
Underclocking
Encyclopedia
Underclocking, also known as downclocking, is the practice of modifying a synchronous circuit's timing settings to run at a lower clock rate
than it was specified to operate at. It may be said to be the computer equivalent of driving a car below the speed limit. Usually, underclocking is used to reduce a computer's power consumption and heat emission, sometimes also to increase the system's stability and compatibility
. Underclocking may be implemented by the factory, but many computers and components are end user underclockable.
or decrease the electrical power consumption
. This can provide increased system stability in high-heat environments, or can allow a system to run with a lower airflow (and therefore quieter
) cooling fan or without one at all. For example, a Pentium 4 processor clocked at 2.4 GHz can be "underclocked" to 1.8 GHz and can then be safely run with reduced fan speeds. This invariably comes at the expense of some system performance. However, the performance usually is reduced less than the reduction of clock speed because the performance often is limited by other bottlenecks: the hard disk
, disk controller
, Internet
, network
, etc.
s when performing everyday tasks (e.g. internet browsing and word processing), thus allowing the card to operate at lower temperature and thus lower, quieter fan speeds. The GPU can then be overclocked for more graphically intense applications, such as games. "Underclocking" a GPU will reduce performance, but this decrease will probably not be noticeable except in graphically intensive applications.
may be underclocked to match older systems as an inexpensive way to replace rare or discontinued memory. This might also be necessary if stability problems are encountered at higher settings, especially in a PC with several memory modules of different clock speed. If you underclock a PC processor, and do not change the clock factor or multiplier (the ratio between the processor and the memory clock speed), the memory will also be underclocked.
(automatic underclocking) is very common on laptop computers and has become common on desktop computers as well. In laptops, the processor is usually underclocked automatically whenever the computer is operating on batteries. Most modern notebook and desktop processors (utilizing power-saving schemes like AMD's
Cool'n'Quiet
and PowerNow!
) will underclock themselves automatically under a light processing load, when the machine BIOS and the operating system support it. Intel has also used this method on their Core 2 Duo and later processors, through a feature called SpeedStep
.
Some processors underclock automatically as a defensive measure, to prevent overheating which could cause permanent damage. When such a processor reaches a temperature
level deemed too high for safe operation, the thermal control circuit activates, automatically decreasing the clock and CPU core voltage
until the temperature has returned to a safe level. In a properly cooled environment, this mechanism should trigger rarely (if ever).
There are several different underclocking competitions similar in format to overclocking
competitions, except the goal is to have the lowest clocked computer, as opposed to the highest.
In general, the power consumed by a CPU with a capacitance
C, running at frequency f and voltage V is approximately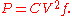
. The kernel includes five governors by default: Conservative, Ondemand, Performance, Powersave, and Userspace. The Conservative and Ondemand governors adjust the clock rate
depending on the CPU load, but each with different algorithms. The Ondemand governor jumps to maximum frequency on CPU load and decreases the frequency step by step on CPU idle, whereas the Conservative governor increases the frequency step by step on CPU load and jumps to lowest frequency on CPU idle. The Performance, Powersave and Userspace governors set the clock rate
statically: Performance to the highest available, Powersave to the lowest available, and Userspace to a frequency determined and controlled by the user.
or with Windows
applications, or dynamically using features such as Intel's SpeedStep
or AMD's Cool'n'Quiet
.
uses a 900 MHz Intel Celeron
M processor underclocked to 630 MHz.
s and PDA
s, such as the Motorola Droid
, Palm Pre
, and Apple iPhone
, iPhone 3G
, iPhone 3GS
, iPhone 4
and iPhone 4s
, use the "underclocking" of a more powerful processor, rather than the full clocking of a less powerful processor, to maximize battery life. The designers for such mobile devices often discover that a slower processor gives worse battery life than a more powerful processor at a lower clock rate
.
They select a processor on the basis of the performance per watt
of the processor.
(and thus clockrate of a CPU), the closer its performance will be to that of the bus, and the less time it will spend waiting.
Clock rate
The clock rate typically refers to the frequency that a CPU is running at.For example, a crystal oscillator frequency reference typically is synonymous with a fixed sinusoidal waveform, a clock rate is that frequency reference translated by electronic circuitry into a corresponding square wave...
than it was specified to operate at. It may be said to be the computer equivalent of driving a car below the speed limit. Usually, underclocking is used to reduce a computer's power consumption and heat emission, sometimes also to increase the system's stability and compatibility
Compatibility
Compatibility may refer to:* Astrological compatibility* Compatibilism – a philosophical position* Compatibility * Compatibility * Compatibility * Electromagnetic compatibility* Interpersonal compatibility-Computing:...
. Underclocking may be implemented by the factory, but many computers and components are end user underclockable.
CPU underclocking
For microprocessors, the purpose is generally to decrease the need for heat dissipation devicesComputer cooling
Computer cooling is required to remove the waste heat produced by computer components, to keep components within their safe operating temperature limits.Various cooling methods help to improve processor performance or reduce the noise of cooling fans....
or decrease the electrical power consumption
CPU power dissipation
Central processing unit power dissipation or CPU power dissipation is the process in which central processing units consume electrical energy, and dissipate this energy both by the action of the switching devices contained in the CPU and by the energy lost in the form of heat due to the impedance...
. This can provide increased system stability in high-heat environments, or can allow a system to run with a lower airflow (and therefore quieter
Quiet PC
A quiet PC is a personal computer that makes little noise. Common uses for quiet PCs include video editing, sound mixing, home servers, and home theater PCs. A typical quiet PC uses quiet cooling and storage devices and energy-efficient parts....
) cooling fan or without one at all. For example, a Pentium 4 processor clocked at 2.4 GHz can be "underclocked" to 1.8 GHz and can then be safely run with reduced fan speeds. This invariably comes at the expense of some system performance. However, the performance usually is reduced less than the reduction of clock speed because the performance often is limited by other bottlenecks: the hard disk
Hard disk
A hard disk drive is a non-volatile, random access digital magnetic data storage device. It features rotating rigid platters on a motor-driven spindle within a protective enclosure. Data is magnetically read from and written to the platter by read/write heads that float on a film of air above the...
, disk controller
Disk controller
The disk controller is the circuit which enables the CPU to communicate with a hard disk, floppy disk or other kind of disk drive.Early disk controllers were identified by their storage methods and data encoding. They were typically implemented on a separate controller card...
, Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
, network
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
, etc.
Graphics cards
"Underclocking" can also be performed on graphics card processors (graphics processing units; GPUs), usually with the aim of reducing heat output. For instance, it is possible to set a GPU to run at lower clock rateClock rate
The clock rate typically refers to the frequency that a CPU is running at.For example, a crystal oscillator frequency reference typically is synonymous with a fixed sinusoidal waveform, a clock rate is that frequency reference translated by electronic circuitry into a corresponding square wave...
s when performing everyday tasks (e.g. internet browsing and word processing), thus allowing the card to operate at lower temperature and thus lower, quieter fan speeds. The GPU can then be overclocked for more graphically intense applications, such as games. "Underclocking" a GPU will reduce performance, but this decrease will probably not be noticeable except in graphically intensive applications.
Memory underclocking
Newer and faster RAMRam
-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
may be underclocked to match older systems as an inexpensive way to replace rare or discontinued memory. This might also be necessary if stability problems are encountered at higher settings, especially in a PC with several memory modules of different clock speed. If you underclock a PC processor, and do not change the clock factor or multiplier (the ratio between the processor and the memory clock speed), the memory will also be underclocked.
When used
Dynamic frequency scalingDynamic frequency scaling
Dynamic frequency scaling is a technique in computer architecture whereby the frequency of a microprocessor can be automatically adjusted "on the fly," either to conserve power or to reduce the amount of heat generated by the chip...
(automatic underclocking) is very common on laptop computers and has become common on desktop computers as well. In laptops, the processor is usually underclocked automatically whenever the computer is operating on batteries. Most modern notebook and desktop processors (utilizing power-saving schemes like AMD's
Advanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. or AMD is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Sunnyvale, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for commercial and consumer markets...
Cool'n'Quiet
Cool'n'Quiet
Cool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
and PowerNow!
PowerNow!
PowerNow! is speed throttling and power saving technology of AMD's processors used in laptops. The CPU's clock speed and VCore are automatically decreased when the computer is under low load or idle, to save battery power, reduce heat and noise...
) will underclock themselves automatically under a light processing load, when the machine BIOS and the operating system support it. Intel has also used this method on their Core 2 Duo and later processors, through a feature called SpeedStep
SpeedStep
SpeedStep is a trademark for a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies built into some Intel microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be dynamically changed by software...
.
Some processors underclock automatically as a defensive measure, to prevent overheating which could cause permanent damage. When such a processor reaches a temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
level deemed too high for safe operation, the thermal control circuit activates, automatically decreasing the clock and CPU core voltage
CPU core voltage
The CPU core voltage is the power supply voltage supplied to the CPU , GPU, or other device containing a processing core...
until the temperature has returned to a safe level. In a properly cooled environment, this mechanism should trigger rarely (if ever).
There are several different underclocking competitions similar in format to overclocking
Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of operating a computer component at a higher clock rate than it was designed for or was specified by the manufacturer, but some manufacturers purposely underclock their components to improve battery life. Many people just overclock or 'rightclock' their hardware to...
competitions, except the goal is to have the lowest clocked computer, as opposed to the highest.
Advantages
- Reduced electrical power consumption, especially when combined with undervolting (i.e., reducing the component’s voltage below the nominal). For instance, by underclocking an Athlon XP 1700+ processor from 1466 to 1000 MHz and reducing the core voltage from 1.75 to 1.15V, a computer user reduced the power consumption from 64.0 to 21.6W, i.e., 66% power reduction, with only 26% less performance. The same is true for newer processors: When a single-core Intel CPU was 20% underclocked, the PC’s performance was down only 13% with a 49% power reduction.
In general, the power consumed by a CPU with a capacitance
Capacitance
In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor...
C, running at frequency f and voltage V is approximately

- Reduced heat generation, which is exactly proportional to the power consumption.
- Less noiseNoise pollutionNoise pollution is excessive, displeasing human, animal or machine-created environmental noise that disrupts the activity or balance of human or animal life...
because the cooling fans may be slowed down, or even eliminated. A cooling fan’s efficiency is proportional to its rotation speed, but it noise grows much more. - Longer hardware lifespan.
- Increased stability.
- Reduced noise from cooling parts due to reduced heat dissipation requirements.
- Increased battery life.
- Better compatibility with old applications.
Linux
Linux kernel supports CPU frequency modulation. In supported processors, using cpufreq to gain access to this feature gives the system administrator a variable level of control over the CPU's clock rateClock rate
The clock rate typically refers to the frequency that a CPU is running at.For example, a crystal oscillator frequency reference typically is synonymous with a fixed sinusoidal waveform, a clock rate is that frequency reference translated by electronic circuitry into a corresponding square wave...
. The kernel includes five governors by default: Conservative, Ondemand, Performance, Powersave, and Userspace. The Conservative and Ondemand governors adjust the clock rate
Clock rate
The clock rate typically refers to the frequency that a CPU is running at.For example, a crystal oscillator frequency reference typically is synonymous with a fixed sinusoidal waveform, a clock rate is that frequency reference translated by electronic circuitry into a corresponding square wave...
depending on the CPU load, but each with different algorithms. The Ondemand governor jumps to maximum frequency on CPU load and decreases the frequency step by step on CPU idle, whereas the Conservative governor increases the frequency step by step on CPU load and jumps to lowest frequency on CPU idle. The Performance, Powersave and Userspace governors set the clock rate
Clock rate
The clock rate typically refers to the frequency that a CPU is running at.For example, a crystal oscillator frequency reference typically is synonymous with a fixed sinusoidal waveform, a clock rate is that frequency reference translated by electronic circuitry into a corresponding square wave...
statically: Performance to the highest available, Powersave to the lowest available, and Userspace to a frequency determined and controlled by the user.
Windows
"Underclocking" can be done manually in the BIOSBIOS
In IBM PC compatible computers, the basic input/output system , also known as the System BIOS or ROM BIOS , is a de facto standard defining a firmware interface....
or with Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
applications, or dynamically using features such as Intel's SpeedStep
SpeedStep
SpeedStep is a trademark for a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies built into some Intel microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be dynamically changed by software...
or AMD's Cool'n'Quiet
Cool'n'Quiet
Cool'n'Quiet is a CPU speed throttling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon 64 processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this technology is to reduce overall power consumption and lower heat...
.
Asus Eee PC
Some versions of the Asus Eee PCASUS Eee PC
The Asus Eee PC is a subnotebook/netbook computer line from ASUSTeK Computer Incorporated, and a part of the Asus Eee product family. At the time of its introduction in late 2007, it was noted for its combination of a light weight, Linux operating system, solid-state drive , and relatively low cost...
uses a 900 MHz Intel Celeron
Celeron
Celeron is a brand name given by Intel Corp. to a number of different x86 computer microprocessor models targeted at budget personal computers....
M processor underclocked to 630 MHz.
Smartphones and PDAs
Most smartphoneSmartphone
A smartphone is a high-end mobile phone built on a mobile computing platform, with more advanced computing ability and connectivity than a contemporary feature phone. The first smartphones were devices that mainly combined the functions of a personal digital assistant and a mobile phone or camera...
s and PDA
PDA
A PDA is most commonly a Personal digital assistant, also known as a Personal data assistant, a mobile electronic device.PDA may also refer to:In science, medicine and technology:...
s, such as the Motorola Droid
Motorola Droid
The Motorola Droid is an Internet and multimedia enabled smartphone designed by Motorola, which runs Google's Android operating system. The Droid had been publicized under the codenames Sholes and Tao and the model number A855...
, Palm Pre
Palm Pre
The Palm Pre is a multimedia smartphone designed and marketed by Palm with a multi-touch screen and a sliding keyboard. The smartphone was the first to use Palm's Linux based mobile operating system, webOS...
, and Apple iPhone
IPhone
The iPhone is a line of Internet and multimedia-enabled smartphones marketed by Apple Inc. The first iPhone was unveiled by Steve Jobs, then CEO of Apple, on January 9, 2007, and released on June 29, 2007...
, iPhone 3G
IPhone 3G
The iPhone 3G is the second generation of iPhone designed and marketed by Apple Inc.. It was the successor to the original iPhone, and is succeeded by the iPhone 3GS. Introduced on June 9, 2008 at the WWDC 2008 at the Moscone Center, San Francisco...
, iPhone 3GS
IPhone 3GS
-Camera:The iPhone 3GS features an improved 3 megapixel camera manufactured by OmniVision. In addition to the higher megapixel count, it also features auto-focus, auto white balance and auto macro and is capable of capturing VGA video...
, iPhone 4
IPhone 4
The iPhone 4 is a touchscreen slate smartphone developed by Apple Inc. It is the fourth generation iPhone, and successor to the iPhone 3GS. It is particularly marketed for video calling , consumption of media such as books and periodicals, movies, music, and games, and for general web and e-mail...
and iPhone 4s
IPhone 4S
The iPhone 4S is a touchscreen slate smartphone developed by Apple Inc. It is the fifth generation of the iPhone, a device that combines a widescreen iPod with a touchscreen, mobile phone, and internet communicator. It retains the exterior design of its predecessor, iPhone 4, but is host to a range...
, use the "underclocking" of a more powerful processor, rather than the full clocking of a less powerful processor, to maximize battery life. The designers for such mobile devices often discover that a slower processor gives worse battery life than a more powerful processor at a lower clock rate
Clock rate
The clock rate typically refers to the frequency that a CPU is running at.For example, a crystal oscillator frequency reference typically is synonymous with a fixed sinusoidal waveform, a clock rate is that frequency reference translated by electronic circuitry into a corresponding square wave...
.
They select a processor on the basis of the performance per watt
Performance per watt
In computing, performance per watt is a measure of the energy efficiency of a particular computer architecture or computer hardware. Literally, it measures the rate of computation that can be delivered by a computer for every watt of power consumed....
of the processor.
Performance
The performance of an "underclocked" machine will often be better than might be expected. Under normal desktop use, the full power of the CPU is rarely needed. Even when the system is busy, a large amount of time is usually spent waiting for data from memory, disk, or other devices. Such devices communicate with the CPU through a bus which operates at a much lower bandwidth. Generally, the lower the CPU multiplierCPU multiplier
In computing, the clock multiplier measures the ratio of an internal CPU clock rate to the externally supplied clock. A CPU with a 10x multiplier will thus see 10 internal cycles for every external clock cycle...
(and thus clockrate of a CPU), the closer its performance will be to that of the bus, and the less time it will spend waiting.

