DEVS
Encyclopedia
DEVS abbreviating Discrete Event System Specification is a modular and hierarchical formalism for modeling and analyzing general systems that can be discrete event systems which might be described by state transition table
s, and continuous state systems which might be described by differential equation
s, and hybrid continuous state and discrete event systems. DEVS is a timed event system
.
. DEVS was introduced to the public in Zeigler's first book, Theory of Modeling and Simulation, in 1976, while Zeigler was an associate professor at University of Michigan
. DEVS can be seen as an extension of the Moore machine
formalism , which is a finite state automaton where the outputs are determined by the current state alone (and do not depend directly on the input). The extension was done by
Since the lifespan of each state is a real number (more precisely, non-negative real) or infinity, it is distinguished from discrete time systems, sequential machines, and Moore machine
s, in which time is determined by a tick time multiplied by non-negative integers. Moreover, the lifespan can be a random variable
; for example the lifespan of a given state can be distributed exponentially
or uniformly
. The state transition and output functions of DEVS can also be stochastic
.
Zeigler proposed a hierarchical algorithm for DEVS model simulation in 1984 [Zeigler84] which was published in Simulation journal in 1987. Since then, many extended formalism from DEVS have been introduced with their own purposes: DESS/DEVS for combined continuous and discrete event systems, P-DEVS for parallel DESs, G-DEVS for piecewise continuous state trajectory modeling of DESs, RT-DEVS for realtime DESs, Cell-DEVS for cellular DESs, Fuzzy-DEVS for fuzzy DESs, Dynamic Structuring DEVS for DESs changing their coupling structures dynamically, and so on. In addition to its extensions, there are some subclasses such as SP-DEVS
and FD-DEVS have been researched for achieving decidability of system properties.
Due to the modular and hierarchical modeling views, as well as its simulation-based analysis capability, the DEVS formalism and its variations have been used in many application of engineering (such as hardware design, hardware/software codesign, communications system
s, manufacturing
systems) and science (such as biology
, and sociology
)
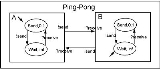
 Intuitive Example
Intuitive Example
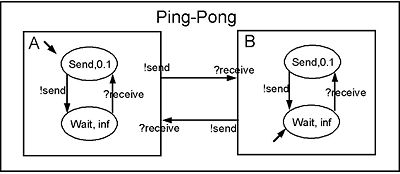
DEVS defines system behavior as well as system structure. System behavior in DEVS formalism is described using input and output events as well as states. For example, for the ping-pong player of Fig. 1, the input event is ?receive, and the output event is !send. Each player, A, B, has its states: Send and Wait. Send state takes 0.1 seconds to send back the ball that is the output event !send, while Wait lasts the state until the player receives the ball that is the input event ?receive.
The structure of ping-pong game is to connect two players: Player A 's output event !send is transmitted to Player B 's input event ?receive, and vice versa.
In the classic DEVS formalism, Atomic DEVS captures the system behavior, while Coupled DEVS describes the structure of system.
The following formal definition is for Classic DEVS [ZKP00]. In this article, we will use the time base,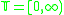 that is the set of non-negative real numbers; the extended time base,
that is the set of non-negative real numbers; the extended time base,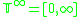 that is the set of non-negative real numbers plus infinity.
that is the set of non-negative real numbers plus infinity.
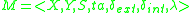
where
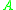 and
and 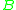 be two arbitrary sets. Then function
be two arbitrary sets. Then function 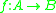 is called deterministic if for
is called deterministic if for 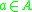 ,
, 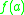 is identical any time.
is identical any time.
Otherwise,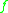 is called non-deterministic.
is called non-deterministic.
A DEVS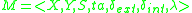 is called deterministic if
is called deterministic if 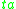 ,
, 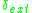 ,
, 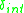 and
and 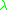
are deterministic. Otherwise,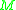 is called non-deterministic.
is called non-deterministic.
The atomic DEVS Model for Ping-Pong Players
The atomic DEVS model for player A of Fig. 1 is given
Player=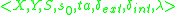
such that
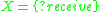
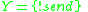
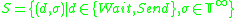
and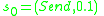
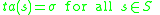
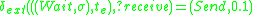
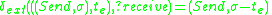
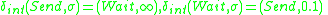
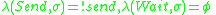
Both Player A and Player B are deterministic DEVS models.
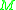 can change its state
can change its state 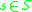 : (1) when an external input
: (1) when an external input 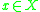 comes into the system
comes into the system 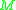 ; (2) when the elapsed time
; (2) when the elapsed time 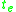 reaches the lifespan of
reaches the lifespan of  which is defined by
which is defined by 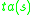 . (At the same time of (2),
. (At the same time of (2), 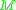 generates an output
generates an output 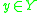 which is defined by
which is defined by 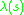 .) .
.) .
For formal behavior description of given an Atomic DEVS model, refer to the page Behavior of DEVS
. Computer algorithms to implement the behavior of a given Atomic DEVS model are available at Simulation Algorithms for Atomic DEVS
.
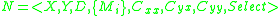
where
The coupled DEVS model for Ping-Pong Game
The ping-pong game of Fig. 1 can be modeled as an coupled DEVS model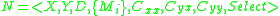 where
where 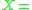 ;
;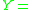 ;
;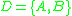 ;
; 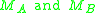 is described as above;
is described as above; 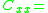 ;
; 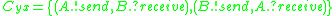 ; and
; and 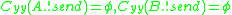 .
.
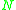 changes its components' states (1) when an external event
changes its components' states (1) when an external event 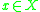 comes into
comes into 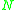 ; (2) when one of components
; (2) when one of components 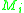 where
where 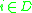 executes its internal state transition and generates its output
executes its internal state transition and generates its output 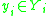 . In both cases (1) and (2), a triggering event is transmitted to all influencees which are defined by coupling sets
. In both cases (1) and (2), a triggering event is transmitted to all influencees which are defined by coupling sets 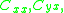 and
and 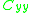 .
.
For formal definition of behavior of the coupled DEVS, you can refer to Behavior of Coupled DEVS
. Computer algorithms to implement the behavior of a given coupled DEVS mode are available at Simulation Algorithms for Coupled DEVS
.
and Simulation Algorithms for Coupled DEVS
.
) and Finite & Deterministic DEVS (FD-DEVS) [HZ09]. As a result, based on the rechability graph, (1) dead-lock and live-lock freeness as qualitative properties are decidable with SP-DEVS [Hwang05] and FD-DEVS [HZ06], and (2) min/max processing time bounds as a quantitative property are decidable with SP-DEVS so far by 2009.
Among them formalisms which allow to have changing model structures while the simulation time evolves.
G-DEVS, Parallel DEVS, Dynamic Structuring DEVS, Cell-DEVS [Wainer09], dynDEVS, Fuzzy-DEVS, GK-DEVS, ml-DEVS, Symbolic DEVS, Real-Time DEVS, rho-DEVS
) and Finite and Deterministic DEVS (FD-DEVS) which were designated to support verification analysis.
SP-DEVS
and FD-DEVS whose expressiveness are E(SP-DEVS
)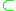 E(FD-DEVS)
E(FD-DEVS)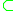 E(DEVS) where E(formalism) denotes the expressiveness of formalism.
E(DEVS) where E(formalism) denotes the expressiveness of formalism.
State transition table
In automata theory and sequential logic, a state transition table is a table showing what state a finite semiautomaton or finite state machine will move to, based on the current state and other inputs...
s, and continuous state systems which might be described by differential equation
Differential equation
A differential equation is a mathematical equation for an unknown function of one or several variables that relates the values of the function itself and its derivatives of various orders...
s, and hybrid continuous state and discrete event systems. DEVS is a timed event system
Timed event system
The General System has been described in [Zeigler76] and [ZPK00] with the stand points to define the time base, the admissible input segments, the system states, the state trajectory with an admissible input segment, the output for a given state....
.
History
DEVS is a formalism for modeling and analysis of discrete event systems (DESs). The DEVS formalism was invented by Dr. Bernard P. Zeigler, who is a professor at the University of ArizonaUniversity of Arizona
The University of Arizona is a land-grant and space-grant public institution of higher education and research located in Tucson, Arizona, United States. The University of Arizona was the first university in the state of Arizona, founded in 1885...
. DEVS was introduced to the public in Zeigler's first book, Theory of Modeling and Simulation, in 1976, while Zeigler was an associate professor at University of Michigan
University of Michigan
The University of Michigan is a public research university located in Ann Arbor, Michigan in the United States. It is the state's oldest university and the flagship campus of the University of Michigan...
. DEVS can be seen as an extension of the Moore machine
Moore machine
In the theory of computation, a Moore machine is a finite-state machine, whose output values are determined solely by its current state.-Name:The Moore machine is named after Edward F...
formalism , which is a finite state automaton where the outputs are determined by the current state alone (and do not depend directly on the input). The extension was done by
- associating a lifespan with each state [Zeigler76],
- providing a hierarchical concept with an operation, called coupling [Zeigler84].
Since the lifespan of each state is a real number (more precisely, non-negative real) or infinity, it is distinguished from discrete time systems, sequential machines, and Moore machine
Moore machine
In the theory of computation, a Moore machine is a finite-state machine, whose output values are determined solely by its current state.-Name:The Moore machine is named after Edward F...
s, in which time is determined by a tick time multiplied by non-negative integers. Moreover, the lifespan can be a random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
; for example the lifespan of a given state can be distributed exponentially
Exponential distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions. It describes the time between events in a Poisson process, i.e...
or uniformly
Uniform distribution (continuous)
In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distribution or rectangular distribution is a family of probability distributions such that for each member of the family, all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. The support is defined by...
. The state transition and output functions of DEVS can also be stochastic
Stochastic
Stochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
.
Zeigler proposed a hierarchical algorithm for DEVS model simulation in 1984 [Zeigler84] which was published in Simulation journal in 1987. Since then, many extended formalism from DEVS have been introduced with their own purposes: DESS/DEVS for combined continuous and discrete event systems, P-DEVS for parallel DESs, G-DEVS for piecewise continuous state trajectory modeling of DESs, RT-DEVS for realtime DESs, Cell-DEVS for cellular DESs, Fuzzy-DEVS for fuzzy DESs, Dynamic Structuring DEVS for DESs changing their coupling structures dynamically, and so on. In addition to its extensions, there are some subclasses such as SP-DEVS
SP-DEVS
SP-DEVS abbreviating “Schedule-Preserving Discrete Event System Specification” is a formalism for modeling and analyzing discrete event systems in both simulation and verification ways...
and FD-DEVS have been researched for achieving decidability of system properties.
Due to the modular and hierarchical modeling views, as well as its simulation-based analysis capability, the DEVS formalism and its variations have been used in many application of engineering (such as hardware design, hardware/software codesign, communications system
Communications system
In telecommunication, a communications system is a collection of individual communications networks, transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and data terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole...
s, manufacturing
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
systems) and science (such as biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
, and sociology
Sociology
Sociology is the study of society. It is a social science—a term with which it is sometimes synonymous—which uses various methods of empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge about human social activity...
)
Formalism

DEVS defines system behavior as well as system structure. System behavior in DEVS formalism is described using input and output events as well as states. For example, for the ping-pong player of Fig. 1, the input event is ?receive, and the output event is !send. Each player, A, B, has its states: Send and Wait. Send state takes 0.1 seconds to send back the ball that is the output event !send, while Wait lasts the state until the player receives the ball that is the input event ?receive.
The structure of ping-pong game is to connect two players: Player A 's output event !send is transmitted to Player B 's input event ?receive, and vice versa.
In the classic DEVS formalism, Atomic DEVS captures the system behavior, while Coupled DEVS describes the structure of system.
The following formal definition is for Classic DEVS [ZKP00]. In this article, we will use the time base,
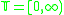 that is the set of non-negative real numbers; the extended time base,
that is the set of non-negative real numbers; the extended time base,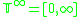 that is the set of non-negative real numbers plus infinity.
that is the set of non-negative real numbers plus infinity.Atomic DEVS
An atomic DEVS model is defined as a 7-tupleTuple
In mathematics and computer science, a tuple is an ordered list of elements. In set theory, an n-tuple is a sequence of n elements, where n is a positive integer. There is also one 0-tuple, an empty sequence. An n-tuple is defined inductively using the construction of an ordered pair...
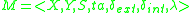
where
is the set of input events;
is the set of output events;
is the set of sequential states (or also called the set of partial states);
is the time advance function which is used to determine the lifespan of a state;
is the external transition function which defines how an input event changes a state of the system, where
is the set of total states, and
is the elapsed time since the last event;
is the internal transition function which defines how a state of the system changes internally (when the elapsed time reaches to the lifetime of the state);
is the output function where
and
is a silent event or an unobserved event. This function defines how a state of the system generates an output event (when the elapsed time reaches to the lifetime of the state);
Deterministic DEVS and Non-deterministic DEVS
Let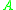 and
and 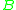 be two arbitrary sets. Then function
be two arbitrary sets. Then function 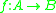 is called deterministic if for
is called deterministic if for 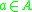 ,
, 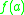 is identical any time.
is identical any time.Otherwise,
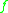 is called non-deterministic.
is called non-deterministic.A DEVS
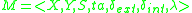 is called deterministic if
is called deterministic if 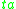 ,
, 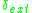 ,
, 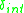 and
and 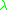
are deterministic. Otherwise,
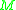 is called non-deterministic.
is called non-deterministic.The atomic DEVS Model for Ping-Pong Players
The atomic DEVS model for player A of Fig. 1 is given
Player=
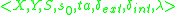
such that
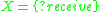
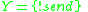
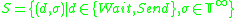
and
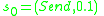
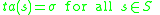
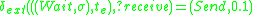
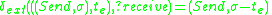
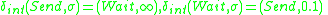
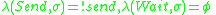
Both Player A and Player B are deterministic DEVS models.
Behavior of Atomic DEVS
Simply speaking, there are two cases that an atomic DEVS model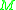 can change its state
can change its state 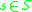 : (1) when an external input
: (1) when an external input 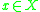 comes into the system
comes into the system 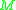 ; (2) when the elapsed time
; (2) when the elapsed time 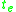 reaches the lifespan of
reaches the lifespan of  which is defined by
which is defined by 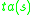 . (At the same time of (2),
. (At the same time of (2), 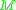 generates an output
generates an output 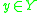 which is defined by
which is defined by 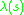 .) .
.) .For formal behavior description of given an Atomic DEVS model, refer to the page Behavior of DEVS
Behavior of DEVS
Behaviors of a given DEVS model is a set of sequences of timed events including null events, called event segments which make the model move one state to another within a set of legal states...
. Computer algorithms to implement the behavior of a given Atomic DEVS model are available at Simulation Algorithms for Atomic DEVS
Simulation Algorithms for Atomic DEVS
Given an atomic DEVS model, simulation algorithms are methods to generate the model's legal behaviors which are trajectories not to reach to illegal states....
.
Coupled DEVS
The coupled DEVS defines which sub-components belong to it and how they are connected with each other. A coupled DEVS model is defined as a 8-tupleTuple
In mathematics and computer science, a tuple is an ordered list of elements. In set theory, an n-tuple is a sequence of n elements, where n is a positive integer. There is also one 0-tuple, an empty sequence. An n-tuple is defined inductively using the construction of an ordered pair...
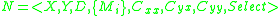
where
is the set of input events;
is the set of output events;
is the name set of sub-components;
is the set of sub-components where for each
can be either an atomic DEVS model or a coupled DEVS model.
is the set of external input couplings;
is the set of internal couplings;
is the external output coupling function;
is the tie-breaking function which defines how to select the event from the set of simultaneous events;
The coupled DEVS model for Ping-Pong Game
The ping-pong game of Fig. 1 can be modeled as an coupled DEVS model
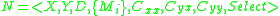 where
where 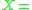 ;
;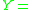 ;
;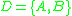 ;
; 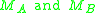 is described as above;
is described as above; 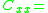 ;
; 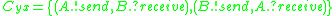 ; and
; and 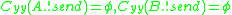 .
.Behavior of Coupled DEVS
Simply speaking, like the behavior of the atomic DEVS class, a coupled DEVS model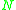 changes its components' states (1) when an external event
changes its components' states (1) when an external event 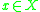 comes into
comes into 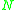 ; (2) when one of components
; (2) when one of components 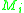 where
where 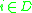 executes its internal state transition and generates its output
executes its internal state transition and generates its output 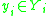 . In both cases (1) and (2), a triggering event is transmitted to all influencees which are defined by coupling sets
. In both cases (1) and (2), a triggering event is transmitted to all influencees which are defined by coupling sets 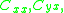 and
and 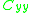 .
.For formal definition of behavior of the coupled DEVS, you can refer to Behavior of Coupled DEVS
Behavior of Coupled DEVS
DEVS is closed under coupling [Zeigper84] [ZPK00]. In other words, given a coupled DEVS model N , its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model M...
. Computer algorithms to implement the behavior of a given coupled DEVS mode are available at Simulation Algorithms for Coupled DEVS
Simulation Algorithms for Coupled DEVS
Given a coupled DEVS model, simulation algorithms are methods to generate the model's legal behaviors, which are a set of trajectories not to reach illegal states...
.
Simulation for Discrete Event Systems
The simulation algorithm of DEVS models considers two issues: time synchronization and message propagation. Time synchronization of DEVS is to control all models to have the identical current time. However, for an efficient execution, the algorithm makes the current time jump to the most urgent time when an event is scheduled to execute its internal state transition as well as its output generation. Message propagation is to transmit a triggering message which can be either an input or output event along the associated couplings which are defined in a coupled DEVS model. For more detailed information, the reader can refer to Simulation Algorithms for Atomic DEVSSimulation Algorithms for Atomic DEVS
Given an atomic DEVS model, simulation algorithms are methods to generate the model's legal behaviors which are trajectories not to reach to illegal states....
and Simulation Algorithms for Coupled DEVS
Simulation Algorithms for Coupled DEVS
Given a coupled DEVS model, simulation algorithms are methods to generate the model's legal behaviors, which are a set of trajectories not to reach illegal states...
.
Simulation for Continuous State Systems
By introducing a quantization method which abstracts a continuous segment as a piecewise const segment, DEVS can simulate behaviors of continuous state systems which are described by networks of differential algebraic equations. This research has been initiated by Zeigler in 90's and many properties have been clarified by Prof. Kofman in 2000's and Dr. Nutaro. In 2006, Prof. Cellier who is the author of Continuous System Modeling[Cellier91], and Prof. Kofman wrote a text book, Continuous System Simulation[CK06] in which Chapters 11 and 12 cover how DEVS simulates continuous state systems. Dr. Nutaro's book [Nutaro10], covers the discrete event simulation of continuous state systems too.Verification for Discrete Event Systems
As an alternative analysis method against the sampling-based simulation method, an exhaustive generating behavior approach, generally called verification has been applied for analysis of DEVS models. It is proven that infinite states of a given DEVS model (especially a coupled DEVS model ) can be abstracted by behaviorally isomorphic finite structre, called a reachability graph when the given DEVS model is a sub-class of DEVS such as Schedule-Preserving DEVS (SP-DEVSSP-DEVS
SP-DEVS abbreviating “Schedule-Preserving Discrete Event System Specification” is a formalism for modeling and analyzing discrete event systems in both simulation and verification ways...
) and Finite & Deterministic DEVS (FD-DEVS) [HZ09]. As a result, based on the rechability graph, (1) dead-lock and live-lock freeness as qualitative properties are decidable with SP-DEVS [Hwang05] and FD-DEVS [HZ06], and (2) min/max processing time bounds as a quantitative property are decidable with SP-DEVS so far by 2009.
Extensions (Superclassing)
Numerous extensions of the classic DEVS formalism have been developed in the last decades.Among them formalisms which allow to have changing model structures while the simulation time evolves.
G-DEVS, Parallel DEVS, Dynamic Structuring DEVS, Cell-DEVS [Wainer09], dynDEVS, Fuzzy-DEVS, GK-DEVS, ml-DEVS, Symbolic DEVS, Real-Time DEVS, rho-DEVS
Restrictions (Subclassing)
There are some sub-classes known as Schedule-Preserving DEVS (SP-DEVSSP-DEVS
SP-DEVS abbreviating “Schedule-Preserving Discrete Event System Specification” is a formalism for modeling and analyzing discrete event systems in both simulation and verification ways...
) and Finite and Deterministic DEVS (FD-DEVS) which were designated to support verification analysis.
SP-DEVS
SP-DEVS
SP-DEVS abbreviating “Schedule-Preserving Discrete Event System Specification” is a formalism for modeling and analyzing discrete event systems in both simulation and verification ways...
and FD-DEVS whose expressiveness are E(SP-DEVS
SP-DEVS
SP-DEVS abbreviating “Schedule-Preserving Discrete Event System Specification” is a formalism for modeling and analyzing discrete event systems in both simulation and verification ways...
)
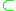 E(FD-DEVS)
E(FD-DEVS)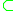 E(DEVS) where E(formalism) denotes the expressiveness of formalism.
E(DEVS) where E(formalism) denotes the expressiveness of formalism.DEVS Related Articles
- Event Segment
- Timed Event SystemTimed event systemThe General System has been described in [Zeigler76] and [ZPK00] with the stand points to define the time base, the admissible input segments, the system states, the state trajectory with an admissible input segment, the output for a given state....
- Verifiable sub-classes of DEVS: SP-DEVSSP-DEVSSP-DEVS abbreviating “Schedule-Preserving Discrete Event System Specification” is a formalism for modeling and analyzing discrete event systems in both simulation and verification ways...
, FD-DEVS - Behavior of Atomic DEVS
- Behavior of Coupled DEVSBehavior of Coupled DEVSDEVS is closed under coupling [Zeigper84] [ZPK00]. In other words, given a coupled DEVS model N , its behavior is described as an atomic DEVS model M...
- Simulation Algorithms for Atomic DEVSSimulation Algorithms for Atomic DEVSGiven an atomic DEVS model, simulation algorithms are methods to generate the model's legal behaviors which are trajectories not to reach to illegal states....
- Simulation Algorithms for Coupled DEVSSimulation Algorithms for Coupled DEVSGiven a coupled DEVS model, simulation algorithms are methods to generate the model's legal behaviors, which are a set of trajectories not to reach illegal states...
Other Formalisms
- Automata TheoryAutomata theoryIn theoretical computer science, automata theory is the study of abstract machines and the computational problems that can be solved using these machines. These abstract machines are called automata...
: a formal method for state transition systems - Finite State MachineFinite state machineA finite-state machine or finite-state automaton , or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model used to design computer programs and digital logic circuits. It is conceived as an abstract machine that can be in one of a finite number of states...
: a state transition machine with finite sets of events and states - Petri Nets: a graphical representation of state and transition relations
- Markov ChainMarkov chainA Markov chain, named after Andrey Markov, is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another, between a finite or countable number of possible states. It is a random process characterized as memoryless: the next state depends only on the current state and not on the...
: a stochasticStochasticStochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
process in which the future will be determined by the current
External links to DEVS Research Groups
Alphabetical Order- DEVS Standardization Group: http://cell-devs.sce.carleton.ca/devsgroup/
- DEVS Study Group: http://tech.groups.yahoo.com/group/DEVSTD/
- DEVS Tools: http://cell-devs.sce.carleton.ca/devsgroup/?q=node/8
- Dr. Barros' Lab at Universidade de Coimbra: http://eden.dei.uc.pt/~barros/
- Dr. Giambiasi's Lab at Laboratoire des Sciences de I'Information et des Systemes (LSIS): http://www.lsis.org/fiche.php?id=72&page=&afficher=&presentation_publis=&processus=ok
- Dr. Hu's Lab at Georgia State University: http://www.cs.gsu.edu/~cscxlh/
- Dr. Hwang's Homepage: http://moonho.hwang.googlepages.com/
- Dr. Jamshidi's Virtual Laboratory for Autonomous Agents at University of New Mexico: http://vlab.unm.edu/
- Dr. Kim's Systems Modeling Simulation Lab at KAIST: http://smslab.kaist.ac.kr/
- Dr. Kofman's Laboratory for System Dynamics and Signal Processing at Universidad Nacional de Rosario: http://www.fceia.unr.edu.ar/lsd/
- Dr. Mittal's startup Dunip Technologies: http://www.duniptechnologies.com
- Dr. Tolk's Interoperability and Composability Research Group at the Virginia Modeling, Analysis and Simulation Center
- Dr. Uhrmacher's Modeling and Simulation Group at University of Rostock: http://wwwmosi.informatik.uni-rostock.de/mosi
- Dr. Vangheluwe's Modeling, Simulation & Design Lab at McGill University: http://msdl.cs.mcgill.ca/
- Dr. Wainer's Lab at Carleton University: http://www.sce.carleton.ca/faculty/wainer/ (Lab).
- Dr. Zeigler and Dr. Sarjoughian's Arizona Center for Integrative Modeling and Simulation (ACIMS): http://www.acims.arizona.edu
- Dr. Zhang's Homepage: http://www.ece.arizona.edu/~mingz/
DEVS Tools
- adevs: A C++ library for constructing discrete event simulations based on the Parallel DEVS and Dynamic DEVS (dynDEVS) formalisms
- CD++ An environment for development of DEVS and Cellular DEVS formalisms.
- CD++Modeler A graphical interface for modeling DEVS and Cell-DEVS applications (with source code).
- CD++Builder An Eclipse Plugin for developing DEVS and Cell-DEVS models (with source code).
- CoSMo-Sim: A unified logical, visual, and persistence environment for specifying families of DEVS, Cellular Automata, and XML models. It supports simulation of parallel DEVS models [open source at SourceForge].
- DEVS++: C++ Open Source Library of DEVS Formalism for simulation analysis
- DEVS#: C# Open Source Library of DEVS Formalism for simulation and verification analysis
- DEVS/C++ Implementation of Parallel DEVS in C++.
- DEVS/HLA/CORBA Extends DEVSJAVA and DEVS-C++ with HLA and CORBA.
- DEVSJAVA It supports Parallel DEVS models with software real-time, variable structure, 2D/3D cellular automata, and animation.
- DEVSim++
- DEVS-Suite Next generation of DEVSJAVA supporting integrated automated design of experiments, run-time data trajectory plotting, and animation with multiple degrees of control for simulation execution, plotting, and animation speeds [open source at SourceForge]
- GALATEA
- JAMES II M&S Framework for many different formalisms including PDEVS and ml-DEVS.
- JDEVS
- LSIS DME
- Mimosa
- PF3S
- PowerDEVSPowerDEVSPowerDEVS is a general purpose software tool for DEVS [Zeigler76] modeling and simulation oriented to the simulation of hybrid systems. The environment allows defining atomic DEVS models in C++ language that can be then graphically coupled in hierarchical block diagrams to create more complex...
A general purpose software tool for DEVS modeling and simulation oriented to the simulation of hybrid systems - Python DEVS
- SimBeans
- SmallDEVS
- VLE An environment and C++ libraries for development of DEVS, Cellular DEVS, DESS, QSS, Celluar QSS, Petri net and UML Statechart formalisms.

