Tonometry
Encyclopedia
Tonometry is the procedure eye care professional
s perform to determine the intraocular pressure
(IOP), the fluid pressure
inside the eye
. It is an important test in the evaluation of patients at risk from glaucoma
. Most tonometers are calibrated to measure pressure in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).

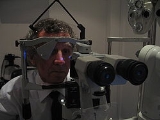
Applanation tonometry
In applanation tonometry the intraocular pressure is inferred from the force required to flatten (applanate) a constant area of the cornea, as per the Imbert-Fick law
. The Maklakoff was an early example of this method, while the Goldmann tonometer is the most widely used version in current practice. Because the probe makes contact with the cornea, a topical anesthetic
, such as proxymetacaine
is introduced on to the surface of the eye in the form of an eye drop
s.
Goldmann tonometry
Goldmann tonometry is considered to be the gold standard
test and is the most widely accepted method. A special disinfected prism is mounted on the tonometer head and then placed against the cornea. The examiner then uses a cobalt blue filter to view two green semi circles. The force applied to the tonometer head is then adjusted using a dial connected to a variable tension spring until the inner edges of the green semicircles in the viewfinder meet. When an area of 3.06mm has been flattened, the opposing forces of corneal rigidity and the tear film are roughly approximate and cancel each other out allowing the pressure in the eye to be determined from the force applied. Like all non-invasive methods, it is inherently imprecise.
Perkins tonometer
The Perkins is a type of portable applanation tonometer, useful in children, patients unable to co-operate with a sitting slit lamp examination or in anesthetised patients who need to lie flat.
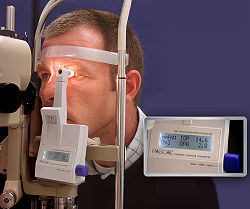
Dynamic Contour tonometry
Dynamic contour tonometry (DCT)(PASCAL Tonometer)uses the principle of contour matching instead of applanation. The tip contains a hollow the same shape as the cornea with a miniature pressure sensor
in its centre. In contrast to applanation tonometry it is designed to avoid deforming the cornea during measurement and is therefore thought to be less influenced by corneal thickness and other biomechanical properties of the cornea than other methods but because the tip shape is designed for the shape of a normal cornea, it is more influenced by corneal curvature.
The probe is placed on the pre-corneal tear film on the central cornea (see gallery) and the integrated piezoresistive
pressure sensor
automatically begins to acquire data, measuring IOP 100 times per second. The tonometer tip rests on the cornea with a constant appositional force of one gram. When the sensor is subjected to a change in pressure, the electrical resistance is altered and the PASCAL's computer calculates a change in pressure according to the change in resistance. A complete measurement cycle requires about 8 seconds of contact time. The device also measures the variation in pressure that occurs with the cardiac cycle.
Non-contact tonometry
Non-contact tonometry (or air-puff tonometry) is different from pneumatonometry and was invented by Bernard Grolman of Reichert, Inc (formerly American Optical). It uses a rapid air pulse to applanate (flatten) the cornea. Corneal applanation is detected via an electro-optical system. Intraocular pressure is estimated by detecting the force of the air jet at the instance of applanation. Historically, Non-contact tonometers were not considered to be an accurate way to measure IOP but instead a fast and simple way to screen for high IOP. However, modern non-contact tonometers have been shown to correlate well with Goldmann tonometry measurements and are particularly useful for measuring IOP in children and other non-compliant patient groups.
Ocular response analyzer
The ocular response analyser (ORA) is a non-contact (air puff) tonometer that does not require topical anaesthesia and provides additional information on the biomechanical properties of the cornea. It uses an air pulse to deform the cornea in to a slight concavity. The difference between the pressures at which the cornea flattens inward and outward is measured by the machine and termed corneal hysteresis (CH). The machine uses this value to correct for the effects of the cornea on measurement.
Electronic indentation tonometry
The Tono-Pen (Reichert, Inc) and AccuPen (Accutome, Inc) are modified Mackay-Marg tonometers that use a free floating transducer to detect the transmitted pressure. The transducer is surrounded by an outer ring that flattens the adjacent cornea reducing its influence on measurement. Because the device touches the cornea, Topical anesthetic
eye drop
s are used to numb the eye but as with non-contact tonometry, these devices are often used in children and non-cooperative patients because of their portability and ease of use. Portable electronic tonometers also play a major role in veterinary tonometry.
Rebound tonometry
Rebound tonometers (Icare Tonometer ) determine intraocular pressure by bouncing a small plastic tipped metal probe against the cornea. The device uses an induction coil to magnetise the probe and fire it against the cornea. As the probe bounces against the cornea and back in to the device, it creates an induction current from which the intraocular pressure is calculated. The device is simple and easy to use and self use versions are available. It is portable, does not require the use of eye drops and is particularly suitable for children and non-cooperative patients.
Pneumatonometry
A pneumatonometer utilizes a pneumatic sensor (consisting of a piston floating on an air bearing). Filtered air is pumped into the piston and travels through a small (5-mm dia.) fenestrated membrane at one end. This membrance is placed against the cornea. The balance between the flow of air from the machine and the resistance to flow from the cornea affect the movement of the piston and this movement is used to calculate the intra-ocular pressure.
Impression tonometry
Impression tonometry (also known as indentation tonometry) measures the depth of corneal indentation made by a small plunger carrying a known weight. The higher the intraocular pressure, the harder it is to push against and indent the cornea. For very high levels of IOP, extra weights can be added to make the plunger push harder. The movement of the plunger is measured using a calibrated scale. The Schiötz tonometry is the most common device to use this principle.
Non-corneal and Transpalpebral tonometry
Diaton tonometer (BiCOM, Inc) Transpalpebral tonometry refers to methods of measuring intraocular pressure through the Eyelid
. The Diaton non-corneal tonometer calculates pressure by measuring the response of a free falling rod, as it rebounds against the tarsal plate of the eyelid through the sclera
. The patient is positioned so that the tip of the device and lid are overlying sclera. Non-corneal and transpalpebral tonometry does not involve contact with the cornea
and does not require topical anesthetic
during routine use. The tonometer is not a substitute or alternative for more established methods.
Palpation
Palpation (also known as digital tonometry) is the method of estimating intraocular pressure by gently pressing your index finger against the cornea of a closed eye. This method is notoriously unreliable.
OCT Tonometry
Non-contact tonometry using optical coherence tomography
(OCT) is currently under development. Like many other forms of tonometry, this methodology relies on a force being applied to the cornea and simultaneous measurement of the corneal reaction. In the case of OCT tonometry, the force applied to the cornea can be air pressure in the form of a high pressure jet (like air-puff tonometry), a shock or acoustic wave, or low pressure air using air pumped into a sealed chamber around the eye (like a snorkeling or scuba mask). The OCT device is used to measure changes in the curvature of the cornea or movement of the apical corneal interface. This deflection can be compared to the pressure measured around the eye and corrected for corneal thickness and potentially, corneal hysteresis.
The thickness of the cornea affects most non-invasive methods by varying resistance to the tonometer probe. A thick cornea gives rise to a greater probability of an IOP being over-estimated (and a thin cornea of an IOP being under-estimated), but the extent of measurement error in individual patients cannot be ascertained from the CCT alone. The Ocular Response Analyzer and Pascal DCT Tonometers are less affected by CCT than the Goldmann tonometer. Conversley, Non-contact and rebound tonometers are more affected. Corneal thickness varies among individuals as well as with age and race. It is reduced in certain disease and following LASIK surgery.
Eye care professional
An eye care professional is an individual who provides a service related to the eyes or vision. It is a general term that can refer to any healthcare worker involved in eye care, from one with a small amount of post-secondary training to practitioners with a doctoral level of education.-Current...
s perform to determine the intraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure is the fluid pressure inside the eye. Tonometry is the method eye care professionals use to determine this. IOP is an important aspect in the evaluation of patients at risk from glaucoma...
(IOP), the fluid pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
inside the eye
Eye
Eyes are organs that detect light and convert it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons. The simplest photoreceptors in conscious vision connect light to movement...
. It is an important test in the evaluation of patients at risk from glaucoma
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye disorder in which the optic nerve suffers damage, permanently damaging vision in the affected eye and progressing to complete blindness if untreated. It is often, but not always, associated with increased pressure of the fluid in the eye...
. Most tonometers are calibrated to measure pressure in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
Methods



Applanation tonometry
In applanation tonometry the intraocular pressure is inferred from the force required to flatten (applanate) a constant area of the cornea, as per the Imbert-Fick law
Imbert-Fick law
The Imbert-Fick "law" was invented by Hans Goldmann to give his newly marketed tonometer a quasi-scientific basis; it is mentioned in the ophthalmic and optometric literature, but not in any books of physics...
. The Maklakoff was an early example of this method, while the Goldmann tonometer is the most widely used version in current practice. Because the probe makes contact with the cornea, a topical anesthetic
Topical anesthetic
A topical anesthetic is a local anesthetic that is used to numb the surface of a body part. They can be used to numb any area of the skin as well as the front of the eyeball, the inside of the nose, ear or throat, the anus and the genital area. Topical anesthetics are available in creams,...
, such as proxymetacaine
Proxymetacaine
Proxymetacaine or proparacaine is a topical anesthetic drug of the aminoester group.-Indications and usage:Proxymetacaine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution is indicated for procedures such as tonometry, gonioscopy, removal of foreign bodies, or other similar procedures requiring topical...
is introduced on to the surface of the eye in the form of an eye drop
Eye drop
Eye drops are saline-containing drops used as a route to administer medication in the eye. Depending on the condition being treated, they may contain steroids, antihistamines, sympathomimetics, beta receptor blockers, parasympathomimetics, parasympatholytics, prostaglandins, non-steroidal...
s.
Goldmann tonometry
Goldmann tonometry is considered to be the gold standard
Gold standard (test)
In medicine and statistics, gold standard test refers to a diagnostic test or benchmark that is the best available under reasonable conditions. It does not have to be necessarily the best possible test for the condition in absolute terms...
test and is the most widely accepted method. A special disinfected prism is mounted on the tonometer head and then placed against the cornea. The examiner then uses a cobalt blue filter to view two green semi circles. The force applied to the tonometer head is then adjusted using a dial connected to a variable tension spring until the inner edges of the green semicircles in the viewfinder meet. When an area of 3.06mm has been flattened, the opposing forces of corneal rigidity and the tear film are roughly approximate and cancel each other out allowing the pressure in the eye to be determined from the force applied. Like all non-invasive methods, it is inherently imprecise.
Perkins tonometer
The Perkins is a type of portable applanation tonometer, useful in children, patients unable to co-operate with a sitting slit lamp examination or in anesthetised patients who need to lie flat.
Dynamic Contour tonometry
Dynamic contour tonometry (DCT)(PASCAL Tonometer)uses the principle of contour matching instead of applanation. The tip contains a hollow the same shape as the cornea with a miniature pressure sensor
Pressure sensor
A pressure sensor measures pressure, typically of gases or liquids. Pressure is an expression of the force required to stop a fluid from expanding, and is usually stated in terms of force per unit area. A pressure sensor usually acts as a transducer; it generates a signal as a function of the...
in its centre. In contrast to applanation tonometry it is designed to avoid deforming the cornea during measurement and is therefore thought to be less influenced by corneal thickness and other biomechanical properties of the cornea than other methods but because the tip shape is designed for the shape of a normal cornea, it is more influenced by corneal curvature.
The probe is placed on the pre-corneal tear film on the central cornea (see gallery) and the integrated piezoresistive
Piezoresistive effect
The piezoresistive effect describe the changing resistivity of a semiconductor due to applied mechanical stress. The piezoresistive effect differs from the piezoelectric effect...
pressure sensor
Pressure sensor
A pressure sensor measures pressure, typically of gases or liquids. Pressure is an expression of the force required to stop a fluid from expanding, and is usually stated in terms of force per unit area. A pressure sensor usually acts as a transducer; it generates a signal as a function of the...
automatically begins to acquire data, measuring IOP 100 times per second. The tonometer tip rests on the cornea with a constant appositional force of one gram. When the sensor is subjected to a change in pressure, the electrical resistance is altered and the PASCAL's computer calculates a change in pressure according to the change in resistance. A complete measurement cycle requires about 8 seconds of contact time. The device also measures the variation in pressure that occurs with the cardiac cycle.
Non-contact tonometry
Non-contact tonometry (or air-puff tonometry) is different from pneumatonometry and was invented by Bernard Grolman of Reichert, Inc (formerly American Optical). It uses a rapid air pulse to applanate (flatten) the cornea. Corneal applanation is detected via an electro-optical system. Intraocular pressure is estimated by detecting the force of the air jet at the instance of applanation. Historically, Non-contact tonometers were not considered to be an accurate way to measure IOP but instead a fast and simple way to screen for high IOP. However, modern non-contact tonometers have been shown to correlate well with Goldmann tonometry measurements and are particularly useful for measuring IOP in children and other non-compliant patient groups.
Ocular response analyzer
The ocular response analyser (ORA) is a non-contact (air puff) tonometer that does not require topical anaesthesia and provides additional information on the biomechanical properties of the cornea. It uses an air pulse to deform the cornea in to a slight concavity. The difference between the pressures at which the cornea flattens inward and outward is measured by the machine and termed corneal hysteresis (CH). The machine uses this value to correct for the effects of the cornea on measurement.
Electronic indentation tonometry
The Tono-Pen (Reichert, Inc) and AccuPen (Accutome, Inc) are modified Mackay-Marg tonometers that use a free floating transducer to detect the transmitted pressure. The transducer is surrounded by an outer ring that flattens the adjacent cornea reducing its influence on measurement. Because the device touches the cornea, Topical anesthetic
Topical anesthetic
A topical anesthetic is a local anesthetic that is used to numb the surface of a body part. They can be used to numb any area of the skin as well as the front of the eyeball, the inside of the nose, ear or throat, the anus and the genital area. Topical anesthetics are available in creams,...
eye drop
Eye drop
Eye drops are saline-containing drops used as a route to administer medication in the eye. Depending on the condition being treated, they may contain steroids, antihistamines, sympathomimetics, beta receptor blockers, parasympathomimetics, parasympatholytics, prostaglandins, non-steroidal...
s are used to numb the eye but as with non-contact tonometry, these devices are often used in children and non-cooperative patients because of their portability and ease of use. Portable electronic tonometers also play a major role in veterinary tonometry.
Rebound tonometry
Rebound tonometers (Icare Tonometer ) determine intraocular pressure by bouncing a small plastic tipped metal probe against the cornea. The device uses an induction coil to magnetise the probe and fire it against the cornea. As the probe bounces against the cornea and back in to the device, it creates an induction current from which the intraocular pressure is calculated. The device is simple and easy to use and self use versions are available. It is portable, does not require the use of eye drops and is particularly suitable for children and non-cooperative patients.
Pneumatonometry
A pneumatonometer utilizes a pneumatic sensor (consisting of a piston floating on an air bearing). Filtered air is pumped into the piston and travels through a small (5-mm dia.) fenestrated membrane at one end. This membrance is placed against the cornea. The balance between the flow of air from the machine and the resistance to flow from the cornea affect the movement of the piston and this movement is used to calculate the intra-ocular pressure.
Impression tonometry
Impression tonometry (also known as indentation tonometry) measures the depth of corneal indentation made by a small plunger carrying a known weight. The higher the intraocular pressure, the harder it is to push against and indent the cornea. For very high levels of IOP, extra weights can be added to make the plunger push harder. The movement of the plunger is measured using a calibrated scale. The Schiötz tonometry is the most common device to use this principle.
Non-corneal and Transpalpebral tonometry
Diaton tonometer (BiCOM, Inc) Transpalpebral tonometry refers to methods of measuring intraocular pressure through the Eyelid
Eyelid
An eyelid is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. With the exception of the prepuce and the labia minora, it has the thinnest skin of the whole body. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid to "open" the eye. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily...
. The Diaton non-corneal tonometer calculates pressure by measuring the response of a free falling rod, as it rebounds against the tarsal plate of the eyelid through the sclera
Sclera
The sclera , also known as the white or white of the eye, is the opaque , fibrous, protective, outer layer of the eye containing collagen and elastic fiber. In the development of the embryo, the sclera is derived from the neural crest...
. The patient is positioned so that the tip of the device and lid are overlying sclera. Non-corneal and transpalpebral tonometry does not involve contact with the cornea
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Together with the lens, the cornea refracts light, with the cornea accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is...
and does not require topical anesthetic
Topical anesthetic
A topical anesthetic is a local anesthetic that is used to numb the surface of a body part. They can be used to numb any area of the skin as well as the front of the eyeball, the inside of the nose, ear or throat, the anus and the genital area. Topical anesthetics are available in creams,...
during routine use. The tonometer is not a substitute or alternative for more established methods.
Palpation
Palpation (also known as digital tonometry) is the method of estimating intraocular pressure by gently pressing your index finger against the cornea of a closed eye. This method is notoriously unreliable.
OCT Tonometry
Non-contact tonometry using optical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography is an optical signal acquisition and processing method. It captures micrometer-resolution, three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media . Optical coherence tomography is an interferometric technique, typically employing near-infrared light...
(OCT) is currently under development. Like many other forms of tonometry, this methodology relies on a force being applied to the cornea and simultaneous measurement of the corneal reaction. In the case of OCT tonometry, the force applied to the cornea can be air pressure in the form of a high pressure jet (like air-puff tonometry), a shock or acoustic wave, or low pressure air using air pumped into a sealed chamber around the eye (like a snorkeling or scuba mask). The OCT device is used to measure changes in the curvature of the cornea or movement of the apical corneal interface. This deflection can be compared to the pressure measured around the eye and corrected for corneal thickness and potentially, corneal hysteresis.
Influencing factors
Central Corneal Thickness (CCT)The thickness of the cornea affects most non-invasive methods by varying resistance to the tonometer probe. A thick cornea gives rise to a greater probability of an IOP being over-estimated (and a thin cornea of an IOP being under-estimated), but the extent of measurement error in individual patients cannot be ascertained from the CCT alone. The Ocular Response Analyzer and Pascal DCT Tonometers are less affected by CCT than the Goldmann tonometer. Conversley, Non-contact and rebound tonometers are more affected. Corneal thickness varies among individuals as well as with age and race. It is reduced in certain disease and following LASIK surgery.
External links
- Tonometry - WebMD
- Tonometry - The Johns Hopkins Consumer Guide to Medical Tests
- Kirstein, E. "An Update on Methods for Assessing Intraocular Pressure." Retrieved June 7, 2006.
- Rebound Tonometer from Icare Finland
- Trans-Scleral Tonometry
- Tonometers in the market
- Tonometer from Keeler Ltd, UK based Company
- Dynamic Contour Tonometry Pascal

