
United States Secretary of Defense
Encyclopedia
The Secretary of Defense (SecDef) is the head and chief executive officer
of the Department of Defense
of the United States of America. This position corresponds to what is generally known as a Defense Minister in other countries. Under the direction of the President
, the Secretary of Defense has per federal law "authority, direction and control over the Department of Defense", and is further designated by statute as "the principal assistant to the President in all matters relating to the Department of Defense".
The Secretary of Defense is in the chain of command
and exercises command and control, subject only to the orders of the President, over all Department of Defense forces – i.e. Army
, Navy
, Air Force
, and Marine Corps
– for both operational and administrative purposes. Only the Secretary of Defense or the President can authorize the transfer of forces from one Combatant Command
to another. The Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
is the principal military adviser to the Secretary of Defense and the President, and while the Chairman may assist them in their command functions, the Chairman is not in the chain of command.
The Secretary of Defense is appointed by the President
with the advice and consent
of the Senate
, and is by custom a member of the Cabinet
, and by law a member of the National Security Council
. An individual may not be appointed as Secretary of Defense within seven years after relief from active duty as a commissioned officer of a regular component of an armed force
.
Along with the Secretary of State
, the Attorney General
and the Secretary of the Treasury
, the Secretary of Defense is generally regarded as one of the Big Four important cabinet officials. Secretary of Defense is a Level I position of the Executive Schedule
and thus earns a salary of $199,700 per year. The current Secretary is Leon Panetta
who assumed office July 1, 2011.
. The War Department
, headed by the Secretary of War
, was created by Act of Congress
in 1789 and was responsible for both the Army and Navy until the founding of a separate Department of the Navy
in 1798.
Based on the experiences of World War II
, proposals were soon made on how to more effectively manage the large combined military establishment over which only the President had direct line authority. The Army generally favored centralization while the Navy had institutional preferences for decentralization and the status quo. The resulting National Security Act of 1947
was largely a compromise between these divergent viewpoints. The Act split the War Department into the Department of the Army and the Department of the Air Force
, each with their own Secretary, and created a sui generis
National Military Establishment led by a Secretary of Defense. At first, each of the service secretaries maintained quasi-cabinet status The first Secretary of Defense, James Forrestal
, who as Secretary of the Navy had opposed creation of the new position, found it difficult to exercise authority over them with the limited powers his office had. To address this and other problems, the Act was amended in 1949 to further consolidate the national defense structure in order to reduce interservice rivalry
, directly subordinate the Secretaries of the Army, the Navy and the Air Force
to the Secretary of Defense in the chain of command, and rename the National Military Establishment to the Department of Defense. The position of the Deputy Secretary of Defense
, the number two position in the department, was also created at this time.
The general trend since 1949 has been to further centralize management in the Department of Defense, elevating the status and authorities of civilian OSD
appointees and defense-wide organizations at the expense of the military departments and the services within them. The last major revision of the statutory framework concerning the position was done in the Goldwater–Nichols Department of Defense Reorganization Act of 1986. In particular, it elevated the status of joint service for commissioned officers, making it in practice a requirement before appointments to general officer and flag officer grades could be made.
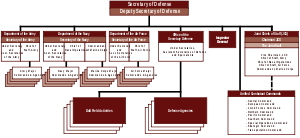
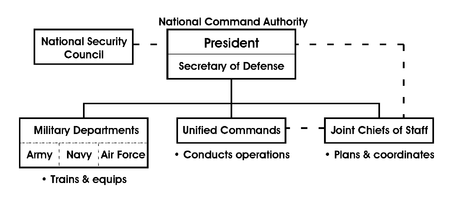 In the U.S. Armed Forces
In the U.S. Armed Forces
, the Secretary of Defense is often referred to as SecDef or SD. The Secretary of Defense and the President together constitute the National Command Authorities (NCA), which has sole authority to launch strategic nuclear weapons. All nuclear weapons are governed by this dual-authority – both must concur before a strategic nuclear strike may be ordered.
The Secretary's staff element is called the Office of the Secretary of Defense
(OSD) and is composed of a Deputy Secretary of Defense
(DEPSECDEF) and five Under Secretaries of Defense in the fields of Acquisition, Technology & Logistics
; Comptroller/Chief Financial Officer
; Intelligence
; Personnel & Readiness
; and Policy
.
The Secretary of Defense by statute also exercises "authority, direction and control" over the three Secretaries of the military departments (Secretary of the Army, Secretary of the Navy, and Secretary of the Air Force), the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, the other members of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
(Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
, Army Chief of Staff
, Commandant of the Marine Corps
, Chief of Naval Operations
, and Air Force Chief of Staff
), the Combatant Commanders of the Unified Combatant Command
s, the Directors of the Defense Agencies (for example the Director of the National Security Agency
) and of the DoD Field Activities. All of these high-ranking positions require Senate confirmation.
The Secretary is one of few civilians who is authorized to act as convening authority
in the military justice system
for General Courts-Martial
(: article 22, UCMJ
), Special Courts-Martial (: article 23, UCMJ), and Summary Courts-Martial (: article 24 UCMJ).
, who served for a total of 2,595 days.
Parties
Status
, following the Secretary of the Treasury
and preceding the Attorney General
.
modified the line of succession regarding who would act as Secretary of Defense in the event of a vacancy or incapacitation, thus reversing the changes made by President George W. Bush
in as to the relative positions of the Secretaries of the Military Departments. All of the officials in the line of succession are civilians appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate:
Chief executive officer
A chief executive officer , managing director , Executive Director for non-profit organizations, or chief executive is the highest-ranking corporate officer or administrator in charge of total management of an organization...
of the Department of Defense
United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
of the United States of America. This position corresponds to what is generally known as a Defense Minister in other countries. Under the direction of the President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
, the Secretary of Defense has per federal law "authority, direction and control over the Department of Defense", and is further designated by statute as "the principal assistant to the President in all matters relating to the Department of Defense".
The Secretary of Defense is in the chain of command
Chain of Command
Chain of Command may refer to:* Chain of command, in a military context, the line of authority and responsibility along which orders are passed* "Chain of Command" , the fifth episode of the first season of Beast Wars...
and exercises command and control, subject only to the orders of the President, over all Department of Defense forces – i.e. Army
United States Army
The United States Army is the main branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is the largest and oldest established branch of the U.S. military, and is one of seven U.S. uniformed services...
, Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
, Air Force
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the American uniformed services. Initially part of the United States Army, the USAF was formed as a separate branch of the military on September 18, 1947 under the National Security Act of...
, and Marine Corps
United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps is a branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for providing power projection from the sea, using the mobility of the United States Navy to deliver combined-arms task forces rapidly. It is one of seven uniformed services of the United States...
– for both operational and administrative purposes. Only the Secretary of Defense or the President can authorize the transfer of forces from one Combatant Command
Unified Combatant Command
A Unified Combatant Command is a United States Department of Defense command that is composed of forces from at least two Military Departments and has a broad and continuing mission. These commands are established to provide effective command and control of U.S. military forces, regardless of...
to another. The Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is by law the highest ranking military officer in the United States Armed Forces, and is the principal military adviser to the President of the United States, the National Security Council, the Homeland Security Council and the Secretary of Defense...
is the principal military adviser to the Secretary of Defense and the President, and while the Chairman may assist them in their command functions, the Chairman is not in the chain of command.
The Secretary of Defense is appointed by the President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
with the advice and consent
Advice and consent
Advice and consent is an English phrase frequently used in enacting formulae of bills and in other legal or constitutional contexts, describing a situation in which the executive branch of a government enacts something previously approved of by the legislative branch.-General:The expression is...
of the Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
, and is by custom a member of the Cabinet
United States Cabinet
The Cabinet of the United States is composed of the most senior appointed officers of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States, which are generally the heads of the federal executive departments...
, and by law a member of the National Security Council
United States National Security Council
The White House National Security Council in the United States is the principal forum used by the President of the United States for considering national security and foreign policy matters with his senior national security advisors and Cabinet officials and is part of the Executive Office of the...
. An individual may not be appointed as Secretary of Defense within seven years after relief from active duty as a commissioned officer of a regular component of an armed force
Military of the United States
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. They consist of the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Coast Guard.The United States has a strong tradition of civilian control of the military...
.
Along with the Secretary of State
United States Secretary of State
The United States Secretary of State is the head of the United States Department of State, concerned with foreign affairs. The Secretary is a member of the Cabinet and the highest-ranking cabinet secretary both in line of succession and order of precedence...
, the Attorney General
United States Attorney General
The United States Attorney General is the head of the United States Department of Justice concerned with legal affairs and is the chief law enforcement officer of the United States government. The attorney general is considered to be the chief lawyer of the U.S. government...
and the Secretary of the Treasury
United States Secretary of the Treasury
The Secretary of the Treasury of the United States is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, which is concerned with financial and monetary matters, and, until 2003, also with some issues of national security and defense. This position in the Federal Government of the United...
, the Secretary of Defense is generally regarded as one of the Big Four important cabinet officials. Secretary of Defense is a Level I position of the Executive Schedule
Executive Schedule
Executive Schedule refers to the highest-ranked appointed positions in the executive branch of the U.S. government. The President of the United States, an elected official, appoints incumbents to these positions, most of them with the advice and consent of the Senate. They include members of the...
and thus earns a salary of $199,700 per year. The current Secretary is Leon Panetta
Leon Panetta
Leon Edward Panetta is the 23rd and current United States Secretary of Defense, serving in the administration of President Barack Obama since 2011. Prior to taking office, he served as Director of the Central Intelligence Agency...
who assumed office July 1, 2011.
History
The Army, Navy, and Marine Corps were established in 1775, in concurrence with the American RevolutionAmerican Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
. The War Department
United States Department of War
The United States Department of War, also called the War Department , was the United States Cabinet department originally responsible for the operation and maintenance of the United States Army...
, headed by the Secretary of War
United States Secretary of War
The Secretary of War was a member of the United States President's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War," was appointed to serve the Congress of the Confederation under the Articles of Confederation...
, was created by Act of Congress
Act of Congress
An Act of Congress is a statute enacted by government with a legislature named "Congress," such as the United States Congress or the Congress of the Philippines....
in 1789 and was responsible for both the Army and Navy until the founding of a separate Department of the Navy
United States Department of the Navy
The Department of the Navy of the United States of America was established by an Act of Congress on 30 April 1798, to provide a government organizational structure to the United States Navy and, from 1834 onwards, for the United States Marine Corps, and when directed by the President, of the...
in 1798.
Based on the experiences of World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, proposals were soon made on how to more effectively manage the large combined military establishment over which only the President had direct line authority. The Army generally favored centralization while the Navy had institutional preferences for decentralization and the status quo. The resulting National Security Act of 1947
National Security Act of 1947
The National Security Act of 1947 was signed by United States President Harry S. Truman on July 26, 1947, and realigned and reorganized the U.S. Armed Forces, foreign policy, and Intelligence Community apparatus in the aftermath of World War II...
was largely a compromise between these divergent viewpoints. The Act split the War Department into the Department of the Army and the Department of the Air Force
Department of the Air Force
The Department of the Air Force is one of the three Military Departments within the Department of Defense of the United States of America...
, each with their own Secretary, and created a sui generis
Sui generis
Sui generis is a Latin expression, literally meaning of its own kind/genus or unique in its characteristics. The expression is often used in analytic philosophy to indicate an idea, an entity, or a reality which cannot be included in a wider concept....
National Military Establishment led by a Secretary of Defense. At first, each of the service secretaries maintained quasi-cabinet status The first Secretary of Defense, James Forrestal
James Forrestal
James Vincent Forrestal was the last Cabinet-level United States Secretary of the Navy and the first United States Secretary of Defense....
, who as Secretary of the Navy had opposed creation of the new position, found it difficult to exercise authority over them with the limited powers his office had. To address this and other problems, the Act was amended in 1949 to further consolidate the national defense structure in order to reduce interservice rivalry
Interservice rivalry
Interservice rivalry is a military term referring to rivalries that can arise between different branches of a country's armed forces, such as between a nation's land forces , naval and air forces. It also applies to the rivalries between a country's intelligence services, Central Intelligence...
, directly subordinate the Secretaries of the Army, the Navy and the Air Force
United States Secretary of the Air Force
The Secretary of the Air Force is the Head of the Department of the Air Force, a component organization within the Department of Defense of the United States of America. The Secretary of the Air Force is appointed from civilian life by the President, by and with the advice and consent of the Senate...
to the Secretary of Defense in the chain of command, and rename the National Military Establishment to the Department of Defense. The position of the Deputy Secretary of Defense
United States Deputy Secretary of Defense
The Deputy Secretary of Defense is the second-highest ranking official in the Department of Defense of the United States of America. The Deputy Secretary of Defense is appointed by the President, with the advice and consent of the Senate...
, the number two position in the department, was also created at this time.
The general trend since 1949 has been to further centralize management in the Department of Defense, elevating the status and authorities of civilian OSD
Office of the Secretary of Defense
The Office of the Secretary of Defense is a headquarters-level staff of the Department of Defense of the United States of America. It is the principal civilian staff element of the Secretary of Defense, and it assists the Secretary in carrying out authority, direction and control of the Department...
appointees and defense-wide organizations at the expense of the military departments and the services within them. The last major revision of the statutory framework concerning the position was done in the Goldwater–Nichols Department of Defense Reorganization Act of 1986. In particular, it elevated the status of joint service for commissioned officers, making it in practice a requirement before appointments to general officer and flag officer grades could be made.
Powers and Functions


Military of the United States
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. They consist of the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Coast Guard.The United States has a strong tradition of civilian control of the military...
, the Secretary of Defense is often referred to as SecDef or SD. The Secretary of Defense and the President together constitute the National Command Authorities (NCA), which has sole authority to launch strategic nuclear weapons. All nuclear weapons are governed by this dual-authority – both must concur before a strategic nuclear strike may be ordered.
The Secretary's staff element is called the Office of the Secretary of Defense
Office of the Secretary of Defense
The Office of the Secretary of Defense is a headquarters-level staff of the Department of Defense of the United States of America. It is the principal civilian staff element of the Secretary of Defense, and it assists the Secretary in carrying out authority, direction and control of the Department...
(OSD) and is composed of a Deputy Secretary of Defense
United States Deputy Secretary of Defense
The Deputy Secretary of Defense is the second-highest ranking official in the Department of Defense of the United States of America. The Deputy Secretary of Defense is appointed by the President, with the advice and consent of the Senate...
(DEPSECDEF) and five Under Secretaries of Defense in the fields of Acquisition, Technology & Logistics
Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition, Technology and Logistics
The Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition, Technology and Logistics - USD - is a senior official in the Office of the Secretary of Defense within the Department of Defense of the United States of America...
; Comptroller/Chief Financial Officer
Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller)
The Under Secretary of Defense is the Chief Financial Officer of the United States Department of Defense. The responsibilities of the Department of Defense's Chief Financial Officer include developing and implementing Department of Defense-wide financial policy, financial management systems, and...
; Intelligence
Under Secretary of Defense for Intelligence
The Under Secretary for Intelligence or USD is a high-ranking civilian position in the Office of the Secretary of Defense within the U.S. Department of Defense that acts as the principal advisor and deputy to the Secretary and Deputy Secretary of Defense on matters relating to intelligence...
; Personnel & Readiness
Under Secretary of Defense for Personnel and Readiness
The Under Secretary for Personnel and Readiness, or USD is a high-ranking civilian position in the Office of the Secretary of Defense within the United States Department of Defense responsible for advising the Secretary and Deputy Secretary of Defense on recruitment, career development, pay and...
; and Policy
Under Secretary of Defense for Policy
The Under Secretary of Defense for Policy is a high level civilian official in the United States Department of Defense. The Under Secretary of Defense for Policy is the principal staff assistant and adviser to both the Secretary of Defense and the Deputy Secretary of Defense for all matters...
.
The Secretary of Defense by statute also exercises "authority, direction and control" over the three Secretaries of the military departments (Secretary of the Army, Secretary of the Navy, and Secretary of the Air Force), the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, the other members of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Joint Chiefs of Staff is a body of senior uniformed leaders in the United States Department of Defense who advise the Secretary of Defense, the Homeland Security Council, the National Security Council and the President on military matters...
(Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is by law the second highest ranking military officer in the United States Armed Forces ranking just below the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff...
, Army Chief of Staff
Chief of Staff of the United States Army
The Chief of Staff of the Army is a statutory office held by a four-star general in the United States Army, and is the most senior uniformed officer assigned to serve in the Department of the Army, and as such is the principal military advisor and a deputy to the Secretary of the Army; and is in...
, Commandant of the Marine Corps
Commandant of the Marine Corps
The Commandant of the Marine Corps is normally the highest ranking officer in the United States Marine Corps and is a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff...
, Chief of Naval Operations
Chief of Naval Operations
The Chief of Naval Operations is a statutory office held by a four-star admiral in the United States Navy, and is the most senior uniformed officer assigned to serve in the Department of the Navy. The office is a military adviser and deputy to the Secretary of the Navy...
, and Air Force Chief of Staff
Chief of Staff of the United States Air Force
The Chief of Staff of the Air Force is a statutory office held by a four-star general in the United States Air Force, and is the most senior uniformed officer assigned to serve in the Department of the Air Force, and as such is the principal military advisor and a deputy to the Secretary of the...
), the Combatant Commanders of the Unified Combatant Command
Unified Combatant Command
A Unified Combatant Command is a United States Department of Defense command that is composed of forces from at least two Military Departments and has a broad and continuing mission. These commands are established to provide effective command and control of U.S. military forces, regardless of...
s, the Directors of the Defense Agencies (for example the Director of the National Security Agency
Director of the National Security Agency
The Director of the National Security Agency is the highest-ranking official in the National Security Agency, which is a Defense Agency within the U.S. Department of Defense. The Director of the NSA also concurrently serves as Chief of the Central Security Service and as Commander of U.S. Cyber...
) and of the DoD Field Activities. All of these high-ranking positions require Senate confirmation.
The Secretary is one of few civilians who is authorized to act as convening authority
Convening Authority
The term convening authority is used in United States military law to refer to an individual whose job includes appointing officers to play a role in a court-martial, or similar military tribunal or military commission...
in the military justice system
Uniform Code of Military Justice
The Uniform Code of Military Justice , is the foundation of military law in the United States. It is was established by the United States Congress in accordance with the authority given by the United States Constitution in Article I, Section 8, which provides that "The Congress shall have Power . ....
for General Courts-Martial
Courts-martial in the United States
Courts-martial in the United States are criminal trials conducted by the U.S. military. Most commonly, courts-martial are convened to try members of the U.S. military for violations of the Uniform Code of Military Justice , which is the U.S. military's criminal code...
(: article 22, UCMJ
Uniform Code of Military Justice
The Uniform Code of Military Justice , is the foundation of military law in the United States. It is was established by the United States Congress in accordance with the authority given by the United States Constitution in Article I, Section 8, which provides that "The Congress shall have Power . ....
), Special Courts-Martial (: article 23, UCMJ), and Summary Courts-Martial (: article 24 UCMJ).
List of Secretaries of Defense
The longest-serving Secretary of Defense is the late Robert McNamaraRobert McNamara
Robert Strange McNamara was an American business executive and the eighth Secretary of Defense, serving under Presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson from 1961 to 1968, during which time he played a large role in escalating the United States involvement in the Vietnam War...
, who served for a total of 2,595 days.
Parties
Status
| No. | Portrait | Name | State of Residence | Took Office | Left Office | Days served | President(s) President of the United States The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces.... |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
James Vincent Forrestal James Forrestal James Vincent Forrestal was the last Cabinet-level United States Secretary of the Navy and the first United States Secretary of Defense.... |
New York New York New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east... |
September 19, 1947 | March 19, 1949 | 558 | Harry S. Truman Harry S. Truman Harry S. Truman was the 33rd President of the United States . As President Franklin D. Roosevelt's third vice president and the 34th Vice President of the United States , he succeeded to the presidency on April 12, 1945, when President Roosevelt died less than three months after beginning his... |
||
 |
Louis Arthur Johnson Louis A. Johnson Louis Arthur Johnson was the second United States Secretary of Defense, serving in the cabinet of President Harry S. Truman from March 28, 1949 to September 19, 1950.... |
West Virginia West Virginia West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian and Southeastern regions of the United States, bordered by Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Ohio to the northwest, Pennsylvania to the northeast and Maryland to the east... |
March 28, 1949 | September 19, 1950 | 540 | |||
 |
George Catlett Marshall, Jr. George Marshall George Catlett Marshall was an American military leader, Chief of Staff of the Army, Secretary of State, and the third Secretary of Defense... |
Virginia Virginia The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there... |
September 19, 1950 | September 19, 1951 | 365 | |||
 |
Robert Abercrombie Lovett Robert A. Lovett Robert Abercrombie Lovett was the fourth United States Secretary of Defense, serving in the cabinet of President Harry S. Truman from 1951 to 1953 and in this capacity, directed the Korean War. Promoted to the position from deputy secretary of defense Domhoff described Lovett as a "Cold War... |
New York New York New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east... |
September 19, 1951 | January 20, 1953 | 491 | |||
 |
Charles Erwin Wilson Charles Erwin Wilson Charles Erwin Wilson , American businessman and politician, was United States Secretary of Defense from 1953 to 1957 under President Eisenhower. Known as "Engine Charlie", he previously worked as CEO for General Motors. In the wake of the Korean War, he cut the defense budget significantly.-Early... |
Indiana Indiana Indiana is a US state, admitted to the United States as the 19th on December 11, 1816. It is located in the Midwestern United States and Great Lakes Region. With 6,483,802 residents, the state is ranked 15th in population and 16th in population density. Indiana is ranked 38th in land area and is... |
January 20, 1953 | October 8, 1957 | 1,722 | Dwight D. Eisenhower Dwight D. Eisenhower Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower was the 34th President of the United States, from 1953 until 1961. He was a five-star general in the United States Army... |
||
 |
Neil Hosler McElroy Neil H. McElroy Neil Hosler McElroy was United States Secretary of Defense from 1957 to 1959 under President Eisenhower. He had been president of Procter & Gamble.- Early life :... |
Ohio Ohio Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus... |
October 9, 1957 | December 1, 1959 | 783 | |||
 |
Thomas Sovereign Gates, Jr. | Pennsylvania Pennsylvania The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to... |
December 2, 1959 | January 20, 1961 | 415 | |||
 |
Robert Strange McNamara Robert McNamara Robert Strange McNamara was an American business executive and the eighth Secretary of Defense, serving under Presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson from 1961 to 1968, during which time he played a large role in escalating the United States involvement in the Vietnam War... |
Michigan Michigan Michigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake".... |
January 21, 1961 | February 29, 1968 | 2,595 | John F. Kennedy John F. Kennedy John Fitzgerald "Jack" Kennedy , often referred to by his initials JFK, was the 35th President of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963.... |
||
| Lyndon B. Johnson Lyndon B. Johnson Lyndon Baines Johnson , often referred to as LBJ, was the 36th President of the United States after his service as the 37th Vice President of the United States... |
||||||||
 |
Clark McAdams Clifford Clark Clifford Clark McAdams Clifford was an American lawyer who served United States Presidents Harry S. Truman, John F. Kennedy, Lyndon B. Johnson and Jimmy Carter, serving as United States Secretary of Defense for Johnson.... |
Kansas Kansas Kansas is a US state located in the Midwestern United States. It is named after the Kansas River which flows through it, which in turn was named after the Kansa Native American tribe, which inhabited the area. The tribe's name is often said to mean "people of the wind" or "people of the south... |
March 1, 1968 | January 20, 1969 | 326 | |||
 |
Melvin Robert Laird Melvin R. Laird Melvin Robert Laird is an American politician and writer. Laird was a Republican congressman who also served as Richard Nixon's Secretary of Defense from 1969 to 1973. Laird urged Nixon to maintain a policy of withdrawing US soldiers from Vietnam... |
Wisconsin Wisconsin Wisconsin is a U.S. state located in the north-central United States and is part of the Midwest. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. Wisconsin's capital is... |
January 22, 1969 | January 29, 1973 | 1,469 | Richard Nixon Richard Nixon Richard Milhous Nixon was the 37th President of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. The only president to resign the office, Nixon had previously served as a US representative and senator from California and as the 36th Vice President of the United States from 1953 to 1961 under... |
||
 |
Elliot Lee Richardson Elliot Richardson Elliot Lee Richardson was an American lawyer and politician who was a member of the cabinet of Presidents Richard Nixon and Gerald Ford. As U.S... |
Massachusetts Massachusetts The Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010... |
January 30, 1973 | May 24, 1973 | 114 | |||
| William Perry Clements, Jr. Bill Clements William Perry "Bill" Clements, Jr. was the 42nd and 44th Governor of Texas, serving from 1979 to 1983 and 1987 to 1991. Clements was the first Republican to have served as governor of the U.S. state of Texas since Reconstruction... |
Texas Texas Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in... |
May 24, 1973 | July 2, 1973 | |||||
 |
James Rodney Schlesinger James R. Schlesinger Dr. James Rodney Schlesinger is an American politician. He is best known for serving as Secretary of Defense from 1973 to 1975 under Presidents Richard Nixon and Gerald Ford... |
Virginia Virginia The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there... |
July 2, 1973 | November 19, 1975 | ||||
| Gerald Ford Gerald Ford Gerald Rudolph "Jerry" Ford, Jr. was the 38th President of the United States, serving from 1974 to 1977, and the 40th Vice President of the United States serving from 1973 to 1974... |
||||||||
 |
Donald Henry Rumsfeld Donald Rumsfeld Donald Henry Rumsfeld is an American politician and businessman. Rumsfeld served as the 13th Secretary of Defense from 1975 to 1977 under President Gerald Ford, and as the 21st Secretary of Defense from 2001 to 2006 under President George W. Bush. He is both the youngest and the oldest person to... |
Illinois Illinois Illinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,... |
November 20, 1975 | January 20, 1977 | 427 | |||
 |
Harold Brown Harold Brown (Secretary of Defense) Harold Brown , American scientist, was U.S. Secretary of Defense from 1977 to 1981 in the cabinet of President Jimmy Carter. He had previously served in the Lyndon Johnson administration as Director of Defense Research and Engineering and Secretary of the Air Force.While Secretary of Defense, he... |
New York New York New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east... |
January 21, 1977 | January 20, 1981 | 1,460 | Jimmy Carter Jimmy Carter James Earl "Jimmy" Carter, Jr. is an American politician who served as the 39th President of the United States and was the recipient of the 2002 Nobel Peace Prize, the only U.S. President to have received the Prize after leaving office... |
||
 |
Caspar Willard Weinberger Caspar Weinberger Caspar Willard "Cap" Weinberger , was an American politician, vice president and general counsel of Bechtel Corporation, and Secretary of Defense under President Ronald Reagan from January 21, 1981, until November 23, 1987, making him the third longest-serving defense secretary to date, after... |
California California California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area... |
January 21, 1981 | November 23, 1987 | 2,497 | Ronald Reagan Ronald Reagan Ronald Wilson Reagan was the 40th President of the United States , the 33rd Governor of California and, prior to that, a radio, film and television actor.... |
||
 |
Frank Charles Carlucci III Frank Carlucci Frank Charles Carlucci III is a former official in the United States Government, associated with the Republican Party. The most prominent office held by Carlucci was as Secretary of Defense from 1987 until 1989 in the Reagan Administration.-Early life and career:Carlucci was born in Scranton,... |
Pennsylvania Pennsylvania The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to... |
November 23, 1987 | January 20, 1989 | 424 | |||
 |
William Howard Taft IV William Howard Taft IV William Howard Taft IV is an attorney who has served in the United States government under several Republican administrations. He is the son of William Howard Taft III and the great-grandson of U.S. President William Howard Taft.... |
Ohio Ohio Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus... |
January 20, 1989 | March 20, 1989 | 59 | George H. W. Bush George H. W. Bush George Herbert Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 41st President of the United States . He had previously served as the 43rd Vice President of the United States , a congressman, an ambassador, and Director of Central Intelligence.Bush was born in Milton, Massachusetts, to... |
||
 |
Richard Bruce Cheney Dick Cheney Richard Bruce "Dick" Cheney served as the 46th Vice President of the United States , under George W. Bush.... |
Wyoming Wyoming Wyoming is a state in the mountain region of the Western United States. The western two thirds of the state is covered mostly with the mountain ranges and rangelands in the foothills of the Eastern Rocky Mountains, while the eastern third of the state is high elevation prairie known as the High... |
March 21, 1989 | January 20, 1993 | 1,402 | |||
 |
Leslie Aspin, Jr. Les Aspin Leslie "Les" Aspin, Jr. was a United States Representative from 1971 to 1993, and the United States Secretary of Defense under President Bill Clinton from January 21, 1993 to February 3, 1994.-Early life:... |
Wisconsin Wisconsin Wisconsin is a U.S. state located in the north-central United States and is part of the Midwest. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. Wisconsin's capital is... |
January 21, 1993 | February 3, 1994 | 378 | Bill Clinton Bill Clinton William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation... |
||
 |
William James Perry William Perry William James Perry is an American businessman and engineer who was the United States Secretary of Defense from February 3, 1994, to January 23, 1997, under President Bill Clinton... |
Pennsylvania Pennsylvania The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to... |
February 3, 1994 | January 24, 1997 | 1,085 | |||
 |
William Sebastian Cohen William Cohen William Sebastian Cohen is an author and American politician from the U.S. state of Maine. A Republican, Cohen served as Secretary of Defense under Democratic President Bill Clinton.-Early life and education:... |
Maine Maine Maine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost... |
January 24, 1997 | January 20, 2001 | 1,457 | |||
 |
Donald Henry Rumsfeld Donald Rumsfeld Donald Henry Rumsfeld is an American politician and businessman. Rumsfeld served as the 13th Secretary of Defense from 1975 to 1977 under President Gerald Ford, and as the 21st Secretary of Defense from 2001 to 2006 under President George W. Bush. He is both the youngest and the oldest person to... |
Illinois Illinois Illinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,... |
January 20, 2001 | December 18, 2006 | 2,158 | George W. Bush George W. Bush George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000.... |
||
 |
Robert Michael Gates | Texas Texas Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in... |
December 18, 2006 | July 1, 2011 | 1,643 | |||
| Barack Obama Barack Obama Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in... |
||||||||
| Leon Edward Panetta | California California California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area... |
July 1, 2011 | Incumbent |
Presidential succession
The Secretary of Defense is sixth in the presidential line of successionUnited States presidential line of succession
The United States presidential line of succession defines who may become or act as President of the United States upon the incapacity, death, resignation, or removal from office of a sitting president or a president-elect.- Current order :This is a list of the current presidential line of...
, following the Secretary of the Treasury
United States Secretary of the Treasury
The Secretary of the Treasury of the United States is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, which is concerned with financial and monetary matters, and, until 2003, also with some issues of national security and defense. This position in the Federal Government of the United...
and preceding the Attorney General
United States Attorney General
The United States Attorney General is the head of the United States Department of Justice concerned with legal affairs and is the chief law enforcement officer of the United States government. The attorney general is considered to be the chief lawyer of the U.S. government...
.
Secretary of Defense succession
In of March 1, 2010, President Barack ObamaBarack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
modified the line of succession regarding who would act as Secretary of Defense in the event of a vacancy or incapacitation, thus reversing the changes made by President George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
in as to the relative positions of the Secretaries of the Military Departments. All of the officials in the line of succession are civilians appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate:
Executive Order 13533 (March 1, 2010—Present)
|
Executive Order 13394 (December 22, 2005—March 1, 2010)
|
Living former Secretaries of Defense
- 10th – Melvin Robert Laird
- 12th – James Rodney Schlesinger
- 13th and 21st – Donald Henry RumsfeldDonald RumsfeldDonald Henry Rumsfeld is an American politician and businessman. Rumsfeld served as the 13th Secretary of Defense from 1975 to 1977 under President Gerald Ford, and as the 21st Secretary of Defense from 2001 to 2006 under President George W. Bush. He is both the youngest and the oldest person to...
- 14th – Harold BrownHarold Brown (Secretary of Defense)Harold Brown , American scientist, was U.S. Secretary of Defense from 1977 to 1981 in the cabinet of President Jimmy Carter. He had previously served in the Lyndon Johnson administration as Director of Defense Research and Engineering and Secretary of the Air Force.While Secretary of Defense, he...
- 16th – Frank Charles Carlucci IIIFrank CarlucciFrank Charles Carlucci III is a former official in the United States Government, associated with the Republican Party. The most prominent office held by Carlucci was as Secretary of Defense from 1987 until 1989 in the Reagan Administration.-Early life and career:Carlucci was born in Scranton,...
- 17th – Richard Bruce CheneyDick CheneyRichard Bruce "Dick" Cheney served as the 46th Vice President of the United States , under George W. Bush....
- 19th – William James PerryWilliam PerryWilliam James Perry is an American businessman and engineer who was the United States Secretary of Defense from February 3, 1994, to January 23, 1997, under President Bill Clinton...
- 20th – William Sebastian CohenWilliam CohenWilliam Sebastian Cohen is an author and American politician from the U.S. state of Maine. A Republican, Cohen served as Secretary of Defense under Democratic President Bill Clinton.-Early life and education:...
- 22nd – Robert Michael GatesRobert GatesDr. Robert Michael Gates is a retired civil servant and university president who served as the 22nd United States Secretary of Defense from 2006 to 2011. Prior to this, Gates served for 26 years in the Central Intelligence Agency and the National Security Council, and under President George H. W....
External links
- The Reinvention of Robert Gates by Michael Crowley, The New Republic, November 9, 2009 – Includes the Secretary of Defense
- More information on each position and biographies of the current Deputy Secretary (DepSecDef) and Under Secretaries (USDs)

