Toxic encephalopathy
Encyclopedia
Toxic encephalopathy, also known as toxic-metabolic encephalopathy, is a degenerative neurologic disorder caused by exposure to toxic substances. It can be an acute
or a chronic
disorder. Exposure to toxic substances can lead to a variety of symptoms, characterized by an altered mental status. Toxic encephalopathy can be caused by various chemicals, some of which are commonly used in everyday life. Toxic encephalopathy can permanently damage the brain and currently, treatment is mainly just for the symptoms.
, small personality changes/increased irritability, insidious onset of concentration difficulties, involuntary movements, fatigue, seizures
, arm strength problems, and depression
. . The condition may also be referred to as substance-induced persistent dementia
. Acute intoxication symptoms include lightheadedness, dizziness, headache and nausea, and regular cumulative exposure to these toxic solvents over a number of years puts the individual at high risk for developing toxic encephalopathy.
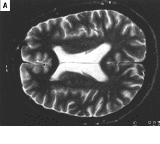
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) analyses have also demonstrated increased rates of dopamine
synthesis in the putamen, reduced anterior and total corpus callosum volume, demyelination in the parietal white matter, basal ganglia
, and thalamus
, as well as atypical activation of frontal areas of the brain due to neural compensation. A thorough and standard diagnostic process is paramount with toxic encephalopathy, including a careful occupational history, medical history, and standardized imaging/neurobehavioral testing.
, that could instigate toxic encephalopathy are sometimes found in everyday products such as cleaning products, building materials, pesticides, air fresheners, and even perfumes. These harmful chemicals can be inhaled (in the cause of air fresheners) or applied (in the case of perfumes).. The substances diffuse into the brain rapidly, as they are lipophilic and readily transported across the blood–brain barrier. This is a result of increased membrane solubility and local blood flow, with central nervous system (CNS) solvent uptake being further increased with high levels of physical activity. When they are not detoxified immediately, the symptoms of toxic encephalopathy begin to emerge. However, in chronic situations, these effects may not become severe enough to be noticed until much later. Increased exposure time and increased concentration of the chemical solvents will worsen the effects of toxic encephalopathy, due to the associated structural CNS damage and direct functional impairment consequences.
or organ replacement surgery may be needed in some severe cases..
Management of affected individuals consists of immediate removal from exposure to the toxic substance(s), treatment of the common clinical manifestation of depression if present, and counselling for the provision of life strategies to help cope with the potentially debilitating condition.
Acute (medicine)
In medicine, an acute disease is a disease with either or both of:# a rapid onset, as in acute infection# a short course ....
or a chronic
Chronic (medicine)
A chronic disease is a disease or other human health condition that is persistent or long-lasting in nature. The term chronic is usually applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include asthma, cancer, diabetes and HIV/AIDS.In medicine, the...
disorder. Exposure to toxic substances can lead to a variety of symptoms, characterized by an altered mental status. Toxic encephalopathy can be caused by various chemicals, some of which are commonly used in everyday life. Toxic encephalopathy can permanently damage the brain and currently, treatment is mainly just for the symptoms.
Signs and symptoms
"Encephalopathy" is a general term describing brain malfunctions and "toxic" asserts that the malfunction is caused by toxins or chemicals. The most prominent characteristic of toxic encephalopathy is an altered mental status. Toxic encephalopathy has a wide variety of symptoms, which can include memory lossMemory loss
Memory loss can be partial or total and it is normal when it comes with aging. Sudden memory loss is usually a result of brain trauma and it may be permanent or temporary. When it is caused by medical conditions such as Alzheimers, the memory loss is gradual and tends to be permanent.Brain trauma...
, small personality changes/increased irritability, insidious onset of concentration difficulties, involuntary movements, fatigue, seizures
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
, arm strength problems, and depression
Depression (mood)
Depression is a state of low mood and aversion to activity that can affect a person's thoughts, behaviour, feelings and physical well-being. Depressed people may feel sad, anxious, empty, hopeless, helpless, worthless, guilty, irritable, or restless...
. . The condition may also be referred to as substance-induced persistent dementia
Dementia
Dementia is a serious loss of cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging...
. Acute intoxication symptoms include lightheadedness, dizziness, headache and nausea, and regular cumulative exposure to these toxic solvents over a number of years puts the individual at high risk for developing toxic encephalopathy.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) analyses have also demonstrated increased rates of dopamine
Dopamine
Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter present in a wide variety of animals, including both vertebrates and invertebrates. In the brain, this substituted phenethylamine functions as a neurotransmitter, activating the five known types of dopamine receptors—D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5—and their...
synthesis in the putamen, reduced anterior and total corpus callosum volume, demyelination in the parietal white matter, basal ganglia
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
, and thalamus
Thalamus
The thalamus is a midline paired symmetrical structure within the brains of vertebrates, including humans. It is situated between the cerebral cortex and midbrain, both in terms of location and neurological connections...
, as well as atypical activation of frontal areas of the brain due to neural compensation. A thorough and standard diagnostic process is paramount with toxic encephalopathy, including a careful occupational history, medical history, and standardized imaging/neurobehavioral testing.
Causes
In addition, chemicals, such as leadLead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
, that could instigate toxic encephalopathy are sometimes found in everyday products such as cleaning products, building materials, pesticides, air fresheners, and even perfumes. These harmful chemicals can be inhaled (in the cause of air fresheners) or applied (in the case of perfumes).. The substances diffuse into the brain rapidly, as they are lipophilic and readily transported across the blood–brain barrier. This is a result of increased membrane solubility and local blood flow, with central nervous system (CNS) solvent uptake being further increased with high levels of physical activity. When they are not detoxified immediately, the symptoms of toxic encephalopathy begin to emerge. However, in chronic situations, these effects may not become severe enough to be noticed until much later. Increased exposure time and increased concentration of the chemical solvents will worsen the effects of toxic encephalopathy, due to the associated structural CNS damage and direct functional impairment consequences.
Treatment
Treatment is mainly for the symptoms that toxic encephalopathy brings upon victims, varying depending on how severe the case is. Diet changes and nutritional supplements may help some patients. To reduce or halt seizures, anticonvulsants may be prescribed. DialysisDialysis
In medicine, dialysis is a process for removing waste and excess water from the blood, and is primarily used to provide an artificial replacement for lost kidney function in people with renal failure...
or organ replacement surgery may be needed in some severe cases..
Management of affected individuals consists of immediate removal from exposure to the toxic substance(s), treatment of the common clinical manifestation of depression if present, and counselling for the provision of life strategies to help cope with the potentially debilitating condition.

