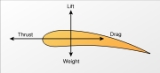
Thrust
Overview
Reaction (physics)
The third of Newton's laws of motion of classical mechanics states that forces always occur in pairs. Every action is accompanied by a reaction of equal magnitude but opposite direction. This principle is commonly known in the Latin language as actio et reactio. The attribution of which of the two...
force described quantitatively by Newton
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
's second and third laws
Newton's laws of motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that form the basis for classical mechanics. They describe the relationship between the forces acting on a body and its motion due to those forces...
. When a system expels or accelerates
Acceleration
In physics, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time. In one dimension, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows down. However, since velocity is a vector, acceleration describes the rate of change of both the magnitude and the direction of velocity. ...
mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
in one direction the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction on that system.
In mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
, force orthogonal to the main load (such as in parallel helical gears) is referred to as thrust.
A fixed-wing aircraft
Fixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is an aircraft capable of flight using wings that generate lift due to the vehicle's forward airspeed. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinct from rotary-wing aircraft in which wings rotate about a fixed mast and ornithopters in which lift is generated by flapping wings.A powered...
generates forward thrust when air is pushed in the direction opposite to flight.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

