
Tokyo dialect
Encyclopedia
refers to the Japanese
dialect
spoken in modern Tokyo
. The dialect in modern Tokyo is often considered to equate standard Japanese, though in fact the Tokyo dialect differs from standard Japanese in a number of areas.
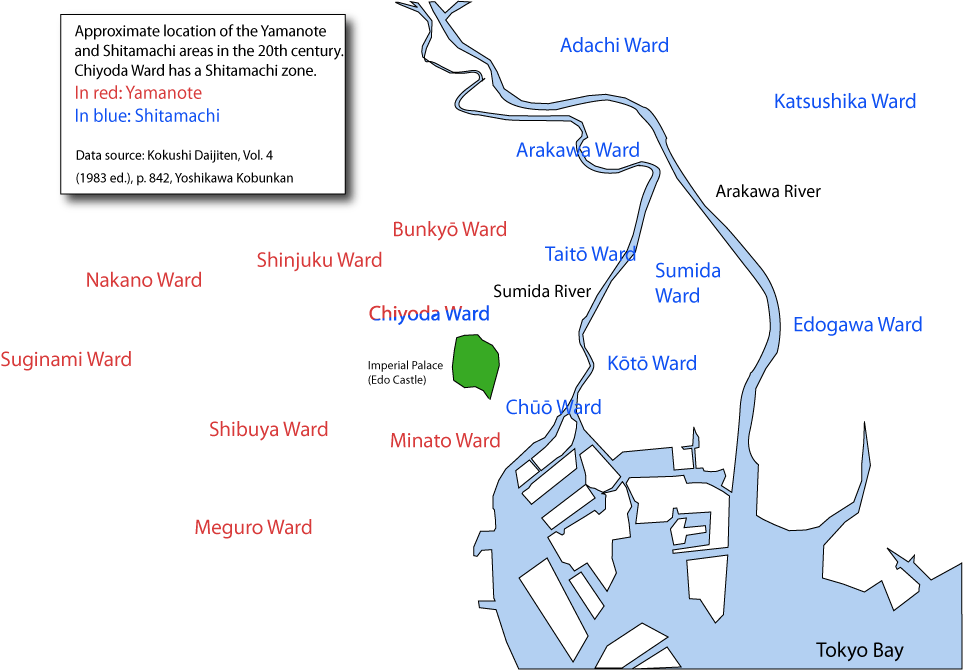
. The Shitamachi dialect is a frank dialect of old working-class from Shitamachi area. The Shitamachi dialect keeps features of Edo
Chōnin
(Edokko
) speech, so also called . Tokyo style rakugo
is typically played in Shitamachi dialect. Roughly speaking, the difference between Yamanote dialect and Shitamachi dialect looks like the difference between RP
and Cockney
in English
.
The origin of Tokyo dialect dates back to the establishment of Edo by Tokugawa Ieyasu
. With the establishment of Edo, people gathered from all over the nation and various dialects brought. The Kyoto dialect was the de facto standard Japanese and had strong influence on the formation of Edo dialect in the early Edo period
, but Edo grew the largest city in Japan and became the new de facto standard Japanese in the late Edo period. Because of its unique history, especially relations with Kyoto dialect, Tokyo is a language island in Kantō region
. For example, traditional Kanto dialects have been characterized by the use of volitional and presumptive suffix -be, but it is hardly used in Tokyo.
) and shujutsu ("operation") becomes shijitsu.
Another notable trait is the diphthong
change [ai] [ae] [ie] [oi] to [ɛː] in the Shitamachi dialect. For example, hidoi ("terrible") become shidee and taihen da ("It's serious") become teehen da. This feature is inherited in standard Japanese as informal masculine speech like wakan'nee (< wakaranai "I don't know") and sugee (< sugoi "great").
In addition, [ɽ] is realized as a trill
[r], when conveying a vulgar nuance in Shitamachi speech. In informal speech, intervocalic [ɽ] is often changed [ɴ] or sokuon
such as okaerinasai becomes okaen'nasai ("welcome back home") and sō suru to becomes sō sutto ("then, and so").
sa, which is roughly analogous to "like" as used in American English slang; tsū (common style) and tee (Shitamachi style) in place of to iu ("to say" or "is called"); the frequent use of emphasis sentence-final particle dai or dee in Shitamachi, which is famous for a typical Shitamachi verbal shot teyandee! (< [nani o] itte iyagaru n dai!, "What are you talking about!?").
Historically, Kanto dialects were lacking keigo (honorific speech). However, because of connection with Kyoto and urbanize with stratified society, the Tokyo dialect has refined keigo system. The Yamanote dialect is primarily known for an extreme use of keigo and characterized by a keigo copula zamasu or zāmasu, sometimes zansu, transformations of gozaimasu. The feminine courtesy imperative mood asobase or asubase is also well-known keigo of traditional Tokyo dialect. For example, "Won't you please wait for me?" equivalents for o-machi kudasai in standard Japanese, and o-machi asobase in traditional Tokyo dialect.
such as oppajimeru for hajimeru meaning "to start" and so on. Atashi is a feminine first person in standard Japanese, but in Shitamachi dialect, it is often used by both men and women.
Many people flock to Tokyo from other regions, they sometimes bring their dialects into Tokyo as well as in the Edo period. For example, jan (じゃん), which is a contraction of ja nai ka ("isn't that right?") came from the eastern Chūbu
and Kanagawa
dialects; and chigakatta, which is non-standard form of chigatta ("it was different") came from the Fukushima
and Tochigi
dialects.
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
dialect
Japanese dialects
The comprise many regional variants. The lingua franca of Japan is called hyōjungo or kyōtsūgo , and while it was based initially on the Tokyo dialect, the language of Japan's capital has since gone in its own direction to become one of Japan's many dialects...
spoken in modern Tokyo
Tokyo
, ; officially , is one of the 47 prefectures of Japan. Tokyo is the capital of Japan, the center of the Greater Tokyo Area, and the largest metropolitan area of Japan. It is the seat of the Japanese government and the Imperial Palace, and the home of the Japanese Imperial Family...
. The dialect in modern Tokyo is often considered to equate standard Japanese, though in fact the Tokyo dialect differs from standard Japanese in a number of areas.

Overview
Traditional dialects in downtown of Tokyo can roughly classify into two groups, and . The Yamanote dialect is a well-mannered dialect of old upper-class from Yamanote area. Standard Japanese was built around the Yamanote dialect in Meiji periodMeiji period
The , also known as the Meiji era, is a Japanese era which extended from September 1868 through July 1912. This period represents the first half of the Empire of Japan.- Meiji Restoration and the emperor :...
. The Shitamachi dialect is a frank dialect of old working-class from Shitamachi area. The Shitamachi dialect keeps features of Edo
Edo
, also romanized as Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of the Japanese capital Tokyo, and was the seat of power for the Tokugawa shogunate which ruled Japan from 1603 to 1868...
Chōnin
Chonin
was a social class that emerged in Japan during the early years of the Tokugawa period. The majority of chōnin were merchants, but some were craftsmen, as well. Nōmin were not considered chōnin...
(Edokko
Edokko
is a Japanese term referring to a person born and raised in Edo . The term is believed to have been coined in the late 18th century in Edo. Being an Edokko also implied that the person had certain personality traits different from the non-native population, such as being assertive, straightforward,...
) speech, so also called . Tokyo style rakugo
Rakugo
is a Japanese verbal entertainment. The lone sits on the stage, called the . Using only a paper fan and a small cloth as props, and without standing up from the seiza sitting position, the rakugo artist depicts a long and complicated comical story...
is typically played in Shitamachi dialect. Roughly speaking, the difference between Yamanote dialect and Shitamachi dialect looks like the difference between RP
Received Pronunciation
Received Pronunciation , also called the Queen's English, Oxford English or BBC English, is the accent of Standard English in England, with a relationship to regional accents similar to the relationship in other European languages between their standard varieties and their regional forms...
and Cockney
Cockney
The term Cockney has both geographical and linguistic associations. Geographically and culturally, it often refers to working class Londoners, particularly those in the East End...
in English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
.
The origin of Tokyo dialect dates back to the establishment of Edo by Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first shogun of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan , which ruled from the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. Ieyasu seized power in 1600, received appointment as shogun in 1603, abdicated from office in 1605, but...
. With the establishment of Edo, people gathered from all over the nation and various dialects brought. The Kyoto dialect was the de facto standard Japanese and had strong influence on the formation of Edo dialect in the early Edo period
Edo period
The , or , is a division of Japanese history which was ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family, running from 1603 to 1868. The political entity of this period was the Tokugawa shogunate....
, but Edo grew the largest city in Japan and became the new de facto standard Japanese in the late Edo period. Because of its unique history, especially relations with Kyoto dialect, Tokyo is a language island in Kantō region
Kanto region
The is a geographical area of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. The region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures: Gunma, Tochigi, Ibaraki, Saitama, Tokyo, Chiba, and Kanagawa. Within its boundaries, slightly more than 40 percent of the land area is the Kantō Plain....
. For example, traditional Kanto dialects have been characterized by the use of volitional and presumptive suffix -be, but it is hardly used in Tokyo.
Phonology
The Shitamachi dialect is primarily known for its lack of distinction between some phonemes which are considered wholly distinct in standard Japanese. Most famous is the decreased distinction between [çi] and [ʃi], so that shiohigari ("shellfish gathering") becomes shioshigari and shichi ("seven") becomes hichi. Another famous is that change [ʃɯ] [ʤɯ] to [ʃi] [ʤi], so that Shinjuku becomes Shinjiku (ShinjukuShinjuku, Tokyo
is one of the 23 special wards of Tokyo, Japan. It is a major commercial and administrative center, housing the busiest train station in the world and the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Building, the administration center for the government of Tokyo.As of 2008, the ward has an estimated population...
) and shujutsu ("operation") becomes shijitsu.
Another notable trait is the diphthong
Diphthong
A diphthong , also known as a gliding vowel, refers to two adjacent vowel sounds occurring within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: That is, the tongue moves during the pronunciation of the vowel...
change [ai] [ae] [ie] [oi] to [ɛː] in the Shitamachi dialect. For example, hidoi ("terrible") become shidee and taihen da ("It's serious") become teehen da. This feature is inherited in standard Japanese as informal masculine speech like wakan'nee (< wakaranai "I don't know") and sugee (< sugoi "great").
In addition, [ɽ] is realized as a trill
Trill consonant
In phonetics, a trill is a consonantal sound produced by vibrations between the articulator and the place of articulation. Standard Spanish <rr> as in perro is an alveolar trill, while in Parisian French it is almost always uvular....
[r], when conveying a vulgar nuance in Shitamachi speech. In informal speech, intervocalic [ɽ] is often changed [ɴ] or sokuon
Sokuon
The is a Japanese symbol consisting of a small hiragana or katakana tsu. In less formal language it is called or , meaning "little tsu". Compare to a full-sized tsu:The sokuon is used for various purposes...
such as okaerinasai becomes okaen'nasai ("welcome back home") and sō suru to becomes sō sutto ("then, and so").
Pitch accent
A few words are pronounced different pitch accent between Yamanote and Shitamachi. The following words are typical examples.- Bandō (another name of Kantō region) - Accent on ba in Yamanote, Accentless in Shitamachi.
- saka ("slope") - Accent on ka in Yamanote, Accent on sa in Shitamachi.
- tsugi ("next") - Accent on gi in Yamanote, Accent on tsu in Shitamachi.
- sushi - Accent on shi in Yamanote, Accent on su in Shitamachi.
- suna ("sand") - Accentless in Yamanote, Accent on na in Shitamachi.
- asahi ("morning sun") - Accent on a in Yamanote, Accent on sa in Shitamachi.
- aniki ("big brother") - Accent on a in Yamanote, Accent on ni in Shitamachi.
- itsumo ("always") - Accent on i in Yamanote, Accent on tsu in Shitamachi.
- hanashi ("talk") - Accentless in Yamanote, Accent on na mora in Shitamachi.
- tamago ("egg") - Accent on ma in Yamanote, Accentless in Shitamachi.
- accentless word -sama (a honorificJapanese honorificsThe Japanese language has many honorifics, parts of speech which show respect, and their use is mandatory in many social situations. Honorifics in Japanese may be used to emphasize social distance or disparity in rank, or to emphasize social intimacy or similarity in rank.The system of honorifics...
) - Accent on sa in Yamanote, Accentless in Shitamachi.
Grammar
Most of grammatical features of Tokyo dialect are treated as the colloquial form of standard Japanese like examples mentioned in "Colloquial contractions" in the article "Japanese grammar". Noticeable earmarks of the Tokyo dialect include the frequent use of interjectory particleJapanese particles
Japanese particles, or , are suffixes or short words in Japanese grammar that immediately follow the modified noun, verb, adjective, or sentence. Their grammatical range can indicate various meanings and functions, such as speaker affect and assertiveness....
sa, which is roughly analogous to "like" as used in American English slang; tsū (common style) and tee (Shitamachi style) in place of to iu ("to say" or "is called"); the frequent use of emphasis sentence-final particle dai or dee in Shitamachi, which is famous for a typical Shitamachi verbal shot teyandee! (< [nani o] itte iyagaru n dai!, "What are you talking about!?").
Historically, Kanto dialects were lacking keigo (honorific speech). However, because of connection with Kyoto and urbanize with stratified society, the Tokyo dialect has refined keigo system. The Yamanote dialect is primarily known for an extreme use of keigo and characterized by a keigo copula zamasu or zāmasu, sometimes zansu, transformations of gozaimasu. The feminine courtesy imperative mood asobase or asubase is also well-known keigo of traditional Tokyo dialect. For example, "Won't you please wait for me?" equivalents for o-machi kudasai in standard Japanese, and o-machi asobase in traditional Tokyo dialect.
Vocabulary
Though it also includes a few distinctive words, today it is largely indistinguishable from the standard speech of Tokyo other than the phonemic difference. Famous Shitamachi words are a swearword berabōme! or beranmee! (masculine Shitamachi speech is commonly known as Beranmee kuchō or "Beranmee tone"), atabō for atarimae meaning "of course" and an emphasis prefix o + sokuonSokuon
The is a Japanese symbol consisting of a small hiragana or katakana tsu. In less formal language it is called or , meaning "little tsu". Compare to a full-sized tsu:The sokuon is used for various purposes...
such as oppajimeru for hajimeru meaning "to start" and so on. Atashi is a feminine first person in standard Japanese, but in Shitamachi dialect, it is often used by both men and women.
New Tokyo dialect
Traditional Tokyo dialects are now barely used as most families living in Tokyo speak standard Japanese or standardization Tokyo dialect. The difference between Shitamachi and Yamanote becomes almost extinct.Many people flock to Tokyo from other regions, they sometimes bring their dialects into Tokyo as well as in the Edo period. For example, jan (じゃん), which is a contraction of ja nai ka ("isn't that right?") came from the eastern Chūbu
Chubu region
The is the central region of Honshū, Japan's main island. Chūbu has a population estimate of 21,886,324 as of 2008.Chūbu, which means "central region", encompasses nine prefectures : Aichi, Fukui, Gifu, Ishikawa, Nagano, Niigata, Shizuoka, Toyama, Yamanashi, and often Mie.It is located directly...
and Kanagawa
Kanagawa Prefecture
is a prefecture located in the southern Kantō region of Japan. The capital is Yokohama. Kanagawa is part of the Greater Tokyo Area.-History:The prefecture has some archaeological sites going back to the Jōmon period...
dialects; and chigakatta, which is non-standard form of chigatta ("it was different") came from the Fukushima
Fukushima Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region on the island of Honshu. The capital is the city of Fukushima.-History:Until the Meiji Restoration, the area of Fukushima prefecture was known as Mutsu Province....
and Tochigi
Tochigi Prefecture
is a prefecture located in the Kantō region on the island of Honshū, Japan. The capital is the city of Utsunomiya.Nikkō, whose ancient Shintō shrines and Buddhist temples UNESCO has recognized by naming them a World Heritage Site, is in this prefecture...
dialects.

