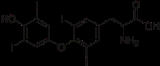
Thyroxine
Encyclopedia
Thyroxine, or 3,5,3',5'-tetraiodothyronine (often abbreviated as T4), a form of thyroid hormones, is the major hormone
secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid
gland.
residues found in an initial peptide, thyroglobulin
, which is secreted into thyroid granules. These iodinated diphenyl compounds are cleaved from their peptide backbone upon being stimulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone
.
(TBG), and, to a lesser extent, to transthyretin
and serum albumin
. The half-life of thyroxine once released into the blood circulatory system is about 1 week.
in the brains of adult mice.
Thyroxine is a prohormone
and a reservoir for the active thyroid hormone triiodothyronine
(T3), which is about four times more potent. T4 is converted in the tissues by deiodinase
s, including thyroid hormone iodine peroxidase (TPO), to T3. The "D" isomer is called "Dextrothyroxine" and is used as a lipid modifying agent.
by Edward Calvin Kendall
from extracts of hog thyroid glands. The hormone was synthesised in 1927 by British chemists Charles Robert Harington and George Barger
.
It is marketed e.g. by Sandoz
as Thyrex in form of 25, 100 and 150 µg tablets.
. A related parameter is the free thyroxine index, which is total thyroxine multiplied by thyroid hormone uptake, which, in turn, is a measure of the unbound thyroxine binding globulins.
The normal human adult range of T4 in blood is 4 - 11 µg/dL
Hormone
A hormone is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. In essence, it is a chemical messenger that transports a signal from one...
secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid
Thyroid
The thyroid gland or simply, the thyroid , in vertebrate anatomy, is one of the largest endocrine glands. The thyroid gland is found in the neck, below the thyroid cartilage...
gland.
Synthesis and regulation
Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination and covalent bonding of the phenyl portions of tyrosineTyrosine
Tyrosine or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine, is one of the 22 amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. Its codons are UAC and UAU. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group...
residues found in an initial peptide, thyroglobulin
Thyroglobulin
Thyroglobulin is a 660 kDa, dimeric protein produced by and used entirely within the thyroid gland. In earlier literature, Tg was referred to as colloid....
, which is secreted into thyroid granules. These iodinated diphenyl compounds are cleaved from their peptide backbone upon being stimulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
Thyrotrophin-stimulating hormone is a peptide hormone synthesized and secreted by thyrotrope cells in the anterior pituitary gland, which regulates the endocrine function of the thyroid gland.- Physiology :...
.
Transport
T4 is transported in blood, with 99.95% of the secreted T4 being protein-bound, principally to thyroxine-binding globulinThyroxine-binding globulin
Thyroxine-binding globulin binds thyroid hormone in circulation. It is one of three proteins responsible for carrying the thyroid hormones thyroxine and 3,5,3’-triiodothyronine in the bloodstream. Of these three proteins, TBG has the highest affinity for T4 and T3, but is present in the lowest...
(TBG), and, to a lesser extent, to transthyretin
Transthyretin
Transthyretin is a serum and cerebrospinal fluid carrier of the thyroid hormone thyroxine and retinol binding protein bound to retinol. This is how transthyretin gained its name, transports thyroxine and retinol...
and serum albumin
Serum albumin
Serum albumin, often referred to simply as albumin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ALB gene.Serum albumin is the most abundant plasma protein in mammals. Albumin is essential for maintaining the osmotic pressure needed for proper distribution of body fluids between intravascular...
. The half-life of thyroxine once released into the blood circulatory system is about 1 week.
Effects
T4 is involved in controlling the rate of metabolic processes in the body and influencing physical development. Administration of thyroxine has been shown to significantly increase the concentration of nerve growth factorNerve growth factor
Nerve growth factor is a small secreted protein that is important for the growth, maintenance, and survival of certain target neurons . It also functions as a signaling molecule. It is perhaps the prototypical growth factor, in that it is one of the first to be described...
in the brains of adult mice.
Thyroxine is a prohormone
Prohormone
A prohormone is a substance that is a precursor to a hormone, usually having minimal hormonal effect by itself. The term has been used in medical science since the middle of the 20th century. The primary function of a prohormone is to enhance the strength of the hormone that already occurs in the...
and a reservoir for the active thyroid hormone triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine, C15H12I3NO4, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate....
(T3), which is about four times more potent. T4 is converted in the tissues by deiodinase
Deiodinase
Iodothyronine deiodinases are a subfamily of deiodinase enzymes important in the activation and deactivation of thyroid hormones. Thyroxine , the precursor of 3,5,3’-triiodothyronine is transformed into T3 by deiodinase activity. T3, through binding a nuclear thyroid hormone receptor,...
s, including thyroid hormone iodine peroxidase (TPO), to T3. The "D" isomer is called "Dextrothyroxine" and is used as a lipid modifying agent.
History
Thyroxine was first isolated in pure form in 1914 at the Mayo ClinicMayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a not-for-profit medical practice and medical research group specializing in treating difficult patients . Patients are referred to Mayo Clinic from across the U.S. and the world, and it is known for innovative and effective treatments. Mayo Clinic is known for being at the top of...
by Edward Calvin Kendall
Edward Calvin Kendall
Edward Calvin Kendall was an American chemist. In 1950, Kendall was awarded the 1950 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine along with Swiss chemist Tadeus Reichstein and Mayo Clinic physician Philip S. Hench, for their work with the hormones of the adrenal gland...
from extracts of hog thyroid glands. The hormone was synthesised in 1927 by British chemists Charles Robert Harington and George Barger
George Barger
George Barger FRS was a British chemist.He was born to an English mother and Dutch father in Manchester, England. He was educated at The Hague High School and King's College, Cambridge. His main work focused on the study of alkaloids and investigations of simple nitrogenous compounds of biological...
.
It is marketed e.g. by Sandoz
Sandoz
Founded in 2003, Sandoz presently is the generic drug subsidiary of Novartis, a multinational pharmaceutical company. The company develops, manufactures and markets generic drugs as well as pharmaceutical and biotechnological active ingredients....
as Thyrex in form of 25, 100 and 150 µg tablets.
Measurement
Thyroxine can be measured as free thyroxine, which is an indicator of thyroxine activity in the body. It can also be measured as total thyroxine, which also depends on the thyroxine that is bound to thyroxine-binding globulinThyroxine-binding globulin
Thyroxine-binding globulin binds thyroid hormone in circulation. It is one of three proteins responsible for carrying the thyroid hormones thyroxine and 3,5,3’-triiodothyronine in the bloodstream. Of these three proteins, TBG has the highest affinity for T4 and T3, but is present in the lowest...
. A related parameter is the free thyroxine index, which is total thyroxine multiplied by thyroid hormone uptake, which, in turn, is a measure of the unbound thyroxine binding globulins.
The normal human adult range of T4 in blood is 4 - 11 µg/dL

