Time in Saskatchewan
Encyclopedia
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a prairie province in Canada, which has an area of . Saskatchewan is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota....
observes Central Standard Time year round. However, since the province is geographically located in the Mountain Time Zone (which originally spanned from 97.5° to 112.5° W; Saskatchewan's boundaries are roughly 102° and 110° W), it is effectively on daylight saving time year round.
History
In 1912, the first law was passed that called for the use of standard timeStandard time
Standard time is the result of synchronizing clocks in different geographical locations within a time zone to the same time rather than using the local meridian as in local mean time or solar time. Historically, this helped in the process of weather forecasting and train travel. The concept...
. This law left the choice of time zone
Time zone
A time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
up to the municipal government. The result was a patchwork of towns following either of the two neighbouring time zones (Mountain Standard Time or Central Standard Time) with or without daylight saving time.
During World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
and World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, all municipalities were forced to adopt daylight saving time to save on fuel, but were not forced to adopt the same time zone.
In 1966, the Saskatchewan Provincial Government sought the help of a professional astronomer living in the province. The Milton Study (Earl R.V. Milton - A submission to the Government of Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a prairie province in Canada, which has an area of . Saskatchewan is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota....
regarding Time Zones in Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a prairie province in Canada, which has an area of . Saskatchewan is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota....
, 1966) a) concluded that Saskatchewan is in the Mountain Standard Time Zone, and b) suggested that the three prairie provinces (Alberta
Alberta
Alberta is a province of Canada. It had an estimated population of 3.7 million in 2010 making it the most populous of Canada's three prairie provinces...
, Saskatchewan and Manitoba
Manitoba
Manitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other...
) covered too much area to share a single time zone.
In 1966, based on the Milton Study, the Saskatchewan Government passed Chapter 85, to be known as the Time Act, 1966 (Statutes of Saskatchewan, 1966). The key points of this act were:
- The eastern part of Saskatchewan will permanently be one hour ahead of Mountain Standard Time (the equivalent of Mountain Daylight Time or Central Standard Time).
- In the western part of Saskatchewan, municipal governments will still be able to choose what time zone to follow.
The only city that chose not to match the rest of Saskatchewan's time zone was the city of Lloydminster
Lloydminster
Lloydminster is a Canadian city which has the unusual geographic distinction of straddling the provincial border between Alberta and Saskatchewan...
(partly in Saskatchewan, and partly in Alberta). Lloydminster chose to follow the Alberta side with a combination of Mountain Standard Time and Mountain Daylight Time zones. This may be because the Alberta side of the city did not have a choice of time zone. Swift Current and surrounding communities observed the same time as Lloydminster until April 30, 1972 when they changed to match the rest of the province.
With respect to some province-wide matters (perhaps most notably, provincial elections), CST is effectively used province-wide. This means that during any provincial general election held when DST is not in effect in Lloydminster, polls in that city will open and close an hour earlier local time compared to the rest of the province. For other matters (for example, liquor laws), the local time is always the effective time in Lloydminster.
The town of Creighton
Creighton, Saskatchewan
Creighton, Saskatchewan was named after Thomas Creighton. It had a 2006 census population of 1,502 inhabitants, down 3.47% from 1,556 inhabitants in 2001.The town lies beside the Saskatchewan-Manitoba border, adjacent to Flin Flon, Manitoba...
which is across the border from the larger community of Flin Flon, Manitoba unofficially observes Central Daylight Time with the rest of Manitoba. Unlike Lloydminster, Creighton's use of CDT has no legal sanction at the provincial level. This has some interesting side effects - for example, liquor establishments in Creighton are able to stay open one hour later than establishments in Flin Flon whilst CDT is in effect since a liquor establishtment in Creighton can only be bound to observe CST by provincial law.
Saskatchewan Time Zone
"Saskatchewan" is often a drop-down option for "time zone" in computer programs, as an exception to the typical use of daylight saving time in North America.The current wording of the Time Act says that during the entire year Saskatchewan observes "central standard time", which is defined to be "the time that is six hours behind
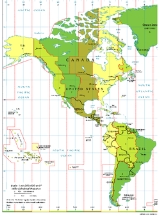
Greenwich time". With respect to mean solar time however, this translates into Saskatchewan effectively being on DST year round. In the map above, Saskatchewan is the rectangle of Central Standard Time protruding into Mountain Standard Time in Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, visually displaying that geographically, Saskatchewan is in the Mountain Time zone.
See also
- Time in CanadaTime in CanadaCanada is divided into six time zones, based on proposals by Scottish Canadian railway engineer Sir Sandford Fleming, who helped pioneer the world's time zone system.Times used:-Pacific Standard Time:...
- Time in Arizona

