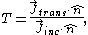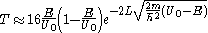
Transmission coefficient
Encyclopedia
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and electrical engineering
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
when wave propagation
Wave propagation
Wave propagation is any of the ways in which waves travel.With respect to the direction of the oscillation relative to the propagation direction, we can distinguish between longitudinal wave and transverse waves....
in a medium containing discontinuities is considered. A transmission coefficient describes the amplitude, intensity, or total power of a transmitted wave relative to an incident wave.
Different fields have different definitions for the term.
Optics
In opticsOptics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, transmission is the property of a substance to permit the passage of light, with some or none of the incident light being absorbed in the process. If some light is absorbed by the substance, then the transmitted light will be a combination of the wavelengths of the light that was transmitted and not absorbed. For example, a blue light filter appears blue because it absorbs red and green wavelengths. If white light is shone through the filter, the light transmitted also appears blue because of the absorption of the red and green wavelengths.
The transmission coefficient is a measure of how much of an electromagnetic wave (light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
) passes through a surface or an optical element. Transmission coefficients can be calculated for either the amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
or the intensity
Intensity (physics)
In physics, intensity is a measure of the energy flux, averaged over the period of the wave. The word "intensity" here is not synonymous with "strength", "amplitude", or "level", as it sometimes is in colloquial speech...
of the wave. Either is calculated by taking the ratio of the value after the surface or element to the value before.
Quantum mechanics
In non-relativistic quantum mechanicsQuantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, the transmission coefficient and related reflection coefficient
Reflection coefficient
The reflection coefficient is used in physics and electrical engineering when wave propagation in a medium containing discontinuities is considered. A reflection coefficient describes either the amplitude or the intensity of a reflected wave relative to an incident wave...
are used to describe the behavior of waves incident on a barrier. The transmission coefficient represents the probability flux of the transmitted wave relative to that of the incident wave. It is often used to describe the probability of a particle tunneling
Quantum tunnelling
Quantum tunnelling refers to the quantum mechanical phenomenon where a particle tunnels through a barrier that it classically could not surmount. This plays an essential role in several physical phenomena, such as the nuclear fusion that occurs in main sequence stars like the sun, and has important...
through a barrier.
The transmission coefficient is defined in terms of the incident and transmitted probability current density
Probability current
In quantum mechanics, the probability current is a mathematical quantity describing the flow of probability density. Intuitively; if one pictures the probability density as an inhomogeneous fluid, then the probability current is the rate of flow of this fluid...
j according to:
where Jinc is the probability current in the wave incident upon the barrier with normal unit vector
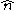 and Jtrans is the probability current in the wave moving away from the barrier on the other side.
and Jtrans is the probability current in the wave moving away from the barrier on the other side.The reflection coefficient R is defined analogously, as R=|jreflected|/|jincident|. Conservation of probability implies that T+R=1, which in one dimension reduces to the fact that the sum of the transmitted and reflected currents is equal in magnitude to the incident current.
For sample calculations, see finite potential barrier or square potential.
WKB approximation
Using the WKB approximation, one can obtain a tunnelling coefficient that looks like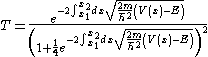
Where
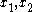 are the two classical turning points for the potential barrier. If we take the classical limit of all other physical parameters much larger than Planck's constant, abbreviated as
are the two classical turning points for the potential barrier. If we take the classical limit of all other physical parameters much larger than Planck's constant, abbreviated as 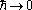 , we see that the transmission coefficient correctly goes to zero. This classical limit would have failed in the situation of a square potential.
, we see that the transmission coefficient correctly goes to zero. This classical limit would have failed in the situation of a square potential.If the transmission coefficient is much less than 1, it can be approximated with the following formula:
where
 is the length of the barrier potential.
is the length of the barrier potential.Telecommunication
The transmission coefficient is the ratio of the amplitude of the complex transmitted wave to that of the incident wave at a discontinuity in the transmission lineTransmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
.
The probability that a portion of a communications system
Communications system
In telecommunication, a communications system is a collection of individual communications networks, transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and data terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole...
, such as a line, circuit
Telecommunication circuit
A telecommunication circuit is any line, conductor, or other conduit by which information is transmitted.A dedicated circuit, private circuit, or leased line is a line that is dedicated to only one use...
, channel
Channel (communications)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
or trunk
Trunking
In modern communications, trunking is a concept by which a communications system can provide network access to many clients by sharing a set of lines or frequencies instead of providing them individually. This is analogous to the structure of a tree with one trunk and many branches. Examples of...
, will meet specified performance criteria is also sometimes called the "transmission coefficient" of that portion of the system. The value of the transmission coefficient is inversely related to the quality of the line, circuit, channel or trunk.
Chemistry
The transmission coefficient is a state of unity for monomolecular reactions. It appears in the Eyring equationEyring equation
The Eyring equation also known as Eyring–Polanyi equation in chemical kinetics relates the reaction rate to temperature. It was developed almost simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, M.G. Evans and Michael Polanyi...
.