
Thule people
Encyclopedia
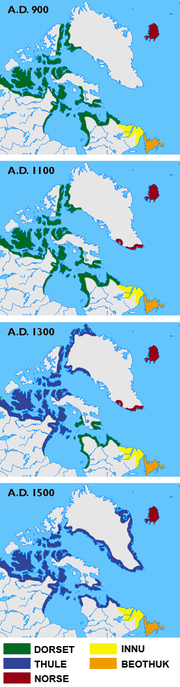
The Thule
or proto-Inuit were the ancestors of all modern Inuit
Inuit
The Inuit are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic regions of Canada , Denmark , Russia and the United States . Inuit means “the people” in the Inuktitut language...
. They developed in coastal Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
by AD 1000 and expanded eastwards across Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, reaching Greenland
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for...
by the 13th century. In the process, they replaced people of the earlier Dorset culture
Dorset culture
The Dorset culture was a Paleo-Eskimo culture that preceded the Inuit culture in Arctic North America. It has been defined as having four phases, with distinct technology related to the people's hunting and tool making...
that had previously inhabited the region. The appellation "Thule
Thule
Thule Greek: Θούλη, Thoulē), also spelled Thula, Thila, or Thyïlea, is, in classical European literature and maps, a region in the far north. Though often considered to be an island in antiquity, modern interpretations of what was meant by Thule often identify it as Norway. Other interpretations...
" originates from the location of Thule
Pituffik
Pituffik is a former settlement in northern Greenland, located at the current site of the American Thule Air Base. The former inhabitants were relocated to the present-day town of Qaanaaq...
(in 1953 relocated to Qaanaaq
Qaanaaq
Qaanaaq is the main town in the northern part of the Qaasuitsup municipality in northwestern Greenland. It is one of the northernmost towns in the world. The inhabitants of Qaanaaq speak the West Greenlandic language and many also speak Inuktun. The town has a population of 626 as of 2010...
) in northwest Greenland, facing Canada, where the archaeological
Archaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
remains of the people were first found at Comer's Midden
Comer's Midden
Comer's Midden is a 1916 archaeological excavation site near the"Arctic Station of Thule" , north of Mt. Dundas , in North Star Bay, northern Greenland. It is the find after which the Thule culture is named...
. The links between the Thule and the Inuit are biological
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
, cultural
Culture
Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions...
, and linguistic
Natural language
In the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
.
History

Skræling
Skræling is the name the Norse Greenlanders used for the indigenous peoples they encountered in North America and Greenland. In surviving sources it is first applied to the Thule people, the Eskimo group with whom the Norse coexisted in Greenland after about the 13th century...
. Some Thule migrated southward, in the "Second Expansion" or "Second Phase". By the 13th or 14th century, the Thule had occupied an area currently inhabited by the Central Inuit
Central Inuit
Central Inuit are the Inuit of Northern Canada, their designation determined by geography and their tradition of snowhouses , fur clothing, and sled dogs. They are differentiated from Alaska's Iñupiat, Greenland's Kalaallit, and Russian Inuit...
, and by the 15th century, the Thule replaced the Dorset culture
Dorset culture
The Dorset culture was a Paleo-Eskimo culture that preceded the Inuit culture in Arctic North America. It has been defined as having four phases, with distinct technology related to the people's hunting and tool making...
. Intensified contacts with Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
ans began in the 18th century. Compounded by the already disruptive effects of the "Little Ice Age
Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age was a period of cooling that occurred after the Medieval Warm Period . While not a true ice age, the term was introduced into the scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939...
" (1650–1850), the Thule communities broke apart, and the people were henceforward known as the Eskimo
Eskimo
Eskimos or Inuit–Yupik peoples are indigenous peoples who have traditionally inhabited the circumpolar region from eastern Siberia , across Alaska , Canada, and Greenland....
and, later, Inuit.
Culture

Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. The result is a foliated rock in which the foliation may not correspond to the original sedimentary layering...
knives, umiaks, seal-skin floats and toggling harpoon
Toggling harpoon
The toggling harpoon is an ancient weapon and tool used in whaling to impale a whale when thrown. Unlike earlier harpoon versions which had only one point, a toggling harpoon has a two-part point...
s, the Thule subsisted primarily on marine animals—especially large sea mammals
Marine mammal
Marine mammals, which include seals, whales, dolphins, and walruses, form a diverse group of 128 species that rely on the ocean for their existence. They do not represent a distinct biological grouping, but rather are unified by their reliance on the marine environment for feeding. The level of...
.
Thule winter settlements usually had one to four houses with about ten people each. Their houses were made of whale
Whale
Whale is the common name for various marine mammals of the order Cetacea. The term whale sometimes refers to all cetaceans, but more often it excludes dolphins and porpoises, which belong to suborder Odontoceti . This suborder also includes the sperm whale, killer whale, pilot whale, and beluga...
bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
s from summer hunts. Other structures included kill sites, food caches, and tent
Tent
A tent is a shelter consisting of sheets of fabric or other material draped over or attached to a frame of poles or attached to a supporting rope. While smaller tents may be free-standing or attached to the ground, large tents are usually anchored using guy ropes tied to stakes or tent pegs...
encampments. Some major settlements may have had more than a dozen houses, although not all were inhabited at the same time by the approximately fifty residents.

