Underwater search and recovery
Encyclopedia
Underwater search and recovery is the process of locating and recovering underwater
objects by divers
. Although most underwater search and recovery is done by commercial divers as part of professional marine salvage
operations, search and recovery diving is also frequently undertaken as part of recreational diving
, and most diver training organisations have dedicated training courses on the subject. Search and recovery is generally considered a more hazardous speciality diving course.For example, PADI
regards search and recovery as one of only three speciality which require the student to already be certified as an Advanced Open Water Diver before commencing (the other two being ice diving
and cave diving
, both of which are considered highly hazardous).http://www.padi.com/padi/en/kd/searchandrecovery.aspx
Underwater search and recovery used to form a mandatory component of the Advanced Open Water Diver
training course for many North American diver training agencies,For example, it was a mandatory part of the PADI
Advanced Open Water Diver course until 1989 which, in addition to learning basic search and recover skills, also assisted in teaching students to cope with task loading
.
Although the scale, value and equipment used in commercial and recreational search and recovery are enormously different, the basic premise remains the same in each case.
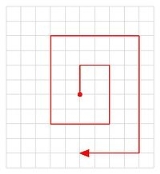
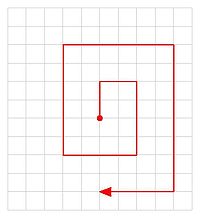 Underwater searches, much like above water searches, are designed around specific search patterns. The most common forms of underwater search patterns are:
Underwater searches, much like above water searches, are designed around specific search patterns. The most common forms of underwater search patterns are:
The patterns are usually performed by divers in pairs or teams below the water, but they can also be conducted by use of a tender who may be a snorkeller
at the surface, a person on a towing boat, or a person located on the shore.
In simple search operations, the patterns will usually be conducted by the divers simply looking visually for the object. In more sophisticated search operations, underwater magnetometer
s or hand held sonar
may be used.
A specific search is an attempt to locate a known object in a known area where it was believed to be lost even if the time period is undefined, and the search terminates upon the location of the object. The classic example of this would be an item lost overboard from a boat, which needs to be recovered.
A non-specific search is a search for either a type of object or anything valuable within the dive locale. Usually the discovery of a relevant object does not usually terminate the search until the entire search area has been covered, or the search terminates early for other reasons (air supply, no decompression limits, etc.). The classic example of this would be an archaeological search, say, for dinosaur bones in a river bed known for them.
 Recovery techniques depend upon the type and size of the object.
Recovery techniques depend upon the type and size of the object.
Smaller objects, such as a coin or camera, can simply be carried up by the diver. Training agencies vary in what they specify to be the maximum weight that can be safely carried up unassisted, but normally the limit is set around 15 pounds (6.8 kg). Anything heavier represents a material change to the diver's buoyancy control, and may put the diver at risk from an uncontrolled ascent if contact with the object is lost during ascent.
Medium sized objects are normally recovered using a lifting bag
, and students are trained in lifting bag technique. The most common hazard is entanglement with lines whilst filling the lifting bag from the diver's alternate air source
. This risk, when coupled with the possibility of rapid ascent following the freeing of the object from suction caused by it resting upon the sea bed, can seriously compromise the safety of the recovery team if done improperly. Lift bags can be rated up to 200 pounds (90.7 kg).
Significantly larger objects usually require specialised commercial lifting equipment, either a winch attached to a boat or platform, or specialised equipment to seal and inflate sunken vessels.
Underwater
Underwater is a term describing the realm below the surface of water where the water exists in a natural feature such as an ocean, sea, lake, pond, or river. Three quarters of the planet Earth is covered by water...
objects by divers
Scuba diving
Scuba diving is a form of underwater diving in which a diver uses a scuba set to breathe underwater....
. Although most underwater search and recovery is done by commercial divers as part of professional marine salvage
Marine salvage
Marine salvage is the process of rescuing a ship, its cargo, or other property from peril. Salvage encompasses rescue towing, refloating a sunken or grounded vessel, or patching or repairing a ship...
operations, search and recovery diving is also frequently undertaken as part of recreational diving
Recreational diving
Recreational diving or sport diving is a type of diving that uses SCUBA equipment for the purpose of leisure and enjoyment. In some diving circles, the term "recreational diving" is used in contradistinction to "technical diving", a more demanding aspect of the sport which requires greater levels...
, and most diver training organisations have dedicated training courses on the subject. Search and recovery is generally considered a more hazardous speciality diving course.For example, PADI
Professional Association of Diving Instructors
The Professional Association of Diving Instructors is the world's largest recreational diving membership and diver training organization founded in 1966 by John Cronin and Ralph Erickson...
regards search and recovery as one of only three speciality which require the student to already be certified as an Advanced Open Water Diver before commencing (the other two being ice diving
Ice diving
Ice diving is a type of penetration diving where the dive takes place under ice. Because diving under ice places the diver in an overhead environment typically with only a single entry/exit point, it is considered an advanced type of diving requiring special training...
and cave diving
Cave diving
Cave diving is a type of technical diving in which specialized equipment is used to enable the exploration of caves which are at least partially filled with water. In the United Kingdom it is an extension of the more common sport of caving, and in the United States an extension of the more common...
, both of which are considered highly hazardous).http://www.padi.com/padi/en/kd/searchandrecovery.aspx
Underwater search and recovery used to form a mandatory component of the Advanced Open Water Diver
Advanced Open Water Diver
Advanced Open Water Diver is a scuba diving certification level provided by several diver training agencies, such as Professional Association of Diving Instructors , Scuba Schools International and Underwater Explorers' Federation...
training course for many North American diver training agencies,For example, it was a mandatory part of the PADI
Professional Association of Diving Instructors
The Professional Association of Diving Instructors is the world's largest recreational diving membership and diver training organization founded in 1966 by John Cronin and Ralph Erickson...
Advanced Open Water Diver course until 1989 which, in addition to learning basic search and recover skills, also assisted in teaching students to cope with task loading
Task loading
Task loading in Scuba diving is a term used to refer to a multiplicity of responsibilities leading to an increased risk failure on the part of the diver to undertake some key basic function which would normally be routine for safety underwater....
.
Although the scale, value and equipment used in commercial and recreational search and recovery are enormously different, the basic premise remains the same in each case.
Search

- Circular search
- Jackstay search
- Expanding square search
- "U" pattern search
The patterns are usually performed by divers in pairs or teams below the water, but they can also be conducted by use of a tender who may be a snorkeller
Snorkeling
Snorkeling is the practice of swimming on or through a body of water while equipped with a diving mask, a shaped tube called a snorkel, and usually swimfins. In cooler waters, a wetsuit may also be worn...
at the surface, a person on a towing boat, or a person located on the shore.
In simple search operations, the patterns will usually be conducted by the divers simply looking visually for the object. In more sophisticated search operations, underwater magnetometer
Magnetometer
A magnetometer is a measuring instrument used to measure the strength or direction of a magnetic field either produced in the laboratory or existing in nature...
s or hand held sonar
Sonar
Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, communicate with or detect other vessels...
may be used.
Types
Diver training traditionally divides searches into two categories, specific and non-specific.A specific search is an attempt to locate a known object in a known area where it was believed to be lost even if the time period is undefined, and the search terminates upon the location of the object. The classic example of this would be an item lost overboard from a boat, which needs to be recovered.
A non-specific search is a search for either a type of object or anything valuable within the dive locale. Usually the discovery of a relevant object does not usually terminate the search until the entire search area has been covered, or the search terminates early for other reasons (air supply, no decompression limits, etc.). The classic example of this would be an archaeological search, say, for dinosaur bones in a river bed known for them.
Recovery

Smaller objects, such as a coin or camera, can simply be carried up by the diver. Training agencies vary in what they specify to be the maximum weight that can be safely carried up unassisted, but normally the limit is set around 15 pounds (6.8 kg). Anything heavier represents a material change to the diver's buoyancy control, and may put the diver at risk from an uncontrolled ascent if contact with the object is lost during ascent.
Medium sized objects are normally recovered using a lifting bag
Lifting bag
A lifting bag is an item of diving equipment consisting of a robust and air-tight bag with straps, which is used to lift heavy objects underwater by means of the bag's buoyancy...
, and students are trained in lifting bag technique. The most common hazard is entanglement with lines whilst filling the lifting bag from the diver's alternate air source
Alternate air source
In underwater diving, an alternative air source, or more generally alternative breathing gas source, is a secondary supply of air or other breathing gas used by the diver in an emergency...
. This risk, when coupled with the possibility of rapid ascent following the freeing of the object from suction caused by it resting upon the sea bed, can seriously compromise the safety of the recovery team if done improperly. Lift bags can be rated up to 200 pounds (90.7 kg).
Significantly larger objects usually require specialised commercial lifting equipment, either a winch attached to a boat or platform, or specialised equipment to seal and inflate sunken vessels.

