
Trafalgar class battleship
Encyclopedia
The two Trafalgar-class battleships of the British
Royal Navy
were late nineteenth century ironclad warships. Both were named after naval battles won by the British during the Napoleonic wars
under the command of Admiral Nelson.
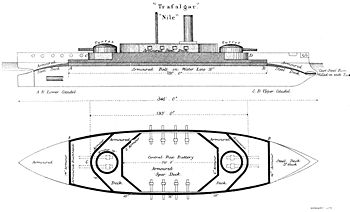 Laid down in 1886, they were designed by William Henry White
Laid down in 1886, they were designed by William Henry White
to be improved versions of the Admiral
and Victoria
classes, having a greater displacement to allow for improved protection. However they sacrificed a full armoured belt for greater thickness amidships in a partial belt.
They were originally intended to have a secondary armament of eight 5 inch guns but this was changed to six quick-firing 4.7 inch guns for use against attacking torpedo boats, which led to a weight increase of 60 tons, partly due to the increased amount of ammunition carried. This was one of the changes which led to the vessels being 600 tons overweight, causing an increase in draught of a foot.
The Trafalgars were the penultimate low freeboard battleships built for the Royal Navy. This design had been favoured for several years because it reduced the size of the target that the ships presented to enemy guns in battle, and because the smaller hull area allowed thicker armour. However, as a consequence of having a freeboard of only about 15 feet, the vessels were unable to cope with very rough seas. This was mitigated by having them spend most of their active service in the relatively calm Mediterranean.
When they were built, many observers over-estimated the vulnerability of large ships to torpedo
es and the perceived inability to avoid them, which made them believe that large warships would inevitably be replaced by smaller, less vulnerable, and less valuable, vessels. For example, John Hibbert
, the parliamentary secretary of the Admiralty
, told Parliament
in March 1886: "I think I may safely say that these two large iron-clads will probably be the last iron-clads of this type that will ever be built in this or any other country. In France they are ceasing to go on with the construction of large iron-clads." In fact it took the development of effective naval aircraft
able to carry bombs and torpedoes in the years immediately preceding the Second World War nearly fifty years later to finally make this true.
programme. Of these, one was a low freeboard design: the Hood
, and nine were high freeboard designs: the seven Royal Sovereign
and two Centurion
class ships.
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Royal Navy
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
were late nineteenth century ironclad warships. Both were named after naval battles won by the British during the Napoleonic wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
under the command of Admiral Nelson.
Design

William Henry White
Sir William Henry White was a prolific British warship designer and Chief Constructor at the Admiralty....
to be improved versions of the Admiral
Admiral class battleship
The British Royal Navy's pre-dreadnought Admiral class battleships of the 1880s followed the pattern of the Devastation class in having the main armament on centre-line mounts with the superstructure in between. This pattern was followed by most following British designs until in 1906...
and Victoria
Victoria class battleship
The Royal Navy's Victoria class battleships of the 1880s was the first class which used triple expansion steam engines, previous battleships having used compound engines.There were only two ships in this class...
classes, having a greater displacement to allow for improved protection. However they sacrificed a full armoured belt for greater thickness amidships in a partial belt.
They were originally intended to have a secondary armament of eight 5 inch guns but this was changed to six quick-firing 4.7 inch guns for use against attacking torpedo boats, which led to a weight increase of 60 tons, partly due to the increased amount of ammunition carried. This was one of the changes which led to the vessels being 600 tons overweight, causing an increase in draught of a foot.
The Trafalgars were the penultimate low freeboard battleships built for the Royal Navy. This design had been favoured for several years because it reduced the size of the target that the ships presented to enemy guns in battle, and because the smaller hull area allowed thicker armour. However, as a consequence of having a freeboard of only about 15 feet, the vessels were unable to cope with very rough seas. This was mitigated by having them spend most of their active service in the relatively calm Mediterranean.
When they were built, many observers over-estimated the vulnerability of large ships to torpedo
Torpedo
The modern torpedo is a self-propelled missile weapon with an explosive warhead, launched above or below the water surface, propelled underwater towards a target, and designed to detonate either on contact with it or in proximity to it.The term torpedo was originally employed for...
es and the perceived inability to avoid them, which made them believe that large warships would inevitably be replaced by smaller, less vulnerable, and less valuable, vessels. For example, John Hibbert
John Tomlinson Hibbert
Sir John Tomlinson Hibbert KCB, PC, JP, DL, DCL , known as J. T. Hibbert, was a British barrister and Liberal politician.-Background and education:...
, the parliamentary secretary of the Admiralty
Admiralty
The Admiralty was formerly the authority in the Kingdom of England, and later in the United Kingdom, responsible for the command of the Royal Navy...
, told Parliament
Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body in the United Kingdom, British Crown dependencies and British overseas territories, located in London...
in March 1886: "I think I may safely say that these two large iron-clads will probably be the last iron-clads of this type that will ever be built in this or any other country. In France they are ceasing to go on with the construction of large iron-clads." In fact it took the development of effective naval aircraft
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
able to carry bombs and torpedoes in the years immediately preceding the Second World War nearly fifty years later to finally make this true.
Subsequent designs
The next British battleships ordered by the Royal Navy were those ordered as part of the 1889 Naval Defence ActNaval Defence Act 1889
The Naval Defence Act 1889 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, instituted on May 31, 1889 to increase the United Kingdom's naval strength and formally adopt the country’s "two-power standard." The standard called for the Royal Navy to maintain a number of battleships at least equal...
programme. Of these, one was a low freeboard design: the Hood
HMS Hood (1891)
The second warship to be named HMS Hood was a modified Royal Sovereign-class battleship of the Royal Navy, and the last of the eight built. She differed from the Royal Sovereign class in that she had cylindrical gun turrets instead of barbettes, a lower freeboard and a higher metacentric height...
, and nine were high freeboard designs: the seven Royal Sovereign
Royal Sovereign class battleship
The Royal Sovereign class was a class of pre-dreadnought battleships of the British Royal Navy. The class comprised seven ships built to the same design: HMS Royal Sovereign, , HMS Ramilles, HMS Repulse, HMS Resolution, HMS Revenge, and HMS Royal Oak, and a half-sister built to a modified design: ....
and two Centurion
Centurion class battleship
The Centurion class battleships were second-class pre-dreadnought battleships of the Royal Navy designed for service on distant stations.-Description:...
class ships.
Bibliograophy
- D. K. Brown, Warrior to Dreadnought, Warship Development 1860–1906, ISBN 1-84067-529-2
- John Beeler, Birth of the Battleship, British capital ship design 1870–1881, ISBN 1-86176-167-8
- K. McBride, Nile and Trafalgar, The Last British Ironclads, in Warship 2000–2001, Conways Maritime Press
- Parkes, Oscar British Battleships, first published Seeley Service & Co, 1957, published United States Naval Institute Press, 1990. ISBN 1-55750-075-4
- Archibald, E.H.H.; Ray Woodward (ill.) (1971). The Metal Fighting Ship in the Royal Navy 1860–1970. New York: Arco Publishing Co.. ISBN 0-6680-2509-3.

