
Tropical cyclone prediction model
Encyclopedia
Meteorology
Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries...
data to forecast
Weather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a given location. Human beings have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia, and formally since the nineteenth century...
aspects of the future state of tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
s. There are three types of models: statistical, dynamical, or combined statistical-dynamic. Dynamical models utilize powerful supercomputer
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer at the frontline of current processing capacity, particularly speed of calculation.Supercomputers are used for highly calculation-intensive tasks such as problems including quantum physics, weather forecasting, climate research, molecular modeling A supercomputer is a...
s with sophisticated mathematical model
Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
ing software and meteorological data to calculate future weather conditions
Numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic...
. Statistical model
Statistical model
A statistical model is a formalization of relationships between variables in the form of mathematical equations. A statistical model describes how one or more random variables are related to one or more random variables. The model is statistical as the variables are not deterministically but...
s forecast the evolution of a tropical cyclone in a simpler manner, by extrapolating from historical datasets, and thus can be run quickly on platforms such as personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s. Statistical-dynamical models use aspects of both types of forecasting. Four primary types of forecasts exist for tropical cyclones: track
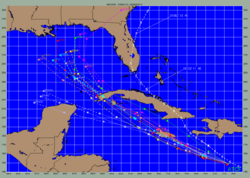
Tropical cyclone track forecasting
Tropical cyclone track forecasting involves predicting where a tropical cyclone is going to track over the next five days, every 6 to 12 hours. The history of tropical cyclone track forecasting has evolved from a single station approach to a comprehensive approach which uses a variety of...
, intensity, storm surge
Storm surge
A storm surge is an offshore rise of water associated with a low pressure weather system, typically tropical cyclones and strong extratropical cyclones. Storm surges are caused primarily by high winds pushing on the ocean's surface. The wind causes the water to pile up higher than the ordinary sea...
, and rainfall
Tropical cyclone rainfall climatology
A tropical cyclone rainfall climatology is developed to determine rainfall characteristics of past tropical cyclones. A tropical cyclone rainfall climatology can be used to help forecast current or upcoming tropical cyclone impacts. The degree of a tropical cyclone rainfall impact depends upon...
. Dynamical models were not developed until the 1970s and the 1980s, with earlier efforts focused on the storm surge problem.
Track models did not show forecast skill
Forecast skill
Skill in forecasting is a scaled representation of forecast error that relates the forecast accuracy of a particular forecast model to some reference model....
when compared to statistical models until the 1980s. Statistical-dynamical models were used from the 1970s into the 1990s. Early models use data from previous model runs while late models produce output after the official hurricane forecast has been sent. The use of consensus, ensemble, and superensemble forecasts lowers errors more than any individual forecast model. Both consensus and superensemble forecasts can use the guidance of global and regional models runs to improve the performance more than any of their respective components. Techniques used at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center
Joint Typhoon Warning Center
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center is a joint United States Navy – United States Air Force task force located at the Naval Maritime Forecast Center in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii...
indicate that superensemble forecasts are a very powerful tool for track forecasting.
Statistical guidance
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center , located at Florida International University in Miami, Florida, is the division of the National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting weather systems within the tropics between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th...
was the Hurricane Analog Technique (HURRAN), which was available in 1969. It used the newly-developed North Atlantic tropical cyclone database
HURDAT
The North Atlantic hurricane database, or HURDAT, is the database for all tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea, since 1851.-History:...
to find storms with similar tracks. It then shifted their tracks through the storm's current path, and used location, direction and speed of motion, and the date to find suitable analogs. The method did well with storms south of the 25th parallel
25th parallel north
The 25th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 25 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, Asia, the Indian Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, North America and the Atlantic Ocean....
which had not yet turned northward, but poorly with systems near or after recurvature. Since 1972, the Climatology and Persistence (CLIPER) statistical model has been used to help generate tropical cyclone track forecasts. In the era of skillful dynamical forecasts, CLIPER is now being used as the baseline to show model and forecaster skill. The Statistical Hurricane Intensity Forecast (SHIFOR) has been used since 1979 for tropical cyclone intensity forecasting. It uses climatology and persistence to predict future intensity, including the current Julian day
Julian day
Julian day is used in the Julian date system of time measurement for scientific use by the astronomy community, presenting the interval of time in days and fractions of a day since January 1, 4713 BC Greenwich noon...
, current cyclone intensity, the cyclone's intensity 12 hours ago, the storm's initial latitude and longitude, as well as its zonal (east-west) and meridional (north-south) components of motion.
A series of statistical-dynamical models, which used regression equations based upon CLIPER output and the latest output from primitive equation
Primitive equations
The primitive equations are a set of nonlinear differential equations that are used to approximate global atmospheric flow and are used in most atmospheric models...
models run at the National Meteorological Center, then National Centers for Environmental Prediction
National Centers for Environmental Prediction
The United States National Centers for Environmental Prediction delivers national and global weather, water, climate and space weather guidance, forecasts, warnings and analyses to its Partners and External User Communities...
, were developed between the 1970s and 1990s and were named NHC73, NHC83, NHC90, NHC91, and NHC98. Within the field of tropical cyclone track forecasting
Tropical cyclone track forecasting
Tropical cyclone track forecasting involves predicting where a tropical cyclone is going to track over the next five days, every 6 to 12 hours. The history of tropical cyclone track forecasting has evolved from a single station approach to a comprehensive approach which uses a variety of...
, despite the ever-improving dynamical model guidance which occurred with increased computational power, it was not until the decade of the 1980s when numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic...
showed skill
Forecast skill
Skill in forecasting is a scaled representation of forecast error that relates the forecast accuracy of a particular forecast model to some reference model....
, and until the 1990s when it consistently outperformed statistical or simple dynamical models. In 1994, a version of SHIFOR was created for the northwest Pacific ocean for typhoon forecasting, known as the Statistical Typhoon Intensity Forecast (STIFOR), which used the 1971-1990 data for that region to develop intensity forecasts out to 72 hours into the future.
In regards to intensity forecasting, the Statistical Hurricane Intensity Prediction Scheme (SHIPS) utilizes relationships between environmental conditions from the Global Forecast System
Global Forecast System
The Global Forecast System is a global numerical weather prediction computer model run by NOAA. This mathematical model is run four times a day and produces forecasts up to 16 days in advance, but with decreasing spatial and temporal resolution over time...
(GFS) such as vertical wind shear
Wind shear
Wind shear, sometimes referred to as windshear or wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere...
and sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature is the water temperature close to the oceans surface. The exact meaning of surface varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a...
s, climatology, and persistence (storm behavior) via multiple regression techniques to come up with an intensity forecast for systems in the northern Atlantic and northeastern Pacific oceans. A similar model was developed for the northwest Pacific ocean and Southern Hemisphere known as the Statistical Intensity Prediction System (STIPS), which accounts for land interactions through the input environmental conditions from the Navy Operational Global Prediction System (NOGAPS) model. The version of SHIPS with an inland decay component is known as Decay SHIPS (DSHIPS). The Logistic Growth Equation Model (LGEM) uses the same input as SHIPS but within a simplified dynamical prediction system. Within tropical cyclone rainfall forecasting
Tropical cyclone rainfall forecasting
Tropical cyclone rainfall forecasting involves using scientific models and other tools to predict the precipitation expected in tropical cyclones such as hurricanes and typhoons. Knowledge of tropical cyclone rainfall climatology is helpful in the determination of a tropical cyclone rainfall...
, the Rainfall Climatology and Persistence (r-CLIPER) model was developed using microwave rainfall data from polar orbiting satellites over the ocean and first-order rainfall measurements from the land, to come up with a realistic rainfall distribution for tropical cyclones based on the National Hurricane Center's track forecast. It has been operational since 2004. A statistical-parametric wind radii model has been developed for use at the National Hurricane Center and Joint Typhoon Warning Center which uses climatology and persistence to predict wind structure out to five days into the future.
Dynamical guidance
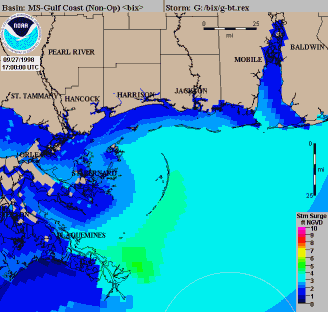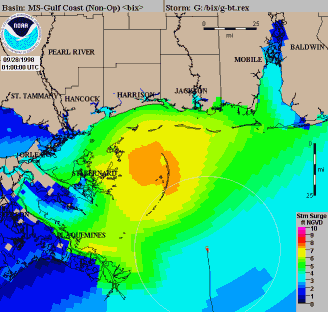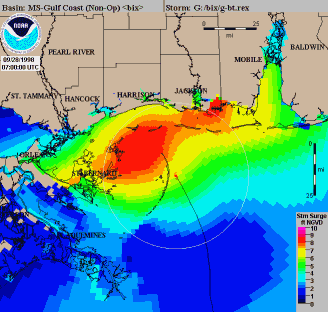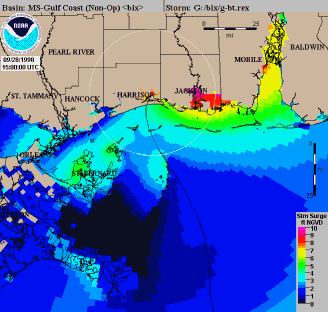
During 1972, the first model to forecast storm surge along the continental shelf
Continental shelf
The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
of the United States was developed, known as the Special Program to List the Amplitude of Surges from Hurricanes (SPLASH). In 1978, the first hurricane-tracking model based on atmospheric dynamics – the movable fine-mesh (MFM) model – began operating. The Quasi-Lagrangian Limited Area (QLM) model is a multi-level primitive equation model using a Cartesian
Cartesian coordinate system
A Cartesian coordinate system specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length...
grid and the Global Forecasting System (GFS) for boundary conditions. In the early 1980's, the assimilation of satellite-derived winds from water vapor, infrared, and visible satellite imagery was found to improve tropical cyclones track forecasting. The Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory
The Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory is a laboratory in the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration /Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research . The current director is Dr. V...
(GFDL) hurricane model was used for research purposes between 1973 and the mid-1980s. Once it was determined that it could show skill in hurricane prediction, a multi-year transition transformed the research model into an operational model which could be used by the National Weather Service
National Weather Service
The National Weather Service , once known as the Weather Bureau, is one of the six scientific agencies that make up the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration of the United States government...
for both track and intensity forecasting in 1995. By 1985, the Sea Lake and Overland Surges from Hurricanes (SLOSH) Model had been developed for use in areas of the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
and near the United States' East coast, which was more robust than the SPLASH model.
The Beta Advection Model (BAM) has been used operationally since 1987 using steering winds averaged through the 850 hPa to 200 hPa layer and the Beta effect which causes a storm to drift northwest due to differences in the coriolis effect
Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects when they are viewed in a rotating reference frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the left of the motion of the object; in one with counter-clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the right...
across the tropical cyclone. The larger the cyclone, the larger the impact of the beta effect is likely to be. Starting in 1990, three versions of the BAM were run operationally: the BAM shallow (BAMS) average winds in a 850 hPa to 700 hPa layer, the BAM Medium (BAMM) which uses average winds in a 850 hPa to 400 hPa layer, and the BAM Deep (BAMD) which is the same as the pre-1990 BAM. For a weak hurricane without well-developed central thunderstorm activity, BAMS works well, because weak storms tend to be steered by low-level winds. As the storm grows stronger and associated thunderstorm activity near its center gets deeper, BAMM and BAMD become more accurate, as these types of storms are steered more by the winds in the upper-level. If the forecast from the three versions is similar, then the forecaster can conclude that there is minimal uncertainty, but if the versions vary by a great deal, then the forecaster has less confidence in the track predicted due to the greater uncertainty. Large differences between model predictions can also indicate wind shear in the atmosphere, which could affect the intensity forecast as well.
Tested in 1989 and 1990, The Vic Ooyama Barotropic (VICBAR) model used a cubic-B spline
Spline (mathematics)
In mathematics, a spline is a sufficiently smooth piecewise-polynomial function. In interpolating problems, spline interpolation is often preferred to polynomial interpolation because it yields similar results, even when using low-degree polynomials, while avoiding Runge's phenomenon for higher...
representation of variables for the objective analysis of observations and solutions to the shallow-water prediction equations on nested domains, with the boundary conditions defined as the global forecast model. It was implemented operationally as the Limited Area Sine Transform Barotropic (LBAR) model in 1992, using the GFS for boundary conditions. By 1990, Australia had developed its own storm surge model which was able to be run in a few minutes on a personal computer. The Japan Meteorological Agency
Japan Meteorological Agency
The or JMA, is the Japanese government's weather service. Charged with gathering and reporting weather data and forecasts in Japan, it is a semi-autonomous part of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport...
(JMA) developed its own Typhoon Model (TYM) in 1994, and in 1998, the agency began using its own dynamic storm surge
Storm surge
A storm surge is an offshore rise of water associated with a low pressure weather system, typically tropical cyclones and strong extratropical cyclones. Storm surges are caused primarily by high winds pushing on the ocean's surface. The wind causes the water to pile up higher than the ordinary sea...
model.
The Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting
Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting model
The Hurricane Weather Research and Forecasting model is a specialized version of the Weather Research and Forecasting model and is used to forecast the track and intensity of tropical cyclones. The model was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , the U.S...
(HWRF) model is a specialized version of the Weather Research and Forecasting
Weather Research and Forecasting model
The Weather Research and Forecasting model, , is a specific computer program with a dual use for forecasting and research. It was created through a partnership that includes the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , the National Center for Atmospheric Research , and more than 150 other...
(WRF) model and is used to forecast
Weather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a given location. Human beings have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia, and formally since the nineteenth century...
the track and intensity
Tropical cyclone scales
Tropical systems are officially ranked on one of several tropical cyclone scales according to their maximum sustained winds and in what oceanic basin they are located...
of tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
s. The model was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , pronounced , like "noah", is a scientific agency within the United States Department of Commerce focused on the conditions of the oceans and the atmosphere...
(NOAA), the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory
United States Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps and conducts a program of scientific research and development. NRL opened in 1923 at the instigation of Thomas Edison...
, the University of Rhode Island
University of Rhode Island
The University of Rhode Island is the principal public research university in the U.S. state of Rhode Island. Its main campus is located in Kingston. Additional campuses include the Feinstein Campus in Providence, the Narragansett Bay Campus in Narragansett, and the W. Alton Jones Campus in West...
, and Florida State University
Florida State University
The Florida State University is a space-grant and sea-grant public university located in Tallahassee, Florida, United States. It is a comprehensive doctoral research university with medical programs and significant research activity as determined by the Carnegie Foundation...
. It became operational in 2007. Despite improvements in track forecasting, predictions of the intensity of a tropical cyclone based on numerical weather prediction continue to be a challenge, since statiscal methods continue to show higher skill over dynamical guidance. Other than the specialized guidance, global guidance such as the GFS, Unified Model
Unified Model
The Unified Model is a Numerical Weather Prediction and climate modeling software suite originally developed by the United Kingdom Met Office, and now both used and further developed by many weather-forecasting agencies around the world...
(UKMET), NOGAPS, Japanese Global Spectral Model (GSM), European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts
European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts
The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts is an independent intergovernmental organisation supported by 19 European Member States and 15 Co-operating States...
model, France's Action de Recherche Petite Echelle Grande Echelle (ARPEGE) and Aire Limit´ee Adaptation Dynamique Initialisation (ALADIN) models, India's National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting
National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting
National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting is a national agency for weather forecasting under the Ministry of Earth Sciences, , Government of India....
(NCMWRF) model, Korea's Global Data Assimilation and Prediction System (GDAPS) and Regional Data Assimilation and Prediction System (RDAPS) models, Hong Kong/China's Operational Regional Spectral Model (ORSM) model, and Canadian Global Environmental Multiscale Model
Global Environmental Multiscale Model
The Global Environmental Multiscale Model is an integrated forecasting and data assimilation system developed in the Recherche en Prévision Numérique , Meteorological Research Branch , and the Canadian Meteorological Centre ....
(GEM) model are used for track and intensity purposes.
Timeliness
Some models do not produce output quickly enough to be used for the forecast cycle immediately after the model starts running (including HWRF, GFDL, and FSSE). Most of the above track models (except CLIPER) require data from global weather modelsAtmospheric model
An atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It can supplement these equations with parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, radiation, moist processes , heat exchange, soil, vegetation, surface...
, such as the GFS, which produce output about four hours after the synoptic times of 0000, 0600, 1200, and 1800 Universal Coordinated Time (UTC). For half of their forecasts, the NHC issues forecasts only three hours after that time, so some "early" models — NHC90, BAM, and LBAR — are run using a 12-hour-old forecast for the current time. "Late" models, such as the GFS and GFDL, finish after the advisory has already been issued. These models are interpolated
Interpolation
In the mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a method of constructing new data points within the range of a discrete set of known data points....
to the current storm position for use in the following forecast cycle — for example, GFDI, the interpolated version of the GFDL model.
Consensus methods
Using a consensus of forecast models reduces forecast error. Trackwise, the GUNA model is a consensus of the interpolated versions of the GFDL, UKMET with quality control applied to the cyclone tracker, United States Navy NOGAPS, and GFS models. The version of the GUNA corrected for model biases is known as the CGUN. The TCON consensus is the GUNA consensus plus the Hurricane WRF model. The version of the TCON corrected for model biases is known as the TCCN. A lagged average of the last two runs of the members within the TCON plus the ECMWF model is known as the TVCN consensus. The version of the TVCN corrected for model biases is the TVCC consensus.For intensity, a combination of the LGEM, interpolated GFDL, interpolated HWRF, and DSHIPS models is known as the ICON consensus. The lagged average of the last two runs of models within the ICON consensus is called the IVCN consensus. Across the northwest Pacific and Southern Hemisphere, a ten-member STIPS consensus is formed from the output of the NOGAPS,
GFS, the Japanese GSM, the Coupled Ocean/Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System (COAMPS), the UKMET, the Japanese TYM, the GFDL with NOGAPS boundary conditions, the Air Force Weather Agency
Air Force Weather Agency
The Air Force Weather Agency is a Field Operating Agency and the lead military meteorology center of the United States Air Force...
(AFWA) Model, the Australian Tropical Cyclone Local Area Prediction System, and the Weber Barotropic Model.
Ensemble methods
No model is ever perfectly accurate because it is impossible to learn exactly everything about the atmosphere in a timely enough manner, and atmospheric measurements that are taken are not completely accurate. The use of the ensemble method of forecasting, whether it be a multi-model ensemble, or numerous ensemble members based on the global model, helps define the uncertainty and further limit errors.The JMA has produced an 11-member ensemble forecast system for typhoons known as the Typhoon Ensemble Prediction System (TEPS) since February 2008, which is run out to 132 hours into the future. It uses a lower resolution version (with larger grid spacing) of its GSM, with ten perturbed members and one non-perturbed member. The system reduces errors by an average of 40 kilometres (24.9 mi) five days into the future when compared to its higher resolution GSM.
The Florida State Super Ensemble (FSSE) is produced from a suite of models which then uses statistical regression equations developed over a training phase to reduce their biases, which produces forecasts better than the member models or their mean solution. It uses 11 global models, including five developed at Florida State University
Florida State University
The Florida State University is a space-grant and sea-grant public university located in Tallahassee, Florida, United States. It is a comprehensive doctoral research university with medical programs and significant research activity as determined by the Carnegie Foundation...
, the Unified Model, the GFS, the NOGAPS, the United States Navy NOGAPS, the Australian Bureau of Meteorology Research Centre (BMRC) model, and Canadian Recherche en Prévision Numérique
Recherche en Prévision Numérique
The center Recherche en Prévision Numérique is responsible for the research and development of the modelling component of the Numerical Weather Prediction System for the Canadian Meteorological Centre and the Regional Meteorological Centers of the Meteorological Service of Canada , Environment...
(RPN) model. It shows significant skill in track, intensity, and rainfall predictions of tropical cyclones.
The Systematic Approach Forecast Aid (SAFA) was developed by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center to create a selective consensus forecast which removed more erroneous forecasts at a 72 hour time frame from consideration using the United States Navy NOGAPS model, the GFDL, the Japan Meteorological Agency's global and typhoon models, as well as the UKMET. It has performed so well that operational forecasters in its first five years of existence went from using it 55 percent of the time to 97 percent of the time.
See also
- Tropical cyclone forecastingTropical cyclone forecastingTropical cyclone forecasting is the science and art of forecasting where a tropical cyclone's center, and its effects, are expected to be at some point in the future. There are several elements to tropical cyclone forecasting: track forecasting, intensity forecasting, rainfall forecasting, storm...
- Tropical cyclone rainfall forecastingTropical cyclone rainfall forecastingTropical cyclone rainfall forecasting involves using scientific models and other tools to predict the precipitation expected in tropical cyclones such as hurricanes and typhoons. Knowledge of tropical cyclone rainfall climatology is helpful in the determination of a tropical cyclone rainfall...
- Weather forecastingWeather forecastingWeather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a given location. Human beings have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia, and formally since the nineteenth century...
External links
- Tropical Cyclone Forecasters Reference Guide, Chapter 5
- Model Analyses and Forecasts from NCEP
- National Hurricane Center Forecast Model Background and Information

