
Three-dimensional graph
Encyclopedia
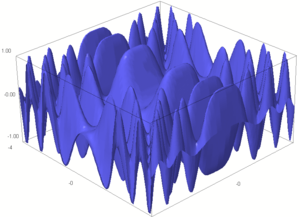
Graph of a function
In mathematics, the graph of a function f is the collection of all ordered pairs . In particular, if x is a real number, graph means the graphical representation of this collection, in the form of a curve on a Cartesian plane, together with Cartesian axes, etc. Graphing on a Cartesian plane is...
of a function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
of two variables
Variable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable is a value that may change within the scope of a given problem or set of operations. In contrast, a constant is a value that remains unchanged, though often unknown or undetermined. The concepts of constants and variables are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and...
f(x, y).
Provided that x, y, and f(x, y) are real number
Real number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
s, the graph can be represented as a planar or curved surface
Surface
In mathematics, specifically in topology, a surface is a two-dimensional topological manifold. The most familiar examples are those that arise as the boundaries of solid objects in ordinary three-dimensional Euclidean space R3 — for example, the surface of a ball...
in a three-dimensional
Three-dimensional space
Three-dimensional space is a geometric 3-parameters model of the physical universe in which we live. These three dimensions are commonly called length, width, and depth , although any three directions can be chosen, provided that they do not lie in the same plane.In physics and mathematics, a...
Cartesian coordinate system
Cartesian coordinate system
A Cartesian coordinate system specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length...
.
Example
The graph of the trigonometric function on the real lineReal line
In mathematics, the real line, or real number line is the line whose points are the real numbers. That is, the real line is the set of all real numbers, viewed as a geometric space, namely the Euclidean space of dimension one...

is
-
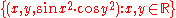 .
.
If this set is plotted on a three dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, the result is a surface (see figure).
See also
- Graph (disambiguation)
- Two-dimensional graphTwo-dimensional graph[Image:cubicpoly.svg||right|thumb|400 px| Graph of the function f=[Image:cubicpoly.svg||right|thumb|400 px| Graph of the function f=[Image:cubicpoly.svg||right|thumb|400 px| Graph of the function f=...
- Analytic geometryAnalytic geometryAnalytic geometry, or analytical geometry has two different meanings in mathematics. The modern and advanced meaning refers to the geometry of analytic varieties...
- Cartesian coordinate systemCartesian coordinate systemA Cartesian coordinate system specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length...
- Euclidean spaceEuclidean spaceIn mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
- Coordinate systemCoordinate systemIn geometry, a coordinate system is a system which uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of a point or other geometric element. The order of the coordinates is significant and they are sometimes identified by their position in an ordered tuple and sometimes by...
- DimensionDimensionIn physics and mathematics, the dimension of a space or object is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus a line has a dimension of one because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on it...

