
Transition radiation detector
Encyclopedia
A transition radiation detector (TRD) is a particle detector
using the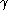 -dependent threshold of transition radiation in a stratified material. It contains many layers of materials with different indices of refraction. At each interface between materials, the probability of transition radiation
-dependent threshold of transition radiation in a stratified material. It contains many layers of materials with different indices of refraction. At each interface between materials, the probability of transition radiation
increases with the relativistic gamma factor
. Thus particles with large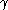 give off many photons, and small
give off many photons, and small  give off few. For a given energy, this allows a discrimination between a lighter particle (which has a high
give off few. For a given energy, this allows a discrimination between a lighter particle (which has a high 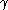 and therefore radiates) and a heavier particle (which has a low
and therefore radiates) and a heavier particle (which has a low 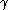 and radiates much less).
and radiates much less).
Particle detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify high-energy particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a...
using the
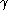 -dependent threshold of transition radiation in a stratified material. It contains many layers of materials with different indices of refraction. At each interface between materials, the probability of transition radiation
-dependent threshold of transition radiation in a stratified material. It contains many layers of materials with different indices of refraction. At each interface between materials, the probability of transition radiationTransition radiation
Optical Transition radiation is produced by relativistic charged particles when they cross the interface of two media of different dielectric constants. The emitted radiation is the homogeneous difference between the two inhomogeneous solutions of Maxwell's equations of the electric and magnetic...
increases with the relativistic gamma factor
Lorentz factor
The Lorentz factor or Lorentz term appears in several equations in special relativity, including time dilation, length contraction, and the relativistic mass formula. Because of its ubiquity, physicists generally represent it with the shorthand symbol γ . It gets its name from its earlier...
. Thus particles with large
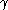 give off many photons, and small
give off many photons, and small  give off few. For a given energy, this allows a discrimination between a lighter particle (which has a high
give off few. For a given energy, this allows a discrimination between a lighter particle (which has a high 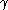 and therefore radiates) and a heavier particle (which has a low
and therefore radiates) and a heavier particle (which has a low 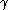 and radiates much less).
and radiates much less).

