
Time of flight detector
Encyclopedia
A time of flight detector is a particle detector
which can discriminate between a lighter and a heavier elementary particle
of same momentum using their time of flight between two scintillator
s. The first of the scintillators activates a clock upon being hit while the other stops the clock upon being hit. If the two masses are denoted by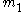 and
and 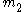 and have velocities
and have velocities 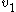 and
and 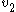 then the time of flight difference is given by
then the time of flight difference is given by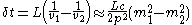
where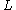 is the distance between the scintillators. The approximation is in the relativistic limit at momentum
is the distance between the scintillators. The approximation is in the relativistic limit at momentum 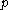 and
and  denotes the speed of light in vacuum. Usually,
denotes the speed of light in vacuum. Usually, 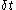 is the apparatus' time resolution (~200 ps).
is the apparatus' time resolution (~200 ps).
Particle detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify high-energy particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a...
which can discriminate between a lighter and a heavier elementary particle
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle not known to have substructure; that is, it is not known to be made up of smaller particles. If an elementary particle truly has no substructure, then it is one of the basic building blocks of the universe from which...
of same momentum using their time of flight between two scintillator
Scintillator
A scintillator is a special material, which exhibits scintillation—the property of luminescence when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate, i.e., reemit the absorbed energy in the form of light...
s. The first of the scintillators activates a clock upon being hit while the other stops the clock upon being hit. If the two masses are denoted by
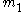 and
and 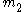 and have velocities
and have velocities 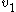 and
and 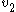 then the time of flight difference is given by
then the time of flight difference is given by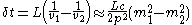
where
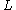 is the distance between the scintillators. The approximation is in the relativistic limit at momentum
is the distance between the scintillators. The approximation is in the relativistic limit at momentum 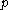 and
and  denotes the speed of light in vacuum. Usually,
denotes the speed of light in vacuum. Usually, 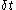 is the apparatus' time resolution (~200 ps).
is the apparatus' time resolution (~200 ps).See also
- Time-of-flightTime-of-flightTime of flight describes a variety of methods that measure the time that it takes for an object, particle or acoustic, electromagnetic or other wave to travel a distance through a medium...
- Time-of-flight mass spectrometryTime-of-flight mass spectrometryTime-of-flight mass spectrometry is a method of mass spectrometry in which an ion's mass-to-charge ratio is determined via a time measurement. Ions are accelerated by an electric field of known strength. This acceleration results in an ion having the same kinetic energy as any other ion that has...

