
Timed event system
Encyclopedia
The General System has been described in [Zeigler76] and [ZPK00] with the stand points to define (1) the time base, (2) the admissible input segments, (3) the system states, (4) the state trajectory with an admissible input segment, (5) the output for a given state.
A Timed Event System defining the state trajectory associated with the current and event segments is a sub-class of the class of General System. Since the behaviors of DEVS
can be described by Timed Event System, DEVS
is a sub-class or a equivalent class of Timed Event System.
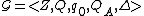
where
A Timed Event System defining the state trajectory associated with the current and event segments is a sub-class of the class of General System. Since the behaviors of DEVS
Behavior of DEVS
Behaviors of a given DEVS model is a set of sequences of timed events including null events, called event segments which make the model move one state to another within a set of legal states...
can be described by Timed Event System, DEVS
DEVS
DEVS abbreviating Discrete Event System Specification is a modular and hierarchical formalism for modeling and analyzing general systems that can be discrete event systems which might be described by state transition tables, and continuous state systems which might be described by differential...
is a sub-class or a equivalent class of Timed Event System.
Timed Event Systems
A timed event system is a structure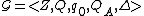
where
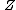 is the set of events;
is the set of events;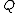 is the set of states;
is the set of states;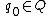 is the initial state;
is the initial state;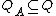 is the set of acceptance states;
is the set of acceptance states;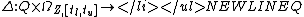 is the state trajectory function that defines how a state
is the state trajectory function that defines how a state 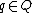 changes into
changes into 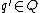 along with an event segment
along with an event segment 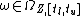 .
.
If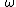 is concatenation of two unit event segments, i.e.,
is concatenation of two unit event segments, i.e., 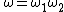 then
then
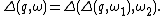
In general, if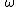 is concatenation of
is concatenation of  unit event segments, i.e.,
unit event segments, i.e., 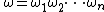 where
where 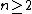 then
then
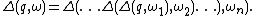
Deterministic System and Non-deterministic System
Let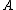 and
and 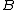 be two arbitrary sets. Then function
be two arbitrary sets. Then function 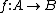 is called deterministic if for
is called deterministic if for 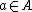 ,
, 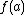 is identical any time.
is identical any time.
Otherwise,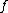 is called non-deterministic.
is called non-deterministic.
A Timed Event System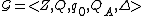 is deterministic if
is deterministic if
- selecting
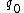 is deterministic, and
is deterministic, and -
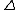 is deterministic.
is deterministic.
Otherwise,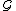 is non-deterministic.
is non-deterministic.
Behaviors and Languages of Timed Event System
Given a timed event system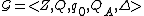 , the set of its behaviors is called its language depending on the
, the set of its behaviors is called its language depending on the
observation time length. Let be the observation time length.
be the observation time length.
If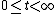 ,
,  -length observation language of
-length observation language of
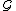 is denoted by
is denoted by 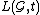 , and defined as
, and defined as

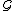 can be nondeterministic so the number of possible results
can be nondeterministic so the number of possible results 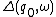 can be many. Finally, we call an event segment
can be many. Finally, we call an event segment 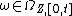 a
a  -length behavior of
-length behavior of 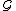 , if
, if 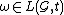 .
.
We can define behaviors with the infinite time length. Given an infinite-observation event segment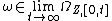 and a timed event system
and a timed event system 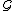 , let
, let 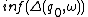 denote the set of
denote the set of 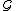 's states that are infinitely many or long visited by
's states that are infinitely many or long visited by 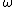 and
and 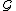 . Then infinite length observation language of
. Then infinite length observation language of 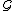
is denoted by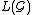 , and defined as
, and defined as

We call an event segment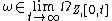 an infinite-length behavior of
an infinite-length behavior of 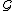 , if
, if 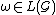 .
.
- selecting

