
Trace amine
Encyclopedia
.svg.png)
Endogenous
Endogenous substances are those that originate from within an organism, tissue, or cell. Endogenous retroviruses are caused by ancient infections of germ cells in humans, mammals and other vertebrates...
compounds structurally related to classical biogenic amine
Biogenic amine
-Examples:Some prominent examples of biogenic amines include:* Histamine - a substance derived from the amino acid histidine that acts as a neurotransmitter mediating arousal and attention, as well as a pro-inflammatory signal released from mast cells in response to allergic reactions or tissue...
s, such as catecholamines, serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
and histamine
Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogen compound involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter. Histamine triggers the inflammatory response. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by...
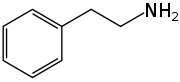
. Trace amines include p-tyramine, β-phenylethylamine, tryptamine
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is a monoamine alkaloid found in plants, fungi, and animals. It is based around the indole ring structure, and is chemically related to the amino acid tryptophan, from which its name is derived...
, octopamine
Octopamine
Octopamine is an endogenous biogenic amine that is closely related to norepinephrine, and has effects on the adrenergic and dopaminergic systems. It is also found naturally in numerous plants, including bitter orange. Biosynthesis of the D--enantiomer of octopamine is by β-hydroxylation of...
, and 3-iodothyronamine
3-Iodothyronamine
3-Iodothyronamine is an endogenous thyronamine. T1AM is a high-affinity ligand for the trace amine-associated receptor TAAR1 , a G protein-coupled receptor...
, and are found in the nervous systems of animals from insects to mammals. Trace amines can also include the endogenous
Endogenous
Endogenous substances are those that originate from within an organism, tissue, or cell. Endogenous retroviruses are caused by ancient infections of germ cells in humans, mammals and other vertebrates...
psychedelic
Psychedelic
The term psychedelic is derived from the Greek words ψυχή and δηλοῦν , translating to "soul-manifesting". A psychedelic experience is characterized by the striking perception of aspects of one's mind previously unknown, or by the creative exuberance of the mind liberated from its ostensibly...
tryptamines, such as DMT
Dimethyltryptamine
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine is a naturally occurring psychedelic compound of the tryptamine family. DMT is found in several plants, and also in trace amounts in humans and other mammals, where it is originally derived from the essential amino acid tryptophan, and ultimately produced by the enzyme INMT...
.
Trace amines overlap substantially with classical biogenic amines neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
s regarding to chemical properties, synthesis, and breakdown; trace amines commonly colocalize in neurons with these neurotransmitters.
Psychiatric disorders such as depression
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
and schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
have been linked to irregular levels of trace amines.
See also
- Trace amine-associated receptorTrace amine-associated receptorTrace amine-associated receptors, abbreviated TAAR and otherwise known as trace amine receptors, abbreviated TAR or TA, are a class of G protein-coupled receptors identified in 2001....
.svg.png)

Endogenous
Endogenous substances are those that originate from within an organism, tissue, or cell. Endogenous retroviruses are caused by ancient infections of germ cells in humans, mammals and other vertebrates...
compounds structurally related to classical biogenic amine
Biogenic amine
-Examples:Some prominent examples of biogenic amines include:* Histamine - a substance derived from the amino acid histidine that acts as a neurotransmitter mediating arousal and attention, as well as a pro-inflammatory signal released from mast cells in response to allergic reactions or tissue...
s, such as catecholamines, serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
and histamine
Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogen compound involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter. Histamine triggers the inflammatory response. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by...
. Trace amines include p-tyramine, β-phenylethylamine, tryptamine
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is a monoamine alkaloid found in plants, fungi, and animals. It is based around the indole ring structure, and is chemically related to the amino acid tryptophan, from which its name is derived...
, octopamine
Octopamine
Octopamine is an endogenous biogenic amine that is closely related to norepinephrine, and has effects on the adrenergic and dopaminergic systems. It is also found naturally in numerous plants, including bitter orange. Biosynthesis of the D--enantiomer of octopamine is by β-hydroxylation of...
, and 3-iodothyronamine
3-Iodothyronamine
3-Iodothyronamine is an endogenous thyronamine. T1AM is a high-affinity ligand for the trace amine-associated receptor TAAR1 , a G protein-coupled receptor...
, and are found in the nervous systems of animals from insects to mammals. Trace amines can also include the endogenous
Endogenous
Endogenous substances are those that originate from within an organism, tissue, or cell. Endogenous retroviruses are caused by ancient infections of germ cells in humans, mammals and other vertebrates...
psychedelic
Psychedelic
The term psychedelic is derived from the Greek words ψυχή and δηλοῦν , translating to "soul-manifesting". A psychedelic experience is characterized by the striking perception of aspects of one's mind previously unknown, or by the creative exuberance of the mind liberated from its ostensibly...
tryptamines, such as DMT
Dimethyltryptamine
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine is a naturally occurring psychedelic compound of the tryptamine family. DMT is found in several plants, and also in trace amounts in humans and other mammals, where it is originally derived from the essential amino acid tryptophan, and ultimately produced by the enzyme INMT...
.
Trace amines overlap substantially with classical biogenic amines neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
s regarding to chemical properties, synthesis, and breakdown; trace amines commonly colocalize in neurons with these neurotransmitters.
Psychiatric disorders such as depression
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
and schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
have been linked to irregular levels of trace amines.
See also
- Trace amine-associated receptorTrace amine-associated receptorTrace amine-associated receptors, abbreviated TAAR and otherwise known as trace amine receptors, abbreviated TAR or TA, are a class of G protein-coupled receptors identified in 2001....
.svg.png)

Endogenous
Endogenous substances are those that originate from within an organism, tissue, or cell. Endogenous retroviruses are caused by ancient infections of germ cells in humans, mammals and other vertebrates...
compounds structurally related to classical biogenic amine
Biogenic amine
-Examples:Some prominent examples of biogenic amines include:* Histamine - a substance derived from the amino acid histidine that acts as a neurotransmitter mediating arousal and attention, as well as a pro-inflammatory signal released from mast cells in response to allergic reactions or tissue...
s, such as catecholamines, serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
and histamine
Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogen compound involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter. Histamine triggers the inflammatory response. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by...
. Trace amines include p-tyramine, β-phenylethylamine, tryptamine
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is a monoamine alkaloid found in plants, fungi, and animals. It is based around the indole ring structure, and is chemically related to the amino acid tryptophan, from which its name is derived...
, octopamine
Octopamine
Octopamine is an endogenous biogenic amine that is closely related to norepinephrine, and has effects on the adrenergic and dopaminergic systems. It is also found naturally in numerous plants, including bitter orange. Biosynthesis of the D--enantiomer of octopamine is by β-hydroxylation of...
, and 3-iodothyronamine
3-Iodothyronamine
3-Iodothyronamine is an endogenous thyronamine. T1AM is a high-affinity ligand for the trace amine-associated receptor TAAR1 , a G protein-coupled receptor...
, and are found in the nervous systems of animals from insects to mammals. Trace amines can also include the endogenous
Endogenous
Endogenous substances are those that originate from within an organism, tissue, or cell. Endogenous retroviruses are caused by ancient infections of germ cells in humans, mammals and other vertebrates...
psychedelic
Psychedelic
The term psychedelic is derived from the Greek words ψυχή and δηλοῦν , translating to "soul-manifesting". A psychedelic experience is characterized by the striking perception of aspects of one's mind previously unknown, or by the creative exuberance of the mind liberated from its ostensibly...
tryptamines, such as DMT
Dimethyltryptamine
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine is a naturally occurring psychedelic compound of the tryptamine family. DMT is found in several plants, and also in trace amounts in humans and other mammals, where it is originally derived from the essential amino acid tryptophan, and ultimately produced by the enzyme INMT...
.
Trace amines overlap substantially with classical biogenic amines neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
s regarding to chemical properties, synthesis, and breakdown; trace amines commonly colocalize in neurons with these neurotransmitters.
Psychiatric disorders such as depression
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
and schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
have been linked to irregular levels of trace amines.

