
Tetrahydroxyborate
Encyclopedia
Tetrahydroxyborate, [H4BO4]− or B(OH), is a boron
oxoanion
with a tetrahedral
geometry
. It is isoelectronic with the hypothetical compound orthocarbonic acid
.
B(OH) is formed by the addition of hydroxide, OH−, to boric acid
, B(OH)3:
Though it is still represented as simple hydrolysis, the formation of tetrahydroxyborate in aqueous solution is responsible for the acidity of boric acid:
The tetrahydroxyborate anion is found in Na[B(OH)4], Na2[B(OH)4]Cl and CuII[B(OH)4]Cl.
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
oxoanion
Oxyanion
An oxyanion or oxoanion is a chemical compound with the generic formula AxOyz− . Oxoanions are formed by a large majority of the chemical elements. The formulae of simple oxoanions are determined by the octet rule...
with a tetrahedral
Tetrahedral molecular geometry
In a tetrahedral molecular geometry a central atom is located at the center with four substituents that are located at the corners of a tetrahedron. The bond angles are cos−1 ≈ 109.5° when all four substituents are the same, as in CH4. This molecular geometry is common throughout the first...
geometry
Molecular geometry
Molecular geometry or molecular structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It determines several properties of a substance including its reactivity, polarity, phase of matter, color, magnetism, and biological activity.- Molecular geometry determination...
. It is isoelectronic with the hypothetical compound orthocarbonic acid
Orthocarbonic acid
Orthocarbonic acid or methanetetraol is the name given to a hypothetical compound with the chemical formula H4CO4 or C4. Its molecular structure consists of a single carbon atom bonded to four hydroxyl groups. It would be therefore a fourfold alcohol...
.
B(OH) is formed by the addition of hydroxide, OH−, to boric acid
Boric acid
Boric acid, also called hydrogen borate or boracic acid or orthoboric acid or acidum boricum, is a weak acid of boron often used as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, as a neutron absorber, and as a precursor of other chemical compounds. It exists in the form of colorless crystals or a...
, B(OH)3:
- B(OH)3 + OH− B(OH)
Though it is still represented as simple hydrolysis, the formation of tetrahydroxyborate in aqueous solution is responsible for the acidity of boric acid:
- B(OH)3 + H2O B(OH) + H+
- pK = 9.25
The tetrahydroxyborate anion is found in Na[B(OH)4], Na2[B(OH)4]Cl and CuII[B(OH)4]Cl.
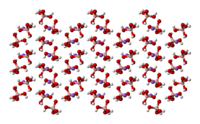 |
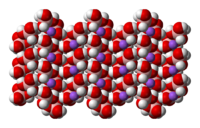 |
Ball-and-stick model In chemistry, the ball-and-stick model is a molecular model of a chemical substance which is to display both the three-dimensional position of the atoms and the bonds between them... of the crystal structure of sodium tetrahydroxyborate |
Space-filling model In chemistry a space-filling model, also known as calotte model, is a type of three-dimensional molecular model where the atoms are represented by spheres whose radii are proportional to the radii of the atoms and whose center-to-center distances are proportional to the distances between the atomic... of the crystal structure of sodium tetrahydroxyborate |

