes from classical GreekGreek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
and means roughly "monstrous tumor".
There are some differences in terminology in the U.S. and U.K. The words "teratoma" (U.S. terminology) and "mature teratoma" (U.K. terminology) both may be used to refer to a benign growth, while the word "teratoma" (U.K. terminology) may refer to "immature teratoma", a cancerous growth. It is therefore important to specify whether one is using U.S. or U.K. terminology.
The term "malignant teratoma" has sometimes been used as a synonym for nonseminomatous germ cell tumor
Germ cell tumor
A germ cell tumor is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ cell tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads...
.
Pathophysiology
Teratomas belong to a class of tumors known as nonseminomatous germ cell tumorGerm cell tumor
A germ cell tumor is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ cell tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads...
(N.S.G.C.T.). All tumors of this class are the result of abnormal development of pluripotent cells: germ cell
Germ cell
A germ cell is any biological cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate near the gut of an embryo and migrate to the developing gonads. There, they undergo cell division of two types, mitosis and meiosis, followed by...
s and embryonal cells
Embryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
. Teratomas of embryonic origin are congenital
Congenital disorder
A congenital disorder, or congenital disease, is a condition existing at birth and often before birth, or that develops during the first month of life , regardless of causation...
; teratomas of germ cell origin may or may not be congenital (this is not known). The kind of pluripotent cell appears to be unimportant, apart from constraining the location of the teratoma in the body.
Pathophysiology
Teratomas derived from germ cells occur in the testes in men and ovariesOvary
The ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ, often found in pairs as part of the vertebrate female reproductive system. Ovaries in anatomically female individuals are analogous to testes in anatomically male individuals, in that they are both gonads and endocrine glands.-Human anatomy:Ovaries...
in women. Teratomas derived from embryonic cells usually occur on the subject's midline: in the brain, elsewhere in the skull
Skull
The skull is a bony structure in the head of many animals that supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. A skull without a mandible is only a cranium. Animals that have skulls are called craniates...
, in the nose, in the tongue, under the tongue, and in the neck
Neck
The neck is the part of the body, on many terrestrial or secondarily aquatic vertebrates, that distinguishes the head from the torso or trunk. The adjective signifying "of the neck" is cervical .-Boner anatomy: The cervical spine:The cervical portion of the human spine comprises seven boney...
(cervical teratoma), mediastinum
Mediastinum
The mediastinum is a non-delineated group of structures in the thorax, surrounded by loose connective tissue. It is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity...
, retroperitoneum
Retroperitoneum
The retroperitoneal space is the anatomical space in the abdominal cavity behind the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures...
, and attached to the coccyx
Coccyx
The coccyx , commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column. Comprising three to five separate or fused vertebrae below the sacrum, it is attached to the sacrum by a fibrocartilaginous joint, the sacrococcygeal symphysis, which permits limited movement between...
. However, teratomas may also occur elsewhere: very rarely in solid organs (most notably the heart and liver) and hollow organs (such as the stomach and bladder), and more commonly on the skull sutures
Cranial sutures
*Surgical suture, to describe stitches and other techniques for holding tissues together.* Geology, to describe a certain type of boundary between layers of rock....
.
Hypotheses of origin
Concerning the origin of teratomas, there exist numerous hypotheses. These hypotheses are not to be confused with the unrelated hypothesis that fetus in fetuFetus in fetu
Fetus in fetu is a developmental abnormality in which a mass of tissue resembling a fetus forms inside the body. There are two theories of origin concerning "fetus in fetu". One theory is that the mass begins as a normal fetus but becomes enveloped inside its twin. The other theory is that the...
(see below) is not a teratoma at all but rather a parasitic twin
Parasitic twin
A parasitic twin is the result of the processes that produce vanishing twins and conjoined twins, and may represent a continuum between the two...
.
Mature teratoma
A mature teratoma is a grade 0 teratoma. Mature teratomas are highly variable in form and histology, and may be solid, cystic, or a combination of solid and cystic. A mature teratoma often contains several different types of tissue such as skinSkin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
, muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
, and bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
. Skin may surround a cyst and grow abundant hair
Hair
Hair is a filamentous biomaterial, that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Found exclusively in mammals, hair is one of the defining characteristics of the mammalian class....
(see Dermoid cyst). Mature teratomas generally are benign; malignant mature teratomas are of several distinct types.
Dermoid cyst

Dermoid cyst
A dermoid cyst is a cystic teratoma that contains developmentally mature skin complete with hair follicles and sweat glands, sometimes clumps of long hair, and often pockets of sebum, blood, fat, bone, nails, teeth, eyes, cartilage, and thyroid tissue. Because it contains mature tissue, a dermoid...
is a mature cystic teratoma containing hair (sometimes very abundant) and other structures characteristic of normal skin and other tissues derived from the ectoderm
Ectoderm
The "ectoderm" is one of the three primary germ cell layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the mesoderm and endoderm , with the ectoderm as the most exterior layer...
. The term is most often applied to teratoma on the skull sutures and in the ovaries of females.
Fetus in fetu and fetiform teratoma
Fetus in fetuFetus in fetu
Fetus in fetu is a developmental abnormality in which a mass of tissue resembling a fetus forms inside the body. There are two theories of origin concerning "fetus in fetu". One theory is that the mass begins as a normal fetus but becomes enveloped inside its twin. The other theory is that the...
and fetiform teratoma are rare forms of mature teratoma that include one or more components resembling a malformed fetus. Both forms may contain or appear to contain complete organ systems, even major body parts such as torso or limbs. Fetus in fetu differs from fetiform teratoma in having an apparent spine
Vertebral column
In human anatomy, the vertebral column is a column usually consisting of 24 articulating vertebrae, and 9 fused vertebrae in the sacrum and the coccyx. It is situated in the dorsal aspect of the torso, separated by intervertebral discs...
and bilateral symmetry.
Most authorities agree that fetiform teratomas are highly developed mature teratomas; the natural history of fetus in fetu, however, is controversial. There also may be a cultural difference, with fetiform teratoma being reported more often in ovarian teratomas (by gynecologists) and fetus in fetu being reported more often in retroperitoneal teratomas (by general surgeons). Fetus in fetu
Fetus in fetu
Fetus in fetu is a developmental abnormality in which a mass of tissue resembling a fetus forms inside the body. There are two theories of origin concerning "fetus in fetu". One theory is that the mass begins as a normal fetus but becomes enveloped inside its twin. The other theory is that the...
has often been interpreted as a fetus
Fetus
A fetus is a developing mammal or other viviparous vertebrate after the embryonic stage and before birth.In humans, the fetal stage of prenatal development starts at the beginning of the 11th week in gestational age, which is the 9th week after fertilization.-Etymology and spelling variations:The...
growing within its twin
Twin
A twin is one of two offspring produced in the same pregnancy. Twins can either be monozygotic , meaning that they develop from one zygote that splits and forms two embryos, or dizygotic because they develop from two separate eggs that are fertilized by two separate sperm.In contrast, a fetus...
. As such, this interpretation assumes a special complication of twin
Twin
A twin is one of two offspring produced in the same pregnancy. Twins can either be monozygotic , meaning that they develop from one zygote that splits and forms two embryos, or dizygotic because they develop from two separate eggs that are fertilized by two separate sperm.In contrast, a fetus...
ning, one of several grouped under the term parasitic twin
Parasitic twin
A parasitic twin is the result of the processes that produce vanishing twins and conjoined twins, and may represent a continuum between the two...
. In this regard, it is noteworthy that in many cases the fetus in fetu is reported to occupy a fluid-filled cyst within a mature teratoma. Cysts within mature teratoma may have partially developed organ systems, reports include cases of partial cranial bones, long bones and a rudimentary beating heart.
Regardless of whether fetus in fetu and fetiform teratoma are one entity or two, they are distinct from and not to be confused with ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy, or eccysis , is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo implants outside the uterine cavity. With rare exceptions, ectopic pregnancies are not viable. Furthermore, they are dangerous for the parent, since internal haemorrhage is a life threatening complication...
.
Struma ovarii
A struma ovarii (literally: goitreGoitre
A goitre or goiter , is a swelling in the thyroid gland, which can lead to a swelling of the neck or larynx...
of the ovary) is a rare form of mature teratoma that contains mostly thyroid
Thyroid
The thyroid gland or simply, the thyroid , in vertebrate anatomy, is one of the largest endocrine glands. The thyroid gland is found in the neck, below the thyroid cartilage...
tissue.
Classification
Regardless of location in the body, a teratoma is classified according to a cancer stagingCancer staging
The stage of a cancer is a description of the extent the cancer has spread. The stage often takes into account the size of a tumor, how deeply it has penetrated, whether it has invaded adjacent organs, how many lymph nodes it has metastasized to , and whether it has spread to distant organs...
system. This indicates whether chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
or radiation therapy
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy , radiation oncology, or radiotherapy , sometimes abbreviated to XRT or DXT, is the medical use of ionizing radiation, generally as part of cancer treatment to control malignant cells.Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control...
may be needed in addition to surgery. Teratomas commonly are classified using the Gonzalez-Crussi grading system: 0 or mature (benign
Benign
A benign tumor is a tumor that lacks the ability to metastasize. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.The term "benign" implies a mild and nonprogressive disease. Indeed, many kinds of benign tumors are harmless to human health...
); 1 or immature, probably benign; 2 or immature, possibly malignant
Malignant
Malignancy is the tendency of a medical condition, especially tumors, to become progressively worse and to potentially result in death. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis...
(cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
ous); and 3 or frankly malignant. If frankly malignant, the tumor is a cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
for which additional cancer staging
Cancer staging
The stage of a cancer is a description of the extent the cancer has spread. The stage often takes into account the size of a tumor, how deeply it has penetrated, whether it has invaded adjacent organs, how many lymph nodes it has metastasized to , and whether it has spread to distant organs...
applies.
Teratomas are also classified by their content: a solid teratoma contains only tissues (perhaps including more complex structures); a cystic teratoma contain only pockets of fluid or semi-fluid such as cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid , Liquor cerebrospinalis, is a clear, colorless, bodily fluid, that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord...
, sebum, or fat; a mixed teratoma contains both solid and cystic parts. Cystic teratomas usually are grade 0 and, conversely, grade 0 teratomas usually are cystic.
Grade 0, 1 and 2 pure teratomas have the potential to become malignant (grade 3), and malignant pure teratomas have the potential to metastasize. These rare forms of teratoma with malignant transformation may contain elements of somatic (non germ cell) malignancy such as leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
, carcinoma
Carcinoma
Carcinoma is the medical term for the most common type of cancer occurring in humans. Put simply, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that generally arises from cells originating in the endodermal or ectodermal germ layer during...
or sarcoma
Sarcoma
A sarcoma is a cancer that arises from transformed cells in one of a number of tissues that develop from embryonic mesoderm. Thus, sarcomas include tumors of bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, vascular, and hematopoietic tissues...
.
A teratoma may contain elements of other germ cell tumors, in which case it is not a pure teratoma but rather is a mixed germ cell tumor
Germ cell tumor
A germ cell tumor is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ cell tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads...
and is malignant. In infants and young children, these elements usually are endodermal sinus tumor
Endodermal sinus tumor
Endodermal sinus tumor , also known as yolk sac tumor , is a member of the germ cell tumor group of cancers. It is the most common testicular tumor in children under 3, and is also known as infantile embryonal carcinoma. This age group has a very good prognosis...
, followed by choriocarcinoma
Choriocarcinoma
Choriocarcinoma is a malignant, trophoblastic and aggressive cancer, usually of the placenta. It is characterized by early hematogenous spread to the lungs...
. Finally, a teratoma can be pure and not malignant yet highly aggressive: this is exemplified by growing teratoma syndrome, in which chemotherapy eliminates the malignant elements of a mixed tumor, leaving pure teratoma which paradoxically begins to grow very rapidly.
Malignant transformation
A "benign" grade 0 (mature) teratoma nonetheless has a risk of malignancy. Recurrence with malignant endodermal sinus tumorEndodermal sinus tumor
Endodermal sinus tumor , also known as yolk sac tumor , is a member of the germ cell tumor group of cancers. It is the most common testicular tumor in children under 3, and is also known as infantile embryonal carcinoma. This age group has a very good prognosis...
has been reported in cases of formerly benign mature teratoma, even in fetiform teratoma and fetus in fetu. Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma , occasionally rendered as "squamous-cell carcinoma", is a histologically distinct form of cancer. It arises from the uncontrolled multiplication of malignant cells deriving from epithelium, or showing particular cytological or tissue architectural characteristics of...
has been found in a mature cystic teratoma at the time of initial surgery.
A grade 1 immature teratoma that appears to be benign (e.g., because AFP is not elevated) has a much higher risk of malignancy, and requires adequate follow-up.
This grade of teratoma also may be difficult to diagnose correctly. It can be confused with other small round cell neoplasms such as neuroblastoma, small cell carcinoma of hypercalcemic type, primitive neuroectodermal tumor, Wilm's tumor, desmoplastic small round cell tumor, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
A teratoma with malignant transformation (TMT) is a very rare form of teratoma that may contain elements of somatic (non germ cell) malignant tumors such as leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
, carcinoma
Carcinoma
Carcinoma is the medical term for the most common type of cancer occurring in humans. Put simply, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that generally arises from cells originating in the endodermal or ectodermal germ layer during...
or sarcoma
Sarcoma
A sarcoma is a cancer that arises from transformed cells in one of a number of tissues that develop from embryonic mesoderm. Thus, sarcomas include tumors of bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, vascular, and hematopoietic tissues...
. Of 641 children with pure teratoma, nine developed TMT: five carcinoma
Carcinoma
Carcinoma is the medical term for the most common type of cancer occurring in humans. Put simply, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that generally arises from cells originating in the endodermal or ectodermal germ layer during...
, two glioma
Glioma
A glioma is a type of tumor that starts in the brain or spine. It is called a glioma because it arises from glial cells. The most common site of gliomas is the brain.-By type of cell:...
, and two embryonal carcinoma (here, these last are classified among germ cell tumors).
Extraspinal ependymoma
Extraspinal ependymomaEpendymoma
Ependymoma is a tumor that arises from the ependyma, a tissue of the central nervous system. Usually, in pediatric cases the location is intracranial, while in adults it is spinal. The common location of intracranial ependymoma is the fourth ventricle...
, usually considered to be a glioma
Glioma
A glioma is a type of tumor that starts in the brain or spine. It is called a glioma because it arises from glial cells. The most common site of gliomas is the brain.-By type of cell:...
(a type of non-germ cell tumor), may be an unusual form of mature teratoma.
Diagnosis
Teratomas are thought to be present since birth, or even before birth, and therefore can be considered congenital tumors. However, many teratomas are not diagnosed until much later in childhood or in adulthood. Large tumors are more likely to be diagnosed early on. Sacrococcygeal and cervical teratomas are often detected by prenatal ultrasoundUltrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
. Additional diagnostic methods may include prenatal MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
. In rare circumstances, the tumor is so large that the fetus
Fetus
A fetus is a developing mammal or other viviparous vertebrate after the embryonic stage and before birth.In humans, the fetal stage of prenatal development starts at the beginning of the 11th week in gestational age, which is the 9th week after fertilization.-Etymology and spelling variations:The...
may be damaged or die. In the case of large sacrococcygeal teratomas, a significant portion of the fetus' blood flow
Blood flow
Blood flow is the continuous running of blood in the cardiovascular system.The human body is made up of several processes all carrying out various functions. We have the gastrointestinal system which aids the digestion and the absorption of food...
is redirected toward the teratoma (a phenomenon called steal syndrome
Steal syndrome
Steal syndrome may refer to:*Cardiac steal syndrome*Subclavian steal syndrome, often associated with fainting, and typically due to atherosclerosis...
), causing heart failure
Congestive heart failure
Heart failure often called congestive heart failure is generally defined as the inability of the heart to supply sufficient blood flow to meet the needs of the body. Heart failure can cause a number of symptoms including shortness of breath, leg swelling, and exercise intolerance. The condition...
, or hydrops
Hydrops fetalis
Hydrops fetalis is a condition in the fetus characterized by an accumulation of fluid, or edema, in at least two fetal compartments. By comparison, hydrops allantois or hydrops amnion are an accumulation of excessive fluid in the allantoic or amniotic space respectively.-Presentation:Locations can...
, of the fetus. In certain cases, fetal surgery
Fetal surgery
Fetal surgery is any of a broad range of surgical techniques that are used to treat birth defects in fetuses who are still in the pregnant uterus.* Open fetal surgery involves completely opening the uterus to operate on the fetus....
may be indicated.
Beyond the newborn period, symptoms of a teratoma depend on its location and organ of origin. Ovarian teratomas often present with abdominal or pelvic pain, caused by torsion
Torsion (mechanics)
In solid mechanics, torsion is the twisting of an object due to an applied torque. In sections perpendicular to the torque axis, the resultant shear stress in this section is perpendicular to the radius....
of the ovary
Ovary
The ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ, often found in pairs as part of the vertebrate female reproductive system. Ovaries in anatomically female individuals are analogous to testes in anatomically male individuals, in that they are both gonads and endocrine glands.-Human anatomy:Ovaries...
or irritation of its ligaments. A recently discovered condition where ovarian teratomas cause encephalitis associated with antibodies against the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) -often simply referred to as "Ovarian Teratoma Encephalitis", has identified a more serious complication from these tumours. Patients develop a multistage illness that progresses from psychosis, memory deficits, seizures, and language disintegration into a state of unresponsiveness with catatonic features often associated with abnormal movements, and autonomic and breathing instability. One such case has been described in popular literature as well. Testicular teratomas present as a palpable mass in the testis; mediastinal
Mediastinum
The mediastinum is a non-delineated group of structures in the thorax, surrounded by loose connective tissue. It is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity...
teratomas often cause compression of the lungs or the airways and may present with chest pain
Chest pain
Chest pain may be a symptom of a number of serious conditions and is generally considered a medical emergency. Even though it may be determined that the pain is non-cardiac in origin, this is often a diagnosis of exclusion made after ruling out more serious causes of the pain.-Differential...
and/or respiratory symptoms.
Some teratomas contain yolk sac
Yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, providing early nourishment in the form of yolk in bony fishes, sharks, reptiles, birds, and primitive mammals...
elements, which secrete alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AFP gene....
(AFP). Detection of AFP may help to confirm the diagnosis and is often used as a marker for recurrence or treatment efficacy, but is rarely the method of initial diagnosis. (Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AFP gene....
, or MSAFP, is a useful screening test
Screening (medicine)
Screening, in medicine, is a strategy used in a population to detect a disease in individuals without signs or symptoms of that disease. Unlike what generally happens in medicine, screening tests are performed on persons without any clinical sign of disease....
for other fetal conditions, including Down syndrome
Down syndrome
Down syndrome, or Down's syndrome, trisomy 21, is a chromosomal condition caused by the presence of all or part of an extra 21st chromosome. It is named after John Langdon Down, the British physician who described the syndrome in 1866. The condition was clinically described earlier in the 19th...
, spina bifida
Spina bifida
Spina bifida is a developmental congenital disorder caused by the incomplete closing of the embryonic neural tube. Some vertebrae overlying the spinal cord are not fully formed and remain unfused and open. If the opening is large enough, this allows a portion of the spinal cord to protrude through...
and abdominal wall
Layers of the abdominal wall
The abdominal wall represents the boundaries of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal wall is split into the posterior , lateral and anterior walls....
defects such as gastroschisis
Gastroschisis
Gastroschisis represents a congenital defect characterized by a defect in the anterior abdominal wall through which the abdominal contents freely protrude. There is no overlying sac and the size of the defect is usually less than 4 cm...
).
Time of Presentation
Teratomas of germ cell origin usually are found (i.e., present) in adult men and women, but they may also be found in children and infants. Teratomas of embryonal origin are most often found in babies at birth, in young children, and, since the advent of ultrasound imagingMedical ultrasonography
Diagnostic sonography is an ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging technique used for visualizing subcutaneous body structures including tendons, muscles, joints, vessels and internal organs for possible pathology or lesions...
, in fetuses.
The most commonly diagnosed fetal teratomas are sacrococcygeal teratoma
Sacrococcygeal teratoma
Sacrococcygeal teratoma is a teratoma located at the base of the coccyx . It is thought to be a derivative of the primitive streak.-Natural history:...
(Altman types I, II, and III) and cervical (neck) teratoma. Because these teratomas project from the fetal body into the surrounding amniotic fluid
Amniotic sac
The amniotic sac is the sac in which the fetus develops in amniotes. It is a tough but thin transparent pair of membranes, which hold a developing embryo until shortly before birth. The inner membrane, the amnion, contains the amniotic fluid and the fetus. The outer membrane, the Chorion,...
, they can be seen during routine prenatal ultrasound exams. Teratomas within the fetal body are less easily seen with ultrasound; for these, MRI of the pregnant uterus is more informative.
Complications
Teratomas are not dangerous for the fetus unless there is either a mass effectMass effect (medicine)
In medicine, a mass effect is the effect of a growing mass , for example the consequences of a growing cancer....
or a large amount of blood flow through the tumor (known as vascular steal). The mass effect frequently consists of obstruction of normal passage of fluids from surrounding organs. The vascular steal can place a strain on the growing heart of the fetus, even resulting in heart failure, and thus must be monitored by fetal echocardiography
Echocardiography
An echocardiogram, often referred to in the medical community as a cardiac ECHO or simply an ECHO, is a sonogram of the heart . Also known as a cardiac ultrasound, it uses standard ultrasound techniques to image two-dimensional slices of the heart...
.
After surgery, there is a risk of regrowth in place, or in nearby organs.
Surgery
The treatment of choice is complete surgical removal (i.e., complete resection). Teratomas normally are well encapsulated and non-invasive of surrounding tissues, hence they are relatively easy to resect from surrounding tissues. Exceptions include teratomas in the brain, and very large, complex teratomas that have pushed into and become interlaced with adjacent muscles and other structures.Prevention of recurrence does not require en bloc resection of surrounding tissues.
Chemotherapy
For malignant teratomas, usually, surgery is followed by chemotherapy.Teratomas that are in surgically inaccessible locations, or are very complex, or are likely to be malignant (due to late discovery and/or treatment) sometimes are treated first with chemotherapy.
Follow-up
Although often described as benign, a teratoma does have malignant potential. In a UK study of 351 infants and children diagnosed with "benign" teratoma reported 227 with MT, 124 with IT. Five years after surgery, event-free survival was 92.2% and 85.9%, respectively, and overall survival was 99% and 95.1%. A similar study in Italy reported on 183 infants and children diagnosed with teratoma. At 10 years after surgery, event free and overall survival were 90.4% and 98%, respectively.Depending on which tissue(s) it contains, a teratoma may secrete a variety of chemicals with systemic effects. Some teratomas secrete the "pregnancy hormone" human chorionic gonadotropin
Human chorionic gonadotropin
Human chorionic gonadotropin or human chorionic gonadotrophin is a glycoprotein hormone produced during pregnancy that is made by the developing embryo after conception and later by the syncytiotrophoblast .. Some tumors make this hormone; measured elevated levels when the patient is not...
(βhCG), which can be used in clinical practice to monitor the successful treatment or relapse in patients with a known HCG-secreting teratoma. This hormone is not recommended as a diagnostic marker, because most teratomas do not secrete it. Some teratomas secrete thyroxine
Thyroxine
Thyroxine, or 3,5,3',5'-tetraiodothyronine , a form of thyroid hormones, is the major hormone secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid gland.-Synthesis and regulation:...
, in some cases to such a degree that it can lead to clinical hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the term for overactive tissue within the thyroid gland causing an overproduction of thyroid hormones . Hyperthyroidism is thus a cause of thyrotoxicosis, the clinical condition of increased thyroid hormones in the blood. Hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis are not synonymous...
in the patient. Of special concern is the secretion of alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AFP gene....
(AFP); under some circumstances AFP can be used as a diagnostic marker specific for the presence of yolk sac
Yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, providing early nourishment in the form of yolk in bony fishes, sharks, reptiles, birds, and primitive mammals...
cells within the teratoma. These cells can develop into a frankly malignant tumor known as yolk sac tumor or endodermal sinus tumor
Endodermal sinus tumor
Endodermal sinus tumor , also known as yolk sac tumor , is a member of the germ cell tumor group of cancers. It is the most common testicular tumor in children under 3, and is also known as infantile embryonal carcinoma. This age group has a very good prognosis...
.
Adequate follow-up requires close observation, involving repeated physical examination, scanning (ultrasound, MRI, or CT), and measurement of AFP and/or βhCG.
Epidemiology
Embryonal teratomas most commonly occur in the sacrococcygeal region: sacrococcygeal teratomaSacrococcygeal teratoma
Sacrococcygeal teratoma is a teratoma located at the base of the coccyx . It is thought to be a derivative of the primitive streak.-Natural history:...
is the single most common tumor found in newly born humans.
Of teratomas on the skull sutures, approximately 50% are found in or adjacent to the orbit
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents...
. Limbal dermoid is a choristoma, not a teratoma.
Teratoma qualifies as a rare disease
Rare disease
A rare disease, also referred to as an orphan disease, is any disease that affects a small percentage of the population.Most rare diseases are genetic, and thus are present throughout the person's entire life, even if symptoms do not immediately appear...
, but is not extremely rare. Sacrococcygeal teratoma alone is diagnosed at birth in one out of 40,000 humans. Given the current human population and birth-rate, this equals five per day or 1800 per year. Add to that number sacrococcygeal teratomas diagnosed later in life, and teratomas in other locales, and the incidence
Incidence (epidemiology)
Incidence is a measure of the risk of developing some new condition within a specified period of time. Although sometimes loosely expressed simply as the number of new cases during some time period, it is better expressed as a proportion or a rate with a denominator.Incidence proportion is the...
approaches ten thousand new diagnoses of teratoma per year.
Obviously, teratomas also occur, rarely, in other species.
Research
In light of the ethical issues surrounding the source of human stem cellsStem cell controversy
The stem cell controversy is the ethical debate primarily concerning the creation, treatment, and destruction of human embryos incident to research involving embryonic stem cells. Not all stem cell research involves the creation, use, or destruction of human embryos...
, teratomas are being looked at as an alternative source for research since they lack the potential to grow into functional human beings.
In other animals
Ovarian teratomas have been reported in mareMare
Female horses are called mares.Mare is the Latin word for "sea".The word may also refer to:-People:* Ahmed Marzooq, also known as Mare, a footballer and Secretary General of Maldives Olympic Committee* Mare Winningham, American actress and singer...
s and in canines.
External links
- humpath pathology images #2657 (Teratomas), #4541 (Mature teratoma), #5350 (Immature teratoma) (also search EMedicine for all articles containing the word teratoma)
- Monster Tumors Show Scientific Potential in War Against Cancer article in the NYTimes
- Mature teratoma entry in the public domain NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms

