
Computer cooling
Encyclopedia

Waste heat
Waste heat sometimes called Secondary heat or Low-grade heat refers to heat produced by machines, electrical equipment and industrial processes for which no useful application is found. Energy is often produced by a heat engine, running on a source of high-temperature heat...
produced by computer components, to keep components within their safe operating temperature
Operating temperature
An operating temperature is the temperature at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the device function and application context, and ranges from the minimum operating temperature to the...
limits.
Various cooling methods help to improve processor
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
performance or reduce the noise of cooling fans.
Components which produce heat and are susceptible to performance loss and damage include integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
s such as CPU
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
s, chipset
Chipset
A chipset, PC chipset, or chip set refers to a group of integrated circuits, or chips, that are designed to work together. They are usually marketed as a single product.- Computers :...
and graphics cards
Video card
A video card, Graphics Card, or Graphics adapter is an expansion card which generates output images to a display. Most video cards offer various functions such as accelerated rendering of 3D scenes and 2D graphics, MPEG-2/MPEG-4 decoding, TV output, or the ability to connect multiple monitors...
, along with hard drives (though excessive cooling of hard drives has been found to have negative effects). Overheated parts fail early and may give sporadic problems resulting in system freezes or crashes.
Both integral and peripheral means are used to keep the temperature of each component at a safe level. With regard to integral means, CPU and GPUs are designed with energy efficiency
Efficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal of efforts to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature...
, including heat dissipation, in mind; though improved efficiency may only allow increased performance instead of reduced heat. Peripheral means include heat sink
Heat sink
A heat sink is a term for a component or assembly that transfers heat generated within a solid material to a fluid medium, such as air or a liquid. Examples of heat sinks are the heat exchangers used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems and the radiator in a car...
s to increase the surface area which dissipates heat, fans
Fan (mechanical)
A mechanical fan is a machine used to create flow within a fluid, typically a gas such as air.A fan consists of a rotating arrangement of vanes or blades which act on the air. Usually, it is contained within some form of housing or case. This may direct the airflow or increase safety by preventing...
to speed up the exchange of air heated by the computer parts for cooler ambient air, and in some cases softcooling, the throttling of computer parts in order to decrease heat generation.
As a safety measure, many computers are designed to turn themselves off if the internal temperature exceeds a certain point. Alternatively, some have an option in their BIOS that allows the user to determine if the system emits an alarm beep or shuts itself down when the core temperature reaches the level set by the user. However, setting this incorrectly can result in hardware damage or erratic system behaviour.
Causes of heat build up
The amount of heat generated by an integrated circuitIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
(e.g., a CPU
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
or GPU
Graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit or GPU is a specialized circuit designed to rapidly manipulate and alter memory in such a way so as to accelerate the building of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display...
), the prime cause of heat build up in modern computers, is a function of the efficiency of its design, the technology used in its construction and the frequency and voltage at which it operates.

Thermodynamic equilibrium
In thermodynamics, a thermodynamic system is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium when it is in thermal equilibrium, mechanical equilibrium, radiative equilibrium, and chemical equilibrium. The word equilibrium means a state of balance...
. For reliable operation, the equilibrium temperature must be sufficiently low for the structure of the computer's circuits to survive.
Cooling can be hindered by:
- Dust acting as a thermal insulator and impeding airflow, thereby reducing heat sink and fan performance.
- Poor airflow including turbulenceTurbulenceIn fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
due to friction against impeding components such as ribbon cables, or improper orientation of fans, can reduce the amount of air flowing through a case and even create localized whirlpools of hot air in the case. - Poor heat transfer due to a lack of, or poor application of thermal compounds and sufficient surface area of heat sinks to radiate off the heat.
Damage prevention
Thermal sensors in some CPUs and GPUs can shut down the computer when high temperatures are detected. However, reliance on such measures may not prevent repeated incidents from permanently damaging the integrated circuit.An integrated circuit may also shut down parts of the circuit when it is idling, or to scale back the clock speed under low workloads or high temperatures, with the goal of reducing both power use and heat generation.
Air cooling
Fans are most commonly used for air cooling. A computer fan may be attached to the computer case, or attached to a CPU, GPUGraphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit or GPU is a specialized circuit designed to rapidly manipulate and alter memory in such a way so as to accelerate the building of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display...
, chipset, PSU
Power supply
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy...
, hard drive
Hard disk
A hard disk drive is a non-volatile, random access digital magnetic data storage device. It features rotating rigid platters on a motor-driven spindle within a protective enclosure. Data is magnetically read from and written to the platter by read/write heads that float on a film of air above the...
or PCI
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Conventional PCI is a computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer...
slot. Common fan sizes include 40, 60, 80, 92, 120, and 140 mm. Recently, 200mm fans have begun to creep into the performance market, as well as even larger sizes such as 230 and 240mm.
In desktops

Desktop computer
A desktop computer is a personal computer in a form intended for regular use at a single location, as opposed to a mobile laptop or portable computer. Early desktop computers are designed to lay flat on the desk, while modern towers stand upright...
s typically use one or more fans for cooling. Almost all desktop power supplies have at least one fan to exhaust air from the case. Most manufacturers recommend bringing cool, fresh air in at the bottom front of the case, and exhausting warm air from the top rear.
If there is more air being forced into the system than is being pumped out (due to an imbalance in the number or strength of fans), this is referred to as a "positive" airflow, as the pressure inside the unit would be higher than outside. A balanced or neutral airflow is the most efficient, although a slightly positive airflow results in less dust build up if dust filters are used. Negative pressure inside the case can create problems such as clogged optical drives due to sucking in air (and dust).
In high density computing
Data centerData center
A data center is a facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems...
s typically contain many racks of flat 1U
Rack unit
A rack unit or U is a unit of measure used to describe the height of equipment intended for mounting in a 19-inch rack or a 23-inch rack...
servers. Air is drawn in at the front of the rack and exhausted at the rear. Because data centers typically contain such large numbers of computers and other power-consuming devices, they risk overheating of the various components if no additional measures are taken. Thus, extensive HVAC
HVAC
HVAC refers to technology of indoor or automotive environmental comfort. HVAC system design is a major subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer...
systems are used. Often a raised floor is used so the area under the floor may be used as a large plenum for cooled air and power cabling.
Another way of accommodating large numbers of systems in a small space are blade chassis
Blade server
A blade server is a stripped down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Whereas a standard rack-mount server can function with a power cord and network cable, blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power...
. In contrast to the horizontal orientation of flat servers, blade chassis are often oriented vertically. This vertical orientation facilitates convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
. When the air is heated by the hot components, it tends to flow to the top on its own, creating a natural air flow along the boards. This stack effect
Stack effect
Stack effect is the movement of air into and out of buildings, chimneys, flue gas stacks, or other containers, and is driven by buoyancy. Buoyancy occurs due to a difference in indoor-to-outdoor air density resulting from temperature and moisture differences. The result is either a positive or...
can help to achieve the desired air flow and cooling. Some manufacturers expressly take advantage of this effect.
In laptop computing
Most laptops use air cooling in order to keep the CPU and other components within their operating temperature range. Because the fan's air is forced through a small port, the fan and heatsinks can be clogged by dust or be obstructed by objects placed near the port. This can cause overheating, and can be a cause of component failure in laptops. The severity of this problem varies with laptop design, its use and power dissipation. With recent reductions in CPU power dissipation, this problem can be anticipated to reduce in severity.Liquid submersion cooling
An uncommon practice is to submerge the computer's components in a thermally conductive liquid. Personal computers that are cooled in this manner do not generally require any fans or pumps, and may be cooled exclusively by passive heat exchange between the computer's parts, the cooling fluid and the ambient air. Extreme component density supercomputers such as the Cray-2Cray-2
The Cray-2 was a four-processor ECL vector supercomputer made by Cray Research starting in 1985. It was the fastest machine in the world when it was released, replacing the Cray Research X-MP designed by Steve Chen in that spot...
and Cray T90
Cray T90
The Cray T90 series was the last of a line of vector processing supercomputers manufactured by Cray Research, Inc, superseding the Cray C90 series...
used additional liquid to chilled liquid heat exchanger
Heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a piece of equipment built for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. The media may be separated by a solid wall, so that they never mix, or they may be in direct contact...
s in order to facilitate heat removal.
The liquid used must have sufficiently low electrical conductivity in order for it not to interfere with the normal operation of the computer's components. If the liquid is somewhat electrically conductive, it may be necessary to insulate certain parts of components susceptible to electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
, such as the CPU. For these reasons, it is preferred that the liquid be dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
.
Liquids commonly used in this manner include various liquids invented and manufactured for this purpose by 3M
3M
3M Company , formerly known as the Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation based in Maplewood, Minnesota, United States....
, such as Fluorinert
Fluorinert
Fluorinert is the trademarked brand name for the line of electronics coolant liquids sold commercially by 3M. It is an electrically insulating, stable fluorocarbon-based fluid which is used in various cooling applications. It is mainly used for cooling electronics...
. Various oils, including but not limited to cooking, motor and silicone oil
Silicone oil
A silicone oil is any polymerized siloxanes with organic side chains. They are formed of alternating silicon-oxygen atoms or siloxane, rather than carbon atoms . Other species attach to the tetravalent silicon atoms, not to the divalent oxygen atoms which are fully committed to forming the...
s have all been successfully used for cooling personal computers.
Evaporation can pose a problem, and the liquid may require either to be regularly refilled or sealed inside the computer's enclosure. Liquid may also slowly seep into and damage components, particularly capacitors, causing an initially functional computer to fail after hours or days immersed.
Waste heat reduction
Where full-power, full-featured modern computers are not required, some companies opt to use less powerful computers or computers with fewer features. For example: in an office setting, the ITInformation technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
department may choose a thin client
Thin client
A thin client is a computer or a computer program which depends heavily on some other computer to fulfill its traditional computational roles. This stands in contrast to the traditional fat client, a computer designed to take on these roles by itself...
or a diskless workstation
Diskless workstation
A diskless node is a workstation or personal computer without disk drives, which employs network booting to load its operating system from a server...
thus cutting out the heat-laden components such as hard drives and optical disks. These devices are also often powered with direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
from an external power supply
Power supply
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy...
brick which still wastes heat, but not inside the computer itself.
The components used can greatly affect the power consumption and hence waste heat. A VIA
VIA Technologies
VIA Technologies is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory, and is part of the Formosa Plastics Group. It is the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets...
EPIA
EPIA
VIA EPIA is a series of mini-ITX, nano-ITX and pico-ITX motherboards with integrated VIA processors...
motherboard with CPU typically generates approximately 25 watts of heat whereas a Pentium 4 motherboard typically generates around 140 watts. While the former has considerably less computing power, both types are adequate and responsive for tasks such as word processing and spreadsheets. Choosing a LCD
Liquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display is a flat panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals . LCs do not emit light directly....
monitor rather than a CRT
Cathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
can also reduce power consumption and excess room heat, as well as the added benefit of increasing available physical desk space.
Conductive and radiative cooling
Some laptopLaptop
A laptop, also called a notebook, is a personal computer for mobile use. A laptop integrates most of the typical components of a desktop computer, including a display, a keyboard, a pointing device and speakers into a single unit...
components, such as hard drives and optical drives, are commonly cooled by having them make contact with the computer's frame, increasing the surface area which can radiate and otherwise exchange heat. Several new 2GB and above DDR2 and DDR3 sticks of RAM, or system memory, are conductive cooled via a finned heatsink that is clipped onto the top edge of the memory stick. This also holds true for video cards that use a finned heatsink over the GPU for silent PC applications.
Spot cooling
In addition to system cooling, various individual components usually have their own cooling systems in place. Components which are frequently individually cooled include, but are not limited to, the CPUCentral processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
, GPU
Graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit or GPU is a specialized circuit designed to rapidly manipulate and alter memory in such a way so as to accelerate the building of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display...
and the Northbridge
Northbridge (computing)
The northbridge has historically been one of the two chips in the core logic chipset on a PC motherboard, the other being the southbridge. Increasingly these functions have migrated to the CPU chip itself, beginning with memory and graphics controllers. For Intel Sandy Bridge and AMD Fusion...
chip. Some cooling solutions employ one or more methods of cooling, and may also utilize logic and/or temperature sensors in order to vary the power used in active cooling components.
Passive heat-sink cooling

Thermal adhesive
Thermal adhesive is a type of thermally conductive glue used for electronic components and heatsinks. Thermal adhesive is similar to thermal paste in that it is used for transferring heat from one surface to another...
may be used. More commonly for a personal-computer CPU, a clamp holds the heat sink
Heat sink
A heat sink is a term for a component or assembly that transfers heat generated within a solid material to a fluid medium, such as air or a liquid. Examples of heat sinks are the heat exchangers used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems and the radiator in a car...
directly over the chip, with a thermal grease
Thermal grease
Thermal grease is a viscous fluid substance, originally with properties akin to grease, which increases the thermal conductivity of a thermal interface by filling...
or thermal pad
Thermal pad (computing)
In computing and electronics, thermal pads are a pre-formed square or rectangle of solid material commonly found on the underside of heatsinks to aid the conduction of heat away from the component being cooled and into the heatsink .As an alternative to thermal grease In computing and...
spread between. This block usually has fins and ridges to increase its surface area. The heat conductivity of metal is much better than that of air, and it radiates heat better than the component that it is protecting (usually an integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
or CPU). Until recently, fan-cooled aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
heat sinks were the norm for desktop computers. Today, many heat sinks feature copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
base-plates or are entirely made of copper.
Dust
Dust
Dust consists of particles in the atmosphere that arise from various sources such as soil dust lifted up by wind , volcanic eruptions, and pollution...
buildup between the metal fins of a heat sink gradually reduces efficiency, but can be countered with a gas duster by blowing away the dust along with any other unwanted excess material.
Passive heat sinks are commonly found on older CPUs, parts that do not get very hot (such as the chipset), and low-power computers.
Usually a heat-sink is attached to the integrated heat spreader (IHS), essentially a large, flat plate attached to the CPU, with conduction paste layered between. This dissipates or spreads the heat locally. Unlike a heat sink, a spreader is meant to redistribute heat, not to remove it. In addition, the IHS protects the fragile CPU.
Passive cooling involves no fan noise.
Active heat-sink cooling
Active heat-sink cooling uses the same principle as passive, with the addition of a fanFan (mechanical)
A mechanical fan is a machine used to create flow within a fluid, typically a gas such as air.A fan consists of a rotating arrangement of vanes or blades which act on the air. Usually, it is contained within some form of housing or case. This may direct the airflow or increase safety by preventing...
that blows over or through the heat sink. The air movement increases the rate at which the heat sink can exchange heat with the ambient air. Active heat sinks are the primary method of cooling modern processors and graphics cards.
The buildup of dust is greatly increased with active heat-sink cooling, because the fan continually takes in the dust present in the surrounding air.
Peltier cooling or thermoelectric cooling
In 1821 T. J. SeebeckThomas Johann Seebeck
Thomas Johann Seebeck was a physicist who in 1821 discovered the thermoelectric effect.Seebeck was born in Reval to a wealthy Baltic German merchant family. He received a medical degree in 1802 from the University of Göttingen, but preferred to study physics...
discovered that different metals, connected at two different junctions, will develop a micro-voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
if the two junctions are held at different temperatures. This effect is known as the "Seebeck effect
Thermoelectric effect
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice-versa. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, it creates a temperature difference...
"; it is the basic theory behind the TEC (thermoelectric cooling).
In 1834 Jean Peltier
Jean Charles Athanase Peltier
Jean Charles Athanase Peltier ]] – October 27, 1845, in Paris) was a French physicist.He discovered the calorific effect of electric current passing through the junction of two different metals...
discovered the inverse of the Seebeck effect, now known as the "Peltier effect
Thermoelectric effect
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice-versa. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, it creates a temperature difference...
". He found that applying a voltage to a thermocouple
Thermocouple
A thermocouple is a device consisting of two different conductors that produce a voltage proportional to a temperature difference between either end of the pair of conductors. Thermocouples are a widely used type of temperature sensor for measurement and control and can also be used to convert a...
creates a temperature differential between two sides. This results in an effective, albeit extremely inefficient heat pump
Heat pump
A heat pump is a machine or device that effectively "moves" thermal energy from one location called the "source," which is at a lower temperature, to another location called the "sink" or "heat sink", which is at a higher temperature. An air conditioner is a particular type of heat pump, but the...
.
Modern TECs use several stacked units each composed of dozens or hundreds of thermocouples laid out next to each other, which allows for a substantial amount of heat transfer
Heat transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the exchange of thermal energy from one physical system to another. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as heat conduction, convection, thermal radiation, and phase-change transfer...
. A combination of bismuth
Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with symbol Bi and atomic number 83. Bismuth, a trivalent poor metal, chemically resembles arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally uncombined, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead...
and tellurium is most commonly used for thermocouples.
As active heat pumps, TECs can cool the surface of components below ambient temperatures. This is impossible with common radiator cooled water cooling systems and heatpipe HSFs.
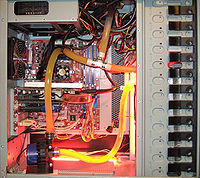
Water cooling
Mainframe computer
Mainframes are powerful computers used primarily by corporate and governmental organizations for critical applications, bulk data processing such as census, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning, and financial transaction processing.The term originally referred to the...
computers, water cooling has become a practice largely associated with overclocking
Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of operating a computer component at a higher clock rate than it was designed for or was specified by the manufacturer, but some manufacturers purposely underclock their components to improve battery life. Many people just overclock or 'rightclock' their hardware to...
in the form of either manufactured kits, or in the form of do-it-yourself setups assembled from individually gathered parts. The past few years has seen water cooling increasing its popularity with pre-assembled, moderate to high performance, desktop computers. Water has the ability to dissipate more heat from the parts being cooled than the various types of metals used in heatsinks, making it suitable for overclocking and high performance computer applications.
Advantages to water cooling include the fact that a system is not limited to cooling one component, but can be set up to cool the central processing unit, graphics processing unit, and/or other components at the same time with the same system. As opposed to air cooling, water cooling is also influenced less by the ambient temperature. Water cooling's comparatively low noise-level compares favorably to that of active cooling, which can become quite noisy. One disadvantage to water cooling is the potential for a coolant leak. Leaked coolant can damage any electronic components with which it comes into contact. Another drawback to water cooling is the complexity of the system; an active heat sink is much simpler to build, install, and maintain than a water cooling solution.
The IBM Aquasar system uses hot water cooling to achieve energy efficiency, the water being used to heat buildings as well.
Heat pipe

Capillary action
Capillary action, or capilarity, is the ability of a liquid to flow against gravity where liquid spontanously rise in a narrow space such as between the hair of a paint-brush, in a thin tube, or in porous material such as paper or in some non-porous material such as liquified carbon fiber, or in a...
, or, in earlier implementations, under gravitation). Heat pipes thus have a much higher effective thermal conductivity than solid materials. For use in computers, the heat sink on the CPU is attached to a larger radiator heat sink. Both heat sinks are hollow as is the attachment between them, creating one large heat pipe that transfers heat from the CPU to the radiator, which is then cooled using some conventional method. This method is expensive and usually used when space is tight (as in small form-factor PCs and laptops), or absolute quiet is needed (such as in computers used in audio production studios during live recording). Because of the efficiency of this method of cooling, many desktop CPUs and GPUs, as well as high end chipsets, use heat pipes in addition to active fan-based cooling to remain within safe operating temperatures.
Phase-change cooling
Phase-change cooling is an extremely effective way to cool the processor. A vapor compression phase-change cooler is a unit which usually sits underneath the PC, with a tube leading to the processor. Inside the unit is a compressor of the same type as in a window air conditioner. The compressor compresses a gas (or mixture of gases) which condenses it into a liquid. Then, the liquid is pumped up to the processor, where it passes through an expansion device, this can be from a simple capillary tube to a more elaborate thermal expansion valve. The liquid evaporates (changing phase), absorbing the heat from the processor as it draws extra energy from its environment to accommodate this change (see latent heatLatent heat
Latent heat is the heat released or absorbed by a chemical substance or a thermodynamic system during a process that occurs without a change in temperature. A typical example is a change of state of matter, meaning a phase transition such as the melting of ice or the boiling of water. The term was...
). The evaporation can produce temperatures reaching around −15 to −150 degrees Celsius. The gas flows down to the compressor and the cycle begins over again. This way, the processor can be cooled to temperatures ranging from −15 to −150 degrees Celsius, depending on the load, wattage of the processor, the refrigeration system (see refrigeration
Refrigeration
Refrigeration is a process in which work is done to move heat from one location to another. This work is traditionally done by mechanical work, but can also be done by magnetism, laser or other means...
) and the gas mixture used. This type of system suffers from a number of issues but, mainly, one must be concerned with dew point and the proper insulation of all sub-ambient surfaces that must be done (the pipes will sweat, dripping water on sensitive electronics).
Alternately, a new breed of cooling system is being developed, inserting a pump into the thermo siphon loop. This adds another degree of flexibility for the design engineer, as the heat can now be effectively transported away from the heat source and either reclaimed or dissipated to ambient. Junction temperature can be tuned by adjusting the system pressure; higher pressure equals higher fluid saturation temperatures. This allows for smaller condensers, smaller fans, and/or the effective dissipation of heat in a high ambient environment. These systems are, in essence, the next generation liquid cooling paradigm, as they are approximately 10 times more efficient than single phase water. Since the system uses a dielectric as the heat transport media, leaks do not cause a catastrophic failure of the electric system.
This type of cooling is seen as a more extreme way to cool components, since the units are relatively expensive compared to the average desktop. They also generate a significant amount of noise, since they are essentially refrigerators, however the compressor choice and air cooling system is the main determinant of this, allowing for flexibility for noise reduction based on the parts chosen.
Liquid nitrogen

Liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen is nitrogen in a liquid state at a very low temperature. It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. Liquid nitrogen is a colourless clear liquid with density of 0.807 g/mL at its boiling point and a dielectric constant of 1.4...
boils at -196 °C, far below the freezing point of water, it is valuable as an extreme coolant for short overclocking sessions.
In a typical installation of liquid nitrogen cooling, a copper or aluminum pipe is mounted on top of the processor or graphics card. After being heavily insulated against condensation, the liquid nitrogen is poured into the pipe, resulting in temperatures well below -100 °C.
Evaporation devices ranging from cut out heat sinks with pipes attached to custom milled copper containers are used to hold the nitrogen as well as to prevent large temperature changes. However, after the nitrogen evaporates, it has to be refilled. In the realm of personal computers, this method of cooling is seldom used in contexts other than overclocking
Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of operating a computer component at a higher clock rate than it was designed for or was specified by the manufacturer, but some manufacturers purposely underclock their components to improve battery life. Many people just overclock or 'rightclock' their hardware to...
trial-runs and record-setting attempts, as the CPU will usually expire within a relatively short period of time due to temperature stress
Stress (physics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a measure of the internal forces acting within a deformable body. Quantitatively, it is a measure of the average force per unit area of a surface within the body on which internal forces act. These internal forces are a reaction to external forces applied on the body...
caused by changes in internal temperature.
Although liquid nitrogen is non-flammable, it can condense oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
directly from air. Mixtures of liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen is nitrogen in a liquid state at a very low temperature. It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. Liquid nitrogen is a colourless clear liquid with density of 0.807 g/mL at its boiling point and a dielectric constant of 1.4...
and flammable materials can be dangerously explosive
Oxyliquit
An oxyliquit, also called liquid air explosive or liquid oxygen explosive, is an explosive material made of a mixture of liquid air or liquid oxygen with a suitable fuel, usually carbon or some organic chemical An oxyliquit, also called liquid air explosive or liquid oxygen explosive, is an...
.
Liquid helium
Liquid heliumLiquid helium
Helium exists in liquid form only at extremely low temperatures. The boiling point and critical point depend on the isotope of the helium; see the table below for values. The density of liquid helium-4 at its boiling point and 1 atmosphere is approximately 0.125 g/mL Helium-4 was first liquefied...
, colder than liquid nitrogen, has also been used for cooling. Liquid helium evaporates at -269 °C, and temperatures ranging from -230 to -240 °C have been measured from the heatsink.
But Helium is more rare and more expensive than Nitrogen. Also, extremely low temperatures can cause integrated circuits to stop functioning.
Soft cooling
Softcooling is the practice of utilizing software to take advantage of CPU power saving technologiesPower management
Power management is a feature of some electrical appliances, especially copiers, computers and computer peripherals such as monitors and printers, that turns off the power or switches the system to a low-power state when inactive. In computing this is known as PC power management and is built...
to minimize energy use. This is done using halt
HLT
In the x86 computer architecture, HLT is an assembly language instruction which halts the CPU until the next external interrupt is fired. Such interrupts are used by devices in order to signal to the CPU that an event occurred which the CPU shall react on...
instructions to turn off or put in standby state CPU subparts that aren't being used or by underclocking
Underclocking
Underclocking, also known as downclocking, is the practice of modifying a synchronous circuit's timing settings to run at a lower clock rate than it was specified to operate at. It may be said to be the computer equivalent of driving a car below the speed limit...
the CPU.
Undervolting
Undervolting is a practice of running the CPU or any other component with voltages below the device specifications. An undervolted component draws less power and thus produces less heat. The ability to do this varies by manufacturer, product line, and even different production runs of the same exact product (as well as that of other components in the system), but modern processors are typically shipped with voltages higher than strictly necessary. This provides a buffer zone so that the processor will have a higher chance of performing correctly under sub-optimal conditions, such as a lower quality mainboard (motherboard). However, too low a voltage will not allow the processor to function correctly, producing errors, system freezes or crashes, or the inability to turn the system on. Undervolting too far does not typically lead to hardware damage, though in worst-case scenarios, program or system files can be corrupted.This technique was generally employed by those seeking low-noise systems, as less cooling is needed because of the reduction of heat production. Since the popularity of hand-held or remote computers (Unmanned vehicles, mobile & cordless phones/camera/viewers, etc), undervolting is used to prolong battery endurance.
Integrated chip cooling techniques
Conventional cooling techniques all attach their “cooling” component to the outside of the computer chip, or via IHS and/or heat sinks. This “attaching” technique will always exhibit some thermal resistance, reducing its effectiveness. The heat can be more efficiently and quickly removed by directly cooling the local hot spots. At these locations, power dissipation of over 300W/cm2 (typical CPU are less than 100W/cm2, although future systems are expected to exceed 1000W/cm2 ) can occur. This form of local cooling is essential to developing high power density chips. This ideology has led to the investigation of integrating cooling elements into the computer chip. Currently there are two techniques: micro-channel heat sinks, and jet impingement cooling.In micro-channel heat sinks, channels are fabricated into the silicon chip (CPU), and coolant is pumped through them. The channels are designed with very large surface area which results in large heat transfers. Heat dissipation of 3000W/cm2 has been reported with this technique. In comparison to the Sun power density of around 7400W/cm2. The heat dissipation can be further increased if two-phase flow cooling is applied. Unfortunately the system requires large pressure drops, due to the small channels, and the heat flux is lower with dielectric coolants used in electronic cooling.
Another local chip cooling technique is jet impingement cooling. In this technique, a coolant is flown through a small orifice to form a jet. The jet is directed toward the surface of the CPU chip, and can effectively remove large heat fluxes. Heat dissipation of over 1000W/cm2has been reported. The system can be operated at lower pressure in comparison to the micro-channel method. The heat transfer can be further increased using two-phase flow cooling and by integrating return flow channels (hybrid between micro-channel heat sinks and jet impingement cooling).
Cooling and overclocking
Extra cooling is usually required by those who run parts of their computer (such as the CPU and GPU) at higher voltages and frequencies than manufacturer specifications call for, called overclockingOverclocking
Overclocking is the process of operating a computer component at a higher clock rate than it was designed for or was specified by the manufacturer, but some manufacturers purposely underclock their components to improve battery life. Many people just overclock or 'rightclock' their hardware to...
. Increasing performance by this modification of settings results in a greater amount of heat generated and thus increasing the risk of damage to components and/or premature failure.
The installation of higher performance, non-stock cooling may also be considered modding
Modding
Modding is a slang expression that is derived from the verb "modify". Modding refers to the act of modifying a piece of hardware or software or anything else for that matter, to perform a function not originally conceived or intended by the designer...
. Many overclockers simply buy more efficient, and often, more expensive fan and heat sink combinations, while others resort to more exotic ways of computer cooling, such as liquid cooling, Peltier effect heatpumps, heat pipe or phase change cooling.
There are also some related practices that have a positive impact in reducing system temperatures:
Heat sink lapping
Heat sink lapping is the smoothing and polishing of the contact (bottom) part of a heat sink to increase its heat transfer efficiency. The desired result is a contact area which has a more even surface, as a less even contact surface creates a larger amount of insulating air between the heat sink and the computer part it is attached to. Polishing the surface using a combination of fine sandpaper and abrasive polishing liquids can produce a mirror-like shine, an indicator of a very smooth metal surface. Even a curved surface can become extremely reflective, yet not particularly flat, as is the case with curved mirrors; thus heat sink quality is based on overall flatness, more than optical properties. Lapping a high quality heat sink can damage it, because, although the heat sink may become shiny, it is likely that more material will be removed from the edges, making the heat sink less effective overall.If attempted, a piece of float glass
Float glass
Float glass is a sheet of glass made by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, typically tin, although lead and various low melting point alloys were used in the past. This method gives the sheet uniform thickness and very flat surfaces. Modern windows are made from float glass...
should be used, as it self-levels as it cools and offers the most economical solution to producing a perfectly flat surface.
Use of exotic thermal conductive compounds
Some overclockers use special thermal compounds whose manufacturers claim to have a much higher efficiency than stock thermal pads. Heat sinks clean of any grease or other thermal transfer compounds have a very thin layer of these products applied, and then are placed normally over the CPU. Many of these compounds have a high proportion of silverSilver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
as their main ingredient due to its high thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity
In physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
. The resulting difference in the temperature of the CPU is measurable (several celsius degrees), so the heat transfer does appear to be superior to stock compounds. Some people experience negligible gains and have called to question the advantages of these exotic compounds, calling the style of application more important than the compound itself. Also note that there may be a 'setting' or 'curing' period and negligible gains may improve over time as the compound reaches its optimum thermal conductivity.
Use of rounded cables
Most older PCs use flat ribbon cableRibbon cable
A ribbon cable is a cable with many conducting wires running parallel to each other on the same flat plane. As a result the cable is wide and flat. Its name comes from the resemblance of the cable to a piece of ribbon.Ribbon cables are usually seen for internal peripherals in computers, such as...
s to connect storage drives (IDE
AT Attachment
Parallel ATA , originally ATA, is an interface standard for the connection of storage devices such as hard disks, solid-state drives, floppy drives, and optical disc drives in computers. The standard is maintained by X3/INCITS committee...
or SCSI
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, and electrical and optical interfaces. SCSI is most commonly used for hard disks and tape drives, but it...
). These large flat cables greatly impede airflow by causing drag and turbulence. Overclockers and modders often replace these with rounded cables, with the conductive wires bunched together tightly to reduce surface area. Theoretically, the parallel strands of conductors in a ribbon cable serve to reduce crosstalk (signal carrying conductors inducing signals in nearby conductors), but there is no empirical evidence of rounding cables reducing performance. This may be because the length of the cable is short enough so that the effect of crosstalk is negligible. Problems usually arise when the cable is not electromagnetically protected
Electromagnetic shielding
Electromagnetic shielding is the process of reducing the electromagnetic field in a space by blocking the field with barriers made of conductive and/or magnetic materials. Shielding is typically applied to enclosures to isolate electrical devices from the 'outside world' and to cables to isolate...
and the length is considerable, a more frequent occurrence with older network cables.
These computer cables can then be cable tied to the chassis or other cables to further increase airflow.
This is less of a problem with new computers that use Serial ATA
Serial ATA
Serial ATA is a computer bus interface for connecting host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives...
which has a much narrower cable.
Airflow optimization
The colder the cooling medium (the air), the more effective the coolingHeat transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the exchange of thermal energy from one physical system to another. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as heat conduction, convection, thermal radiation, and phase-change transfer...
. Cooling air temperature can be improved with these guidelines:
- Supply cool air to the hot components as directly as possible. Examples are air snorkels and tunnels that feed outside air directly and exclusively to the CPU or GPU cooler. For example, the BTXBTX (form factor)BTX is a form factor for motherboards, originally intended to be the replacement for the aging ATX motherboard form factor in late 2004 and early 2005...
case design prescribes a CPU air tunnel. - Expel warm air as directly as possible. Examples are: Conventional PC (ATXATXATX is a motherboard form factor specification developed by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT form factor. It was the first big change in computer case, motherboard, and power supply design in many years, improving standardization and interchangeability of parts...
) power supplies blow the warm air out the back of the case. Many dual-slot graphics cardVideo cardA video card, Graphics Card, or Graphics adapter is an expansion card which generates output images to a display. Most video cards offer various functions such as accelerated rendering of 3D scenes and 2D graphics, MPEG-2/MPEG-4 decoding, TV output, or the ability to connect multiple monitors...
designs blow the warm air through the cover of the adjacent slot. There are also some aftermarket coolers that do this. Some CPU cooling designs blow the warm air directly towards the back of the case, where it can be ejected by a case fan. - Air that has already been used to spot-cool a component should not be reused to spot-cool a different component (this follows from the previous items). The ATX case design can be said to violate this rule, since the power supply gets its "cool" air from the inside of the case, where it has been warmed up already. The BTX case design also violates this rule, since it uses the CPU cooler's exhaust to cool the chipset and often the graphics card.
- Prefer cool intake air, avoid inhaling exhaust air (outside air above or near the exhausts). For example, a CPU cooling air duct at the back of a tower case would inhale warm air from a graphics card exhaust. Moving all exhausts to one side of the case, conventionally the back, helps to keep the intake air cool.
- Hiding cables behind motherboard tray or simply apply ziptie and tucking cables away to provide unhindered airflow.
Fewer fans strategically placed will improve the airflow internally within the PC and thus lower the overall internal case temperature in relation to ambient conditions. The use of larger fans also improves efficiency and lowers the amount of waste heat along with the amount of noise generated by the fans while in operation.
There is little agreement on the effectiveness of different fan placement configurations, and little in the way of systematic testing has been done. For a rectangular PC (ATX) case, a fan in the front with a fan in the rear and one in the top has been found to be a suitable configuration. However, AMD's (somewhat outdated) system cooling guidelines notes that "A front cooling fan does not seem to be essential. In fact, in some extreme situations, testing showed these fans to be recirculating hot air rather than introducing cool air." It may be that fans in the side panels could have a similar detrimental effect—possibly through disrupting the normal air flow through the case. However, this is unconfirmed and probably varies with the configuration.
See also
- CPU power dissipationCPU power dissipationCentral processing unit power dissipation or CPU power dissipation is the process in which central processing units consume electrical energy, and dissipate this energy both by the action of the switching devices contained in the CPU and by the energy lost in the form of heat due to the impedance...
- Thermal design powerThermal Design PowerThe thermal design power , sometimes called thermal design point, refers to the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, a laptop's CPU cooling system may be designed for a 20 watt TDP, which means that it can dissipate up to 20 watts of heat...
- Thermal management of electronic devices and systemsThermal management of electronic devices and systemsHeat generated by electronic devices and circuitry must be dissipated to improve reliability and prevent premature failure. Techniques for heat dissipation can include heatsinks and fans for air cooling, and other forms of computer cooling such as liquid cooling....
External links
- CPU Cooler Rules of Thumb
- Submersion Cooling Patent Application
- DIY Submersion Cooling (Fish Tank + Mineral Oil) Gametrailers.com Forum - Videos [1
]. [2 ], [3 ]. - Home Computer using Submersion Cooling commercially available at Hardcore Computer.
- Oil Submerged PC test rig- Arctic Silver 5/mineral oil conductivity tests. Text article/YouTube Video Driverstorer- Oil Cooled PC Test Rig

