boron.gif)
Tris(pentafluorophenyl)boron
Encyclopedia
Trisboron is the chemical compound
(C6F5)3B. The molecule consists of three pentafluorophenyl groups attached in a "paddle-wheel" manner to a central boron
atom; the BC3 core is planar. It has been described as the “ideal Lewis acid
” because of its versatility and the relative inertness of the B-C bonds. Related fluoro-substituted boron compounds, such as those containing B-CF3 groups, decompose with formation of B-F bonds.
Originally the synthesis employed C6F5Li, but this reagent can detonate with elimination of LiF.
ity: stronger than BF3 but weaker than BCl3. This property indicates that the electronegativity
of the C6F5 group and a halide are similar. An most important application of (C6F5)3B is that it forms noncoordinating anions by removing anionic ligands from metal centers. Illustrative is a reaction that give rise to alkene polymerization
catalyst:3B + (C5H5)2Zr(CH3)2 → [(C5H5)2ZrCH3+][ C6F5)3BCH3−]
In this process, the strongly coordinating methyl group transfers to the boron to expose a reactive site on zirconium. Alkenes can bind to this site, whereupon they couple to the remaining methyl ligand
to give a propyl ligand, thereby starting the growth of a chain of polyethylene.
(C6F5)3B is also capable of abstracting hydride to give [(C6F5)3BH]−, and it catalyzes hydrosilylation
of aldehydes. Otherwise (C6F5)3B binds to a wide range of Lewis bases, even weak ones. The compound is hygroscopic, forming the trihydrate [(C6F5)3BOH2](H2O)2, wherein one water in coordinated to boron and the other two waters are hydrogen-bonded to the coordinated water.
Related compounds are Pentafluorophenylboron halides.
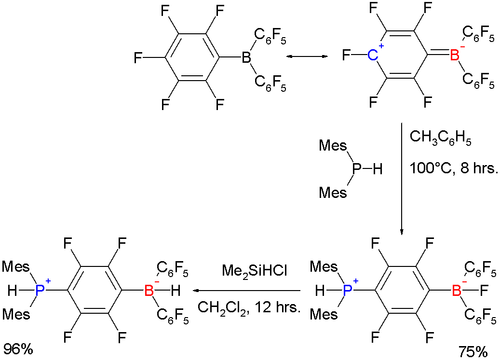
One study reported a nucleophilic aromatic substitution
on one of the pentafluorinephenyl rings by dimesityl phosphane:
The bulky mesityl groups prevent the phosphorus atom from coordinating directly to boron and instead the ring is attacked. When the fluorine atom on boron is replaced by hydrogen with dimethylchlorosilylhydride
, the resulting phosphazenium borate is capable of reversible hydrogen storage
.
With pentafluorophenyllithium the compound lithium tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)borate
is formed.
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
(C6F5)3B. The molecule consists of three pentafluorophenyl groups attached in a "paddle-wheel" manner to a central boron
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
atom; the BC3 core is planar. It has been described as the “ideal Lewis acid
Lewis acid
]The term Lewis acid refers to a definition of acid published by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1923, specifically: An acid substance is one which can employ a lone pair from another molecule in completing the stable group of one of its own atoms. Thus, H+ is a Lewis acid, since it can accept a lone pair,...
” because of its versatility and the relative inertness of the B-C bonds. Related fluoro-substituted boron compounds, such as those containing B-CF3 groups, decompose with formation of B-F bonds.
Preparation
(C6F5)3B is prepared using a Grignard reagent:- 3C6F5MgBr + BCl3 → (C6F5)3B + 3MgBrCl
Originally the synthesis employed C6F5Li, but this reagent can detonate with elimination of LiF.
Lewis acidity
The most noteworthy property of this molecule is its strong Lewis acidLewis acid
]The term Lewis acid refers to a definition of acid published by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1923, specifically: An acid substance is one which can employ a lone pair from another molecule in completing the stable group of one of its own atoms. Thus, H+ is a Lewis acid, since it can accept a lone pair,...
ity: stronger than BF3 but weaker than BCl3. This property indicates that the electronegativity
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbol χ , is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance that its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus...
of the C6F5 group and a halide are similar. An most important application of (C6F5)3B is that it forms noncoordinating anions by removing anionic ligands from metal centers. Illustrative is a reaction that give rise to alkene polymerization
Ziegler-Natta catalyst
A Ziegler–Natta catalyst is a catalyst used in the synthesis of polymers of 1-alkenes . Three types of Ziegler–Natta catalysts are currently employed:* Solid and supported catalysts based on titanium compounds...
catalyst:3B + (C5H5)2Zr(CH3)2 → [(C5H5)2ZrCH3+][ C6F5)3BCH3−]
In this process, the strongly coordinating methyl group transfers to the boron to expose a reactive site on zirconium. Alkenes can bind to this site, whereupon they couple to the remaining methyl ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
to give a propyl ligand, thereby starting the growth of a chain of polyethylene.
(C6F5)3B is also capable of abstracting hydride to give [(C6F5)3BH]−, and it catalyzes hydrosilylation
Hydrosilylation
Hydrosilylation, also called catalytic hydrosilation, describes the addition of Si-H bonds across unsaturated bonds. Ordinarily the reaction is conducted catalytically and usually the substrates are unsaturated organic compounds. Alkenes and alkynes give alkyl and vinyl silanes; aldehydes and...
of aldehydes. Otherwise (C6F5)3B binds to a wide range of Lewis bases, even weak ones. The compound is hygroscopic, forming the trihydrate [(C6F5)3BOH2](H2O)2, wherein one water in coordinated to boron and the other two waters are hydrogen-bonded to the coordinated water.
Related compounds are Pentafluorophenylboron halides.
Other reactions
(C6F5)3B was used to prepare a compound containing a Xe-C bond:3B + XeF2 → [C6F5Xe+][(C6F5)2BF2−]One study reported a nucleophilic aromatic substitution
Nucleophilic aromatic substitution
right|300px|Aromatic nucleophilic substitutionA nucleophilic aromatic substitution is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry in which the nucleophile displaces a good leaving group, such as a halide, on an aromatic ring...
on one of the pentafluorinephenyl rings by dimesityl phosphane:
The bulky mesityl groups prevent the phosphorus atom from coordinating directly to boron and instead the ring is attacked. When the fluorine atom on boron is replaced by hydrogen with dimethylchlorosilylhydride
Organosilicon
Organosilicon compounds are organic compounds containing carbon silicon bonds. Organosilicon chemistry is the corresponding science exploring their properties and reactivity.Like carbon, the organically bound silicon is tetravalent and tetrahedral...
, the resulting phosphazenium borate is capable of reversible hydrogen storage
Hydrogen storage
Hydrogen storage describes the methods for storing H2 for subsequent use. The methods span many approaches, including high pressures, cryogenics, and chemical compounds that reversibly release H2 upon heating...
.
With pentafluorophenyllithium the compound lithium tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)borate
Lithium tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)borate
Lithium tetrakisborate is the lithium salt of the weakly coordinating anion -. Because of its weakly coordinating abilities, lithium tetrakisborate makes it commercially valuable in the salt form for the starting material in polymerization reactions and electrochemistry. It is a water-soluble...
is formed.