Time-bin encoding
Encyclopedia
Time-bin encoding is a technique used in Quantum information science
to encode a qubit
of information on a photon
. Quantum information science makes use of qubits as a basic resource similar to bit
s in classical computing
. Qubits are any two-level quantum mechanical system; there are many different physical implementations of qubits, one of which is time-bin encoding.
While the time-bin encoding technique is very robust against decoherence, it does not allow easy interaction between the different qubits. As such, it is much more useful in quantum communication (such as quantum teleportation
and quantum key distribution) than in quantum computation.
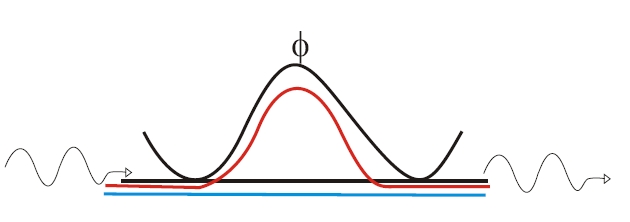
Time-bin encoding is done by having a single-photon go through a Mach-Zender interferometer (MZ), shown in black here. The photon coming from the left is guided through one of two paths (shown in blue and red); the guiding can be made by optical fiber
or simply in free space using mirrors and polarising cubes
. One of the two paths is longer than the other. The difference in path length must be longer than the coherence length
of the photon to make sure the path taken can be unambiguously distinguished. The interferometer has to keep a stable phase, which means that the path length difference must vary by much less than the wavelength of light during the experiment. This usually requires active temperature stabilization.
If the photon takes the short path, it is said to be in the state ; if it takes the long path, it is said to be in the state
; if it takes the long path, it is said to be in the state  . If the photon has a non-zero probability to take either path, then it is in a coherent superposition of the two states:
. If the photon has a non-zero probability to take either path, then it is in a coherent superposition of the two states:
These coherent superpositions of the two possible states are called qubits and are the basic ingredient of Quantum information science
.
In general, it is easy to vary the phase
gained by the photon between the two paths, for example by stretching the fiber, while it is much more difficult to vary the amplitudes which are therefore fixed, typically at 50%. The created qubit is then
which covers only a subset of all possible qubits.
Measurement in the { ,
, } basis is done by measuring the time of arrival of the photon. Measurement in other bases can be achieved by letting the photon go through a second MZ before measurement, though, similar to the state preparation, the possible measurement setups are restricted to only a small subset of possible qubit measurements.
} basis is done by measuring the time of arrival of the photon. Measurement in other bases can be achieved by letting the photon go through a second MZ before measurement, though, similar to the state preparation, the possible measurement setups are restricted to only a small subset of possible qubit measurements.
Quantum information science
Quantum information science is an area of study based on the idea that information science depends on quantum effects in physics. It includes theoretical issues in computational models as well as more experimental topics in quantum physics including what can and cannot be done with quantum...
to encode a qubit
Qubit
In quantum computing, a qubit or quantum bit is a unit of quantum information—the quantum analogue of the classical bit—with additional dimensions associated to the quantum properties of a physical atom....
of information on a photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
. Quantum information science makes use of qubits as a basic resource similar to bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
s in classical computing
Computing
Computing is usually defined as the activity of using and improving computer hardware and software. It is the computer-specific part of information technology...
. Qubits are any two-level quantum mechanical system; there are many different physical implementations of qubits, one of which is time-bin encoding.
While the time-bin encoding technique is very robust against decoherence, it does not allow easy interaction between the different qubits. As such, it is much more useful in quantum communication (such as quantum teleportation
Quantum teleportation
Quantum teleportation, or entanglement-assisted teleportation, is a process by which a qubit can be transmitted exactly from one location to another, without the qubit being transmitted through the intervening space...
and quantum key distribution) than in quantum computation.
How to build a time-bin encoded qubit

Time-bin encoding is done by having a single-photon go through a Mach-Zender interferometer (MZ), shown in black here. The photon coming from the left is guided through one of two paths (shown in blue and red); the guiding can be made by optical fiber
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
or simply in free space using mirrors and polarising cubes
Beam splitter
A beam splitter is an optical device that splits a beam of light in two. It is the crucial part of most interferometers.In its most common form, a rectangle, it is made from two triangular glass prisms which are glued together at their base using Canada balsam...
. One of the two paths is longer than the other. The difference in path length must be longer than the coherence length
Coherence length
In physics, coherence length is the propagation distance from a coherent source to a point where an electromagnetic wave maintains a specified degree of coherence. The significance is that interference will be strong within a coherence length of the source, but not beyond it...
of the photon to make sure the path taken can be unambiguously distinguished. The interferometer has to keep a stable phase, which means that the path length difference must vary by much less than the wavelength of light during the experiment. This usually requires active temperature stabilization.
If the photon takes the short path, it is said to be in the state
 ; if it takes the long path, it is said to be in the state
; if it takes the long path, it is said to be in the state  . If the photon has a non-zero probability to take either path, then it is in a coherent superposition of the two states:
. If the photon has a non-zero probability to take either path, then it is in a coherent superposition of the two states:These coherent superpositions of the two possible states are called qubits and are the basic ingredient of Quantum information science
Quantum information science
Quantum information science is an area of study based on the idea that information science depends on quantum effects in physics. It includes theoretical issues in computational models as well as more experimental topics in quantum physics including what can and cannot be done with quantum...
.
In general, it is easy to vary the phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
gained by the photon between the two paths, for example by stretching the fiber, while it is much more difficult to vary the amplitudes which are therefore fixed, typically at 50%. The created qubit is then
which covers only a subset of all possible qubits.
Measurement in the {
 ,
, } basis is done by measuring the time of arrival of the photon. Measurement in other bases can be achieved by letting the photon go through a second MZ before measurement, though, similar to the state preparation, the possible measurement setups are restricted to only a small subset of possible qubit measurements.
} basis is done by measuring the time of arrival of the photon. Measurement in other bases can be achieved by letting the photon go through a second MZ before measurement, though, similar to the state preparation, the possible measurement setups are restricted to only a small subset of possible qubit measurements.


