
Uncertain inference
Encyclopedia
Uncertain inference was first described by Rijsbergen as a way to formally define a query and document relationship in Information retrieval
. This formalization is a logical implication with an attached measure of uncertainty.
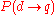
A user's query can be interpreted as a set of assertions about the desired document. It is the system's task to infer, given a particular document, if the query assertions are true. If they are, the document is retrieved.
In many cases the contents of documents are not sufficient to assert the queries. A knowledge base of facts and rules is needed, but some of them may be uncertain because there may be a probability associated to using them for inference. Therefore, we can also refer to this as plausible inference. The plausibility of an inference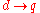 is a function of the plausibility of each query assertion. Rather than retrieving a document that exactly matches the query we should rank the documents based on their plausibility in regards to that query.
is a function of the plausibility of each query assertion. Rather than retrieving a document that exactly matches the query we should rank the documents based on their plausibility in regards to that query.
Since d and q are representations of documents user queries there is a possibility that they have errors and be uncertain. This will affect the plausibility to a given query.
By doing this it accomplishes two things:
Multimedia documents, like images or videos, have different inference properties for each datatype. They are also different from text document properties. The framework of plausible inference allows us to measure and combine the probabilities coming from these different properties.
Uncertain inference generalizes the notions of autoepistemic logic
, where truth values are either known or unknown, and when known, they are true or false.
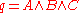
where A, B and C are query assertions, then for a document D we want the probability:
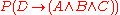
If we transform this into the conditional probability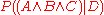 and if the query assertions are independent we can calculate the overall probability of the implication as the product of the individual assertions probabilities.
and if the query assertions are independent we can calculate the overall probability of the implication as the product of the individual assertions probabilities.
Probabilistic logic network
s is a system for performing uncertain inference; crisp true/false truth values are replaced not only by a probability, but also by a confidence level, indicating the certitude of the probability.
Markov logic network
s allow uncertain inference to be performed; uncertainties are computed using the maximum entropy principle, in analogy to the way that Markov chain
s describe the uncertainty of finite state machine
s.
Information retrieval
Information retrieval is the area of study concerned with searching for documents, for information within documents, and for metadata about documents, as well as that of searching structured storage, relational databases, and the World Wide Web...
. This formalization is a logical implication with an attached measure of uncertainty.
Definitions
Rijsbergen proposes that the measure of uncertainty of a document d to a query q be the probability of its logical implication, i.e.: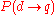
A user's query can be interpreted as a set of assertions about the desired document. It is the system's task to infer, given a particular document, if the query assertions are true. If they are, the document is retrieved.
In many cases the contents of documents are not sufficient to assert the queries. A knowledge base of facts and rules is needed, but some of them may be uncertain because there may be a probability associated to using them for inference. Therefore, we can also refer to this as plausible inference. The plausibility of an inference
 is a function of the plausibility of each query assertion. Rather than retrieving a document that exactly matches the query we should rank the documents based on their plausibility in regards to that query.
is a function of the plausibility of each query assertion. Rather than retrieving a document that exactly matches the query we should rank the documents based on their plausibility in regards to that query.Since d and q are representations of documents user queries there is a possibility that they have errors and be uncertain. This will affect the plausibility to a given query.
By doing this it accomplishes two things:
- Separate the processes of revising probabilities from the logic
- Separate the treatment of relevance from the treatment of requests
Multimedia documents, like images or videos, have different inference properties for each datatype. They are also different from text document properties. The framework of plausible inference allows us to measure and combine the probabilities coming from these different properties.
Uncertain inference generalizes the notions of autoepistemic logic
Autoepistemic logic
The autoepistemic logic is a formal logic for the representation and reasoning of knowledge about knowledge. While propositional logic can only express facts, autoepistemic logic can express knowledge and lack of knowledge about facts....
, where truth values are either known or unknown, and when known, they are true or false.
Example
If we have a query of the form: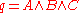
where A, B and C are query assertions, then for a document D we want the probability:
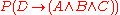
If we transform this into the conditional probability
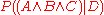 and if the query assertions are independent we can calculate the overall probability of the implication as the product of the individual assertions probabilities.
and if the query assertions are independent we can calculate the overall probability of the implication as the product of the individual assertions probabilities.Further work
Croft and Krovetz applied uncertain inference to an information retrieval system for office documents they called OFFICER. In office documents the independence assumption is valid since the query will focus on their individual attributes. Besides analysing the content of documents one can also query about the author, size, topic or collection for example. They devised methods to compare document and query attributes, infer their plausibility and combine it into an overall rating for each document. Besides that uncertainty of document and query contents also had to be addressed.Probabilistic logic network
Probabilistic logic network
A probabilistic logic network is a novel conceptual, mathematical and computational approach to uncertain inference; inspired by logic programming, but using probabilities in place of crisp truth values, and fractional uncertainty in place of crisp known/unknown values...
s is a system for performing uncertain inference; crisp true/false truth values are replaced not only by a probability, but also by a confidence level, indicating the certitude of the probability.
Markov logic network
Markov logic network
A Markov logic network is a probabilistic logic which applies the ideas of a Markov network to first-order logic, enabling uncertain inference...
s allow uncertain inference to be performed; uncertainties are computed using the maximum entropy principle, in analogy to the way that Markov chain
Markov chain
A Markov chain, named after Andrey Markov, is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another, between a finite or countable number of possible states. It is a random process characterized as memoryless: the next state depends only on the current state and not on the...
s describe the uncertainty of finite state machine
Finite state machine
A finite-state machine or finite-state automaton , or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model used to design computer programs and digital logic circuits. It is conceived as an abstract machine that can be in one of a finite number of states...
s.

