
The central science
Encyclopedia
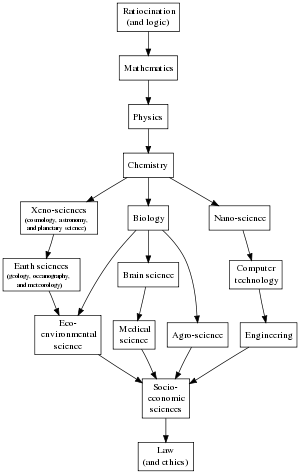
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
is often called the central science because of its role in connecting the physical science
Physical science
Physical science is an encompassing term for the branches of natural science and science that study non-living systems, in contrast to the life sciences...
s, which include chemistry, with the life sciences
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
and applied science
Applied science
Applied science is the application of scientific knowledge transferred into a physical environment. Examples include testing a theoretical model through the use of formal science or solving a practical problem through the use of natural science....
s such as medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
and engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
. The nature of this relationship is one of the main topics in the philosophy of chemistry
Philosophy of chemistry
The philosophy of chemistry considers the methodology and underlying assumptions of the science of chemistry. It is explored by philosophers, chemists, and philosopher-chemist teams...
and in scientometrics
Scientometrics
Scientometrics is the science of measuring and analysing science. In practice, scientometrics is often done using bibliometrics which is a measurement of the impact of publications. Modern scientometrics is mostly based on the work of Derek J. de Solla Price and Eugene Garfield...
. The phrase was popularized by its use in a textbook by Theodore L. Brown and H. Eugene LeMay, titled Chemistry: The Central Science, which was first published in 1977, with a twelfth edition published in 2011.
The central role of chemistry can be seen in the systematic and hierarchical classification of the sciences by Auguste Comte
Auguste Comte
Isidore Auguste Marie François Xavier Comte , better known as Auguste Comte , was a French philosopher, a founder of the discipline of sociology and of the doctrine of positivism...
in which each discipline provides a more general framework for the area it precedes (mathematics → astronomy → physics → chemistry → physiology and medicine → social sciences). Balaban and Klein have more recently proposed a diagram showing partial ordering of sciences in which chemistry may be argued is “the central science” since it provides a significant degree of branching. In forming these connections the lower field cannot be fully reduced
Irreducible (philosophy)
The principle of Irreducibility, in philosophy, has the sense that a complete account of an entity will not be possible at lower levels of explanation and which has novel properties beyond prediction and explanation...
to the higher ones. It is recognized that the lower fields possess emergent
Emergent
It may also mean:* Emergent , Neural Simulation Software* Emergent , a 2003 album by Gordian Knot* emergent plant, a plant which grows in water but which pierces the surface so that it is partially in air...
ideas and concepts that do not exist in the higher fields of science.
Thus chemistry is built on an understanding of laws of physics that govern particles such as atoms, protons, electrons, thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
, etc. although it has been shown that it cannot be “fully 'reduced' to quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
”. Concepts such as the periodicity
Periodic table
The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular display of the 118 known chemical elements organized by selected properties of their atomic structures. Elements are presented by increasing atomic number, the number of protons in an atom's atomic nucleus...
of the elements and chemical bond
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
s in chemistry are emergent in that they are more than the underlying forces that are defined by physics.
In the same way biology cannot be fully reduced to chemistry despite the fact that the machinery that is responsible for life is composed of molecules. For instance, the machinery of evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
may be described in terms of chemistry by the understanding that it is a mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
in the order of genetic
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
base pair
Base pair
In molecular biology and genetics, the linking between two nitrogenous bases on opposite complementary DNA or certain types of RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds is called a base pair...
s in the DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
of an organism. However chemistry cannot fully describe the process since it does not contain concepts, such as natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
that are responsible for driving evolution. Chemistry is fundamental to biology since it provides methodology to study and understand the molecules that compose cells.
Connections made by chemistry are formed through various sub-disciplines that utilize concepts from multiple scientific disciplines. Chemistry and physics are both needed in the areas of physical chemistry
Physical chemistry
Physical chemistry is the study of macroscopic, atomic, subatomic, and particulate phenomena in chemical systems in terms of physical laws and concepts...
, nuclear chemistry
Nuclear chemistry
Nuclear chemistry is the subfield of chemistry dealing with radioactivity, nuclear processes and nuclear properties.It is the chemistry of radioactive elements such as the actinides, radium and radon together with the chemistry associated with equipment which are designed to perform nuclear...
, and theoretical chemistry
Theoretical chemistry
Theoretical chemistry seeks to provide theories that explain chemical observations. Often, it uses mathematical and computational methods that, at times, require advanced knowledge. Quantum chemistry, the application of quantum mechanics to the understanding of valency, is a major component of...
. Chemistry and biology intersect in the areas of biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
, medicinal chemistry
Medicinal chemistry
Medicinal chemistry and pharmaceutical chemistry are disciplines at the intersection of chemistry, especially synthetic organic chemistry, and pharmacology and various other biological specialties, where it is involved with design, chemical synthesis and development for market of pharmaceutical...
, molecular biology
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
, chemical biology
Chemical biology
Chemical biology is a scientific discipline spanning the fields of chemistry and biology that involves the application of chemical techniques and tools, often compounds produced through synthetic chemistry, to the study and manipulation of biological systems. This is a subtle difference from...
, molecular genetics
Molecular genetics
Molecular genetics is the field of biology and genetics that studies the structure and function of genes at a molecular level. The field studies how the genes are transferred from generation to generation. Molecular genetics employs the methods of genetics and molecular biology...
, and immunochemistry
Immunochemistry
Immunochemistry is a branch of chemistry that involves the study of the reactions and components on the immune system.Various methods in immunochemistry have been developed and refined, and been used in scientific study, from virology to molecular evolution....
. Chemistry and the earth sciences intersect in areas like geochemistry
Geochemistry
The field of geochemistry involves study of the chemical composition of the Earth and other planets, chemical processes and reactions that govern the composition of rocks, water, and soils, and the cycles of matter and energy that transport the Earth's chemical components in time and space, and...
and hydrology
Hydrology
Hydrology is the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth and other planets, including the hydrologic cycle, water resources and environmental watershed sustainability...
.
See also
- Philosophy of chemistryPhilosophy of chemistryThe philosophy of chemistry considers the methodology and underlying assumptions of the science of chemistry. It is explored by philosophers, chemists, and philosopher-chemist teams...
- Hard science
- Soft science
- Special sciencesSpecial sciencesThe special sciences are those sciences other than physics that are sometimes thought to be reducible to physics, or to stand in some similar relation of dependence to physics as the "fundamental" science. The usual list includes chemistry, biology, neuroscience, and many others...
- Unity of scienceUnity of scienceThe unity of science is a thesis in philosophy of science that says that all the sciences form a unified whole.Even though, for example, physics and politics are distinct disciplines, the thesis of the unity of science says that in principle they must be part of a unified intellectual endeavor,...

