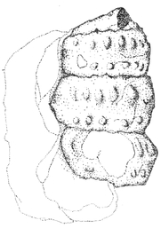
Turrilitidae
Encyclopedia
Turrilitidae is a family
of extinct heteromorph ammonite
cephalopod
s. All members had shells that coiled helically that tended to resemble auger shells.
The ecological roles turrilitids played is largely unknown, as experts are still speculating what niches they filled. Some, such as Didymoceras
, are suspected of floating in the water column, while others, such as the eponymous Turrilites
, are believed to have been bottom-dwellers.
The name of the type genus Turrilites is a hybrid formation based on Latin turris "tower" and Greek lithos "stone", coined by Lamarck in 1801.
Although they were diverse, with a worldwide distribution, the turrilitids, along with all other ammonites, did not survive the Cretaceous-Tertiary Extinction event
.
Family (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
of extinct heteromorph ammonite
Ammonite
Ammonite, as a zoological or paleontological term, refers to any member of the Ammonoidea an extinct subclass within the Molluscan class Cephalopoda which are more closely related to living coleoids Ammonite, as a zoological or paleontological term, refers to any member of the Ammonoidea an extinct...
cephalopod
Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda . These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles modified from the primitive molluscan foot...
s. All members had shells that coiled helically that tended to resemble auger shells.
The ecological roles turrilitids played is largely unknown, as experts are still speculating what niches they filled. Some, such as Didymoceras
Didymoceras
Didymoceras is an extinct genus of ammonite cephalopod. It is one of the most bizarrely shaped genera, with a shell that spirals upwards into a loose, hooked tip...
, are suspected of floating in the water column, while others, such as the eponymous Turrilites
Turrilites
Turrilites is a helically coiled ammonoid cephalopod from the lower part of the Upper Cretaceous ; generally included in the Ancyloceratina. Previously it was included in the ammonoid suborder, Lytoceratina....
, are believed to have been bottom-dwellers.
The name of the type genus Turrilites is a hybrid formation based on Latin turris "tower" and Greek lithos "stone", coined by Lamarck in 1801.
Although they were diverse, with a worldwide distribution, the turrilitids, along with all other ammonites, did not survive the Cretaceous-Tertiary Extinction event
Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, formerly named and still commonly referred to as the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction event, occurred approximately 65.5 million years ago at the end of the Maastrichtian age of the Cretaceous period. It was a large-scale mass extinction of animal and plant...
.

