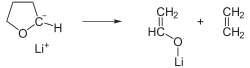
Tert-Butyllithium
Encyclopedia
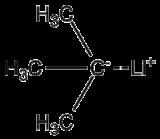
tert-Butyllithium is a chemical compound
with the formula
(CH3)3CLi. As an organometallic compound, it has applications in organic synthesis
(see also Grignard reaction
) since it is a sufficiently strong base
to deprotonate many carbon acids, including benzene
. In regard to molecular aggregation state, the compound exists in clusters
.
tert-Butyllithium is readily available commercially as hydrocarbon solutions; it is not usually prepared in the laboratory.
. The molecule reacts like a carbanion
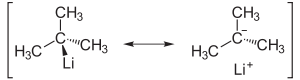
, as is represented by these two resonance structures
. (Given the polarity calculations on the C-Li bond, the "real" structure of a single molecule of t-butyllithium is likely a near-average of the two resonance contributors shown, in which the central carbon atom has a ~50% partial negative charge while the lithium atom has a ~50% partial positive charge.)
Similar to n-butyllithium
, tert-butyllithium can be used for the exchange of lithium with halogens and for the deprotonation of amines and activated C—H compounds.
This compound and other alkyllithium compounds are known to be unstable in ether solvents; the half life of tert-butyllithium is 60 minutes at 0 °C in diethyl ether
, 40 minutes at -20 °C in THF, and about 11 minutes at -70 °C in dimethoxyethane
.
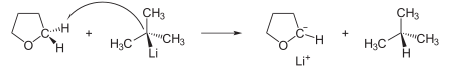
In this example, the reaction of tert-butyllithium with tetrahydrofuran
(THF) is shown:
, traces of tert-butyllithium at the tip of the needle or cannula may catch fire and clog the cannula with lithium salts. Some workers prefer to enclose the needle tip or cannula in a short glass tube which is flushed with an inert gas and sealed via two septa. Serious laboratory accidents involving tert-butyllithium have occurred. For example, in 2009 a staff research assistant, Sheharbano Sangji in the lab of Patrick Harran at the University of California, Los Angeles
, died after being severely burned while working with this compound when her synthetic sweater caught on fire.
Large scale reactions may lead to runaway reactions, fires, and explosions when tert-butyllithium is mixed with ethers such as diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, and glymes. The use of hydrocarbon solvents may be preferred.
Air-free technique
s are important so as to prevent this compound from reacting violently with oxygen and moisture in the air:
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
with the formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
(CH3)3CLi. As an organometallic compound, it has applications in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
(see also Grignard reaction
Grignard reaction
The Grignard reaction is an organometallic chemical reaction in which alkyl- or aryl-magnesium halides add to a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is an important tool for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds...
) since it is a sufficiently strong base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
to deprotonate many carbon acids, including benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
. In regard to molecular aggregation state, the compound exists in clusters
Cluster chemistry
In chemistry, a cluster is an ensemble of bound atoms intermediate in size between a molecule and a bulk solid. Clusters exist of diverse stoichiometries and nuclearities. For example, carbon and boron atoms form fullerene and borane clusters, respectively. Transition metals and main group...
.
tert-Butyllithium is readily available commercially as hydrocarbon solutions; it is not usually prepared in the laboratory.
Chemical properties
The lithium carbon bond in tert-butyllithium is highly polarized, having about 40 percent ionic characterChemical polarity
In chemistry, polarity refers to a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole or multipole moment. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Molecular polarity is dependent on the difference in...
. The molecule reacts like a carbanion
Carbanion
A carbanion is an anion in which carbon has an unshared pair of electrons and bears a negative charge usually with three substituents for a total of eight valence electrons. The carbanion exists in a trigonal pyramidal geometry. Formally a carbanion is the conjugate base of a carbon acid.where B...
, as is represented by these two resonance structures
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula...
. (Given the polarity calculations on the C-Li bond, the "real" structure of a single molecule of t-butyllithium is likely a near-average of the two resonance contributors shown, in which the central carbon atom has a ~50% partial negative charge while the lithium atom has a ~50% partial positive charge.)
Similar to n-butyllithium
N-Butyllithium
n-Butyllithium is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene...
, tert-butyllithium can be used for the exchange of lithium with halogens and for the deprotonation of amines and activated C—H compounds.
This compound and other alkyllithium compounds are known to be unstable in ether solvents; the half life of tert-butyllithium is 60 minutes at 0 °C in diethyl ether
Diethyl ether
Diethyl ether, also known as ethyl ether, simply ether, or ethoxyethane, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula . It is a colorless, highly volatile flammable liquid with a characteristic odor...
, 40 minutes at -20 °C in THF, and about 11 minutes at -70 °C in dimethoxyethane
Dimethoxyethane
Dimethoxyethane, also known as glyme, monoglyme, dimethyl glycol, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, dimethyl cellosolve, and DME, is a clear, colorless, aprotic, and liquid ether that is used as a solvent. Dimethoxyethane is miscible with water.Dimethoxyethane is often used as a higher boiling...
.
In this example, the reaction of tert-butyllithium with tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity at standard temperature and pressure. This heterocyclic compound has the chemical formula 4O. As one of the most polar ethers with a wide liquid range, it is a useful solvent. Its main use, however, is as a precursor...
(THF) is shown:
Safety
tert-Butyllithium is a pyrophoric substance, meaning one that easily catches fire on exposure to air. (A precise definition of a pyrophoric material is one "that ignite[s] spontaneously in air at or below 54.55 °C (130.19 °F)".) The solvents used in common commercial preparations are themselves flammable. While it is possible to work with this compound using cannula transferCannula transfer
Cannula transfer or cannulation is a subset of air-free techniques used with a Schlenk line, in transferring liquid or solution samples between reaction vessels via cannulae, avoiding atmospheric contamination. While the syringes are not the same as cannulae, the techniques remain relevant.There...
, traces of tert-butyllithium at the tip of the needle or cannula may catch fire and clog the cannula with lithium salts. Some workers prefer to enclose the needle tip or cannula in a short glass tube which is flushed with an inert gas and sealed via two septa. Serious laboratory accidents involving tert-butyllithium have occurred. For example, in 2009 a staff research assistant, Sheharbano Sangji in the lab of Patrick Harran at the University of California, Los Angeles
University of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles is a public research university located in the Westwood neighborhood of Los Angeles, California, USA. It was founded in 1919 as the "Southern Branch" of the University of California and is the second oldest of the ten campuses...
, died after being severely burned while working with this compound when her synthetic sweater caught on fire.
Large scale reactions may lead to runaway reactions, fires, and explosions when tert-butyllithium is mixed with ethers such as diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, and glymes. The use of hydrocarbon solvents may be preferred.
Air-free technique
Air-free technique
Air-free techniques refer to a range of manipulations in the chemistry laboratory for the handling of compounds that are air-sensitive. These techniques prevent the compounds from reacting with components of air, usually water and oxygen; less commonly carbon dioxide and nitrogen...
s are important so as to prevent this compound from reacting violently with oxygen and moisture in the air:
- t-BuLi + O2 → t-BuOOLi
- t-BuLi + H2O → t-BuH + LiOH