
United States presidential election, 1900
Encyclopedia
The United States presidential election of 1900 was a re-match of the 1896
race between Republican
President
William McKinley
and his Democratic
challenger, William Jennings Bryan
. The return of economic prosperity and recent victory in the Spanish–American War helped McKinley to score a decisive victory. President McKinley chose New York Governor Theodore Roosevelt
as his running mate as Vice-President
Garret Hobart
had died from heart failure in 1899.
delegates to the
Republican convention
, which met in Philadelphia on June 19-21, renominated William McKinley
by acclamation. Thomas C. Platt
, the "boss" of the New York State Republican Party, did not like Theodore Roosevelt
, New York's popular governor, even though he was a fellow Republican. Roosevelt's efforts to reform New York politics - including Republican politics - led Platt and other state GOP leaders to pressure President McKinley to accept Roosevelt as his new vice-presidential candidate, thus filling the spot left open when Vice-President Garret Hobart
died in 1899. By electing Roosevelt to the vice-presidency, Platt would remove Roosevelt from New York state politics. Although Roosevelt was reluctant to accept the vice-presidency, which he regarded as a relatively trivial and powerless office, his great popularity among most Republican delegates led McKinley to pick him as his new running mate. Ironically, Roosevelt would be elevated to the Presidency in September 1901, when McKinley was assassinated in Buffalo, New York
.
, many suggested he run for president on the Democratic
ticket. However, his candidacy was plagued by public relations gaffes. Newspapers started attacking him as naïve after he was quoted as saying the job of president would be easy, since the chief executive was merely following orders in executing the laws enacted by Congress, and that he would "execute the laws of Congress as faithfully as I have always executed the orders of my superiors." Shortly thereafter he admitted to never having voted in a presidential election. He drew yet more criticism when he offhandedly (and prophetically) told a newspaper reporter that, "Our next war will be with Germany."
Dewey also angered some Protestants
by marrying Catholic Mildred McLean Hazen (the widow of General William Babcock Hazen
and daughter of Washington McLean
, owner of The Washington Post
), in November 1899 and giving her the house that the nation had given him following the war.
Dewey withdrew from the race in mid-May and endorsed William McKinley
.
William Jennings Bryan
was easily nominated after Dewey withdrew from the race. Bryan won at the 1900 Democratic National Convention held Kansas City, Missouri
on July 4-6, garnering 936 delegate votes. Former Vice-President
Adlai Stevenson was nominated for the office again, beating out David B. Hill
and Charles A. Towne
for the nomination.
Source: US President - D Convention. Our Campaigns. (March 10, 2011).
, and nominated Bryan for president and Charles A. Towne
for vice-president (Towne, the national chairman of the Silver Republican Party
, later withdrew from the race). The "Middle of the Road" Populists wanted to maintain their identity as a separate political party; they met in Cincinnati and nominated Wharton Barker and Ignatius L. Donnelly. The "Fusion" group was absorbed into the Democratic Party with this election; and though the "Middle of the Road" faction contested two future presidential elections, the Populists were no longer considered a serious political force after 1900. The Socialist Labor Party
also divided; the larger faction formed the Social Democratic Party
and nominated Eugene V. Debs
for president. This party was renamed the Socialist Party following the election. Both factions of the Prohibition Party
fielded candidates, though it was the last campaign of the National Prohibitionists. Other third party candidates included Seth H. Ellis of the Union Reform Party and Jonah F.R. Leonard of the United Christian Party.
 The economy was booming in 1900, so the Republican slogan of “Four More Years of the Full Dinner Pail”, combined with victory in the brief Spanish–American War in 1898, had a powerful electoral appeal. Teddy Roosevelt had become a national hero fighting in Cuba during the war, and as such he was a popular spokesman for the Republican ticket. In his speeches he repeatedly argued that the war had been just and had liberated the Cubans and Filipinos from Spanish tyranny:
The economy was booming in 1900, so the Republican slogan of “Four More Years of the Full Dinner Pail”, combined with victory in the brief Spanish–American War in 1898, had a powerful electoral appeal. Teddy Roosevelt had become a national hero fighting in Cuba during the war, and as such he was a popular spokesman for the Republican ticket. In his speeches he repeatedly argued that the war had been just and had liberated the Cubans and Filipinos from Spanish tyranny:
Bryan's campaign was a reprise of his major issue from the 1896 campaign
, Free Silver
. It was not as successful in 1900 because of the improved economy and an increase in gold supply caused by new production from Alaska
and South Africa
that allowed more paper dollars to enter the national economy. Bryan's second major campaign theme attacked McKinley's imperialism
; Bryan argued that instead of liberating Cuba and the Philippines, the McKinley administration had simply replaced a cruel Spanish tyranny with a cruel American one. Bryan was especially harsh in his criticisms of the American military effort to suppress a bloody rebellion by Filipino guerillas. This theme won over some previous opponents, especially "hard money" Germans, former Gold Democrats
, and anti-imperialists such as Andrew Carnegie
.
Both candidates repeated their 1896 campaign techniques, with McKinley again campaigning from the front porch of his home in Canton, Ohio
; at its peak, he greeted sixteen delegations and 30,000 cheering supporters in one day. Meanwhile Bryan took to the rails again, traveling 18,000 miles to hundreds of rallies across the Midwest and East. This time, he was matched by Theodore Roosevelt
, McKinley's running mate and the Governor of New York
, who campaigned just as energetically in 24 states, covering 21,000 miles by train.
 The triumph of the American army and navy in the war against Spain was a decisive factor in building Republican support. Democrats tried to argue that the war was not over because of the insurgency in the Philippines, which became their major issue. A perception that the Philippine War was coming to an end would be an electoral asset for the Republicans, and the McKinley administration stated that there were reductions of troops there. Republicans pledged that the fighting in the Philippines would die down of its own accord within sixty days of McKinley's re-election.
The triumph of the American army and navy in the war against Spain was a decisive factor in building Republican support. Democrats tried to argue that the war was not over because of the insurgency in the Philippines, which became their major issue. A perception that the Philippine War was coming to an end would be an electoral asset for the Republicans, and the McKinley administration stated that there were reductions of troops there. Republicans pledged that the fighting in the Philippines would die down of its own accord within sixty days of McKinley's re-election.
However, as one lieutenant explained in a letter to his wife, “It looks good on paper, but there really has been no reduction of the force here. These battalions [being sent home] are made up on men…about to be discharged.”
In addition, Secretary of War Elihu Root
had a report from MacArthur of September 1900 that he did not release until after the election. General Arthur MacArthur, Jr.
had been in command of the Philippines for four months, warning Washington that the war was not lessening and that the end was not even in sight. MacArthur believed that the guerrilla stage of the war was just beginning and that Filipinos were refining their techniques through experience. Furthermore, Philippine leader Emilio Aguinaldo
’s strategy had popular support. MacArthur wrote:
 Nonetheless, the majority of soldiers in the Philippines did not support Bryan. Any mention of the election of 1900 in the soldiers' letters and diaries indicated overwhelming support for the Republican ticket of McKinley and Roosevelt. According to Sergeant Beverly Daley, even the “howling Democrats” favored McKinley. Private Hambleton wrote, “Of course, there are some boys who think Bryan is the whole cheese, but they don't say too much.”
Nonetheless, the majority of soldiers in the Philippines did not support Bryan. Any mention of the election of 1900 in the soldiers' letters and diaries indicated overwhelming support for the Republican ticket of McKinley and Roosevelt. According to Sergeant Beverly Daley, even the “howling Democrats” favored McKinley. Private Hambleton wrote, “Of course, there are some boys who think Bryan is the whole cheese, but they don't say too much.”
. As in 1896, Bryan did best in the traditionally Democratic "Solid South" and among farmers in the West. Bryan won New York City
, but President McKinley won the state of New York, winning all the state's electoral votes.
Source (Electoral Vote):
United States presidential election, 1896
The United States presidential election held on November 3, 1896, saw Republican William McKinley defeat Democrat William Jennings Bryan in a campaign considered by political scientists to be one of the most dramatic and complex in American history....
race between Republican
History of the United States Republican Party
The United States Republican Party is the second oldest currently existing political party in the United States after its great rival, the Democratic Party. It emerged in 1854 to combat the Kansas Nebraska Act which threatened to extend slavery into the territories, and to promote more vigorous...
President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
William McKinley
William McKinley
William McKinley, Jr. was the 25th President of the United States . He is best known for winning fiercely fought elections, while supporting the gold standard and high tariffs; he succeeded in forging a Republican coalition that for the most part dominated national politics until the 1930s...
and his Democratic
History of the United States Democratic Party
The history of the Democratic Party of the United States is an account of the oldest political party in the United States and arguably the oldest democratic party in the world....
challenger, William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan was an American politician in the late-19th and early-20th centuries. He was a dominant force in the liberal wing of the Democratic Party, standing three times as its candidate for President of the United States...
. The return of economic prosperity and recent victory in the Spanish–American War helped McKinley to score a decisive victory. President McKinley chose New York Governor Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore "Teddy" Roosevelt was the 26th President of the United States . He is noted for his exuberant personality, range of interests and achievements, and his leadership of the Progressive Movement, as well as his "cowboy" persona and robust masculinity...
as his running mate as Vice-President
Vice President of the United States
The Vice President of the United States is the holder of a public office created by the United States Constitution. The Vice President, together with the President of the United States, is indirectly elected by the people, through the Electoral College, to a four-year term...
Garret Hobart
Garret Hobart
Garret Augustus Hobart was the 24th Vice President of the United States, serving from March 4, 1897 until his death. He was the sixth American vice president to die in office....
had died from heart failure in 1899.
Republican Party nomination
Republican candidate:- William McKinleyWilliam McKinleyWilliam McKinley, Jr. was the 25th President of the United States . He is best known for winning fiercely fought elections, while supporting the gold standard and high tariffs; he succeeded in forging a Republican coalition that for the most part dominated national politics until the 1930s...
of OhioOhioOhio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
, President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
Candidates gallery
The 926 RepublicanRepublican Party (United States)
The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
delegates to the
Republican convention
1900 Republican National Convention
The 1900 National Convention of the Republican Party of the United States was held June 19 to June 21 in the Exposition Auditorium, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The Exposition Auditorium was located south of the University of Pennsylvania, and the later Convention Hall was constructed along the...
, which met in Philadelphia on June 19-21, renominated William McKinley
William McKinley
William McKinley, Jr. was the 25th President of the United States . He is best known for winning fiercely fought elections, while supporting the gold standard and high tariffs; he succeeded in forging a Republican coalition that for the most part dominated national politics until the 1930s...
by acclamation. Thomas C. Platt
Thomas C. Platt
Thomas Collier Platt was a two-term member of the U.S. House of Representatives and a three-term U.S. Senator from New York in the years 1881 and 1897-1909 — is best known as the "political boss" of the Republican Party in New York State in the late 19th Century and early 20th Century...
, the "boss" of the New York State Republican Party, did not like Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore "Teddy" Roosevelt was the 26th President of the United States . He is noted for his exuberant personality, range of interests and achievements, and his leadership of the Progressive Movement, as well as his "cowboy" persona and robust masculinity...
, New York's popular governor, even though he was a fellow Republican. Roosevelt's efforts to reform New York politics - including Republican politics - led Platt and other state GOP leaders to pressure President McKinley to accept Roosevelt as his new vice-presidential candidate, thus filling the spot left open when Vice-President Garret Hobart
Garret Hobart
Garret Augustus Hobart was the 24th Vice President of the United States, serving from March 4, 1897 until his death. He was the sixth American vice president to die in office....
died in 1899. By electing Roosevelt to the vice-presidency, Platt would remove Roosevelt from New York state politics. Although Roosevelt was reluctant to accept the vice-presidency, which he regarded as a relatively trivial and powerless office, his great popularity among most Republican delegates led McKinley to pick him as his new running mate. Ironically, Roosevelt would be elevated to the Presidency in September 1901, when McKinley was assassinated in Buffalo, New York
Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is the second most populous city in the state of New York, after New York City. Located in Western New York on the eastern shores of Lake Erie and at the head of the Niagara River across from Fort Erie, Ontario, Buffalo is the seat of Erie County and the principal city of the...
.
| Presidential Ballot | Vice Presidential Ballot | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| William McKinley William McKinley William McKinley, Jr. was the 25th President of the United States . He is best known for winning fiercely fought elections, while supporting the gold standard and high tariffs; he succeeded in forging a Republican coalition that for the most part dominated national politics until the 1930s... | 926 | Theodore Roosevelt Theodore Roosevelt Theodore "Teddy" Roosevelt was the 26th President of the United States . He is noted for his exuberant personality, range of interests and achievements, and his leadership of the Progressive Movement, as well as his "cowboy" persona and robust masculinity... | 925 |
| Not voting | 1 |
Democratic Party nomination
Democratic candidates:- George DeweyGeorge DeweyGeorge Dewey was an admiral of the United States Navy. He is best known for his victory at the Battle of Manila Bay during the Spanish-American War...
of VermontVermontVermont is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. The state ranks 43rd in land area, , and 45th in total area. Its population according to the 2010 census, 630,337, is the second smallest in the country, larger only than Wyoming. It is the only New England...
, Admiral of the Navy - William Jennings BryanWilliam Jennings BryanWilliam Jennings Bryan was an American politician in the late-19th and early-20th centuries. He was a dominant force in the liberal wing of the Democratic Party, standing three times as its candidate for President of the United States...
of NebraskaNebraskaNebraska is a state on the Great Plains of the Midwestern United States. The state's capital is Lincoln and its largest city is Omaha, on the Missouri River....
, Democratic presidential nominee in 1896
Candidates gallery
After Admiral George Dewey's return from the Spanish-American WarSpanish-American War
The Spanish–American War was a conflict in 1898 between Spain and the United States, effectively the result of American intervention in the ongoing Cuban War of Independence...
, many suggested he run for president on the Democratic
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
ticket. However, his candidacy was plagued by public relations gaffes. Newspapers started attacking him as naïve after he was quoted as saying the job of president would be easy, since the chief executive was merely following orders in executing the laws enacted by Congress, and that he would "execute the laws of Congress as faithfully as I have always executed the orders of my superiors." Shortly thereafter he admitted to never having voted in a presidential election. He drew yet more criticism when he offhandedly (and prophetically) told a newspaper reporter that, "Our next war will be with Germany."
Dewey also angered some Protestants
Protestantism
Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the...
by marrying Catholic Mildred McLean Hazen (the widow of General William Babcock Hazen
William Babcock Hazen
William Babcock Hazen was a career United States Army officer who served in the Indian Wars, as a Union general in the American Civil War, and as Chief Signal Officer of the U.S. Army...
and daughter of Washington McLean
Washington McLean
Washington McLean was an American businessman of Scottish ancestry best known as the owner of the Cincinnati Enquirer newspaper. Born in Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1848 Washington McLean and his brother S.B.W. McLean acquired a share position in the Cincinnati Enquirer to be partners with editor James...
, owner of The Washington Post
The Washington Post
The Washington Post is Washington, D.C.'s largest newspaper and its oldest still-existing paper, founded in 1877. Located in the capital of the United States, The Post has a particular emphasis on national politics. D.C., Maryland, and Virginia editions are printed for daily circulation...
), in November 1899 and giving her the house that the nation had given him following the war.
Dewey withdrew from the race in mid-May and endorsed William McKinley
William McKinley
William McKinley, Jr. was the 25th President of the United States . He is best known for winning fiercely fought elections, while supporting the gold standard and high tariffs; he succeeded in forging a Republican coalition that for the most part dominated national politics until the 1930s...
.
William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan was an American politician in the late-19th and early-20th centuries. He was a dominant force in the liberal wing of the Democratic Party, standing three times as its candidate for President of the United States...
was easily nominated after Dewey withdrew from the race. Bryan won at the 1900 Democratic National Convention held Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City, Missouri is the largest city in the U.S. state of Missouri and is the anchor city of the Kansas City Metropolitan Area, the second largest metropolitan area in Missouri. It encompasses in parts of Jackson, Clay, Cass, and Platte counties...
on July 4-6, garnering 936 delegate votes. Former Vice-President
Vice President of the United States
The Vice President of the United States is the holder of a public office created by the United States Constitution. The Vice President, together with the President of the United States, is indirectly elected by the people, through the Electoral College, to a four-year term...
Adlai Stevenson was nominated for the office again, beating out David B. Hill
David B. Hill
David Bennett Hill was an American politician from New York who was the 29th Governor of New York from 1885 to 1891.-Life:...
and Charles A. Towne
Charles A. Towne
Charles Arnette Towne was an American politician. Born near Pontiac, Michigan, he graduated from the University of Michigan and served in the United States House of Representatives from Minnesota as a Republican in the 54th congress and from New York as a Democrat in the 59th congress.Towne also...
for the nomination.
| Presidential Ballot | |
| William Jennings Bryan William Jennings Bryan William Jennings Bryan was an American politician in the late-19th and early-20th centuries. He was a dominant force in the liberal wing of the Democratic Party, standing three times as its candidate for President of the United States... | 936 |
|---|
Source: US President - D Convention. Our Campaigns. (March 10, 2011).
| Vice Presidential Ballot | ||
| Ballot | 1st Before Shifts | 1st After Shifts |
|---|---|---|
| Adlai E. Stevenson | 559.5 | 936 |
| David B. Hill David B. Hill David Bennett Hill was an American politician from New York who was the 29th Governor of New York from 1885 to 1891.-Life:... | 200 | 0 |
| Charles A. Towne Charles A. Towne Charles Arnette Towne was an American politician. Born near Pontiac, Michigan, he graduated from the University of Michigan and served in the United States House of Representatives from Minnesota as a Republican in the 54th congress and from New York as a Democrat in the 59th congress.Towne also... | 89.5 | 0 |
| Abraham W. Patrick | 46 | 0 |
| Julian Carr Julian Carr (industrialist) Julian Shakespeare Carr was a North Carolina industrialist and philanthropist. He was married to Nannie Carr, with whom he had two daughters and three sons.... | 23 | 0 |
| John Walter Smith John Walter Smith John Walter Smith , a member of the United States Democratic Party, served the State of Maryland in the United States in several different positions... | 16 | 0 |
| Elliott Danforth Elliott Danforth Elliott Danforth was an American lawyer and politician.-Life:... | 1 | 0 |
| Jim Hogg Jim Hogg James Stephen "Big Jim" Hogg was a Texas lawyer, doctor and statesman, and the 20th Governor of Texas. He was born near Rusk, Texas. Hogg was a follower of the conservative New South Creed which became popular following the U.S. Civil War, and was also associated with populism. He was the first... | 1 | 0 |
Other nominations
The Populist Party, which four years earlier had supported Bryan, split into two factions. One group, the "Fusion" faction, wanted to merge with the Democrats. The Fusion faction held its convention in Sioux Falls, South DakotaSioux Falls, South Dakota
Sioux Falls is the largest city in the U.S. state of South Dakota. Sioux Falls is the county seat of Minnehaha County, and also extends into Lincoln County to the south...
, and nominated Bryan for president and Charles A. Towne
Charles A. Towne
Charles Arnette Towne was an American politician. Born near Pontiac, Michigan, he graduated from the University of Michigan and served in the United States House of Representatives from Minnesota as a Republican in the 54th congress and from New York as a Democrat in the 59th congress.Towne also...
for vice-president (Towne, the national chairman of the Silver Republican Party
Silver Republican Party
The Silver Republican Party was a United States political faction active in the 1890s. It was so named because it split from the Republican Party over the issues of "Free Silver" and bimetallism. The main Republican Party supported the gold standard....
, later withdrew from the race). The "Middle of the Road" Populists wanted to maintain their identity as a separate political party; they met in Cincinnati and nominated Wharton Barker and Ignatius L. Donnelly. The "Fusion" group was absorbed into the Democratic Party with this election; and though the "Middle of the Road" faction contested two future presidential elections, the Populists were no longer considered a serious political force after 1900. The Socialist Labor Party
Socialist Labor Party of America
The Socialist Labor Party of America , established in 1876 as the Workingmen's Party, is the oldest socialist political party in the United States and the second oldest socialist party in the world. Originally known as the Workingmen's Party of America, the party changed its name in 1877 and has...
also divided; the larger faction formed the Social Democratic Party
Social Democratic Party (United States)
The Social Democratic Party of America was a short-lived political party in the United States, established in 1898. The group was formed out of elements of the Social Democracy of America , and was a predecessor to the Socialist Party of America, established in 1901.-Forerunners:Following the...
and nominated Eugene V. Debs
Eugene V. Debs
Eugene Victor Debs was an American union leader, one of the founding members of the International Labor Union and the Industrial Workers of the World , and several times the candidate of the Socialist Party of America for President of the United States...
for president. This party was renamed the Socialist Party following the election. Both factions of the Prohibition Party
Prohibition Party
The Prohibition Party is a political party in the United States best known for its historic opposition to the sale or consumption of alcoholic beverages. It is the oldest existing third party in the US. The party was an integral part of the temperance movement...
fielded candidates, though it was the last campaign of the National Prohibitionists. Other third party candidates included Seth H. Ellis of the Union Reform Party and Jonah F.R. Leonard of the United Christian Party.
Campaign

Four years ago the nation was uneasy because at our very doors an American island was writhing in hideous agony under a worse than medieval despotism. We had our Armenia at our threshold. The situation in Cuba had become such that we could no longer stand quiet and retain one shred of self-respect…. We drew the sword and waged the most righteous and brilliantly successful foreign war that this generation has seen.
Bryan's campaign was a reprise of his major issue from the 1896 campaign
United States presidential election, 1896
The United States presidential election held on November 3, 1896, saw Republican William McKinley defeat Democrat William Jennings Bryan in a campaign considered by political scientists to be one of the most dramatic and complex in American history....
, Free Silver
Free Silver
Free Silver was an important United States political policy issue in the late 19th century and early 20th century. Its advocates were in favor of an inflationary monetary policy using the "free coinage of silver" as opposed to the less inflationary Gold Standard; its supporters were called...
. It was not as successful in 1900 because of the improved economy and an increase in gold supply caused by new production from Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
and South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
that allowed more paper dollars to enter the national economy. Bryan's second major campaign theme attacked McKinley's imperialism
Imperialism
Imperialism, as defined by Dictionary of Human Geography, is "the creation and/or maintenance of an unequal economic, cultural, and territorial relationships, usually between states and often in the form of an empire, based on domination and subordination." The imperialism of the last 500 years,...
; Bryan argued that instead of liberating Cuba and the Philippines, the McKinley administration had simply replaced a cruel Spanish tyranny with a cruel American one. Bryan was especially harsh in his criticisms of the American military effort to suppress a bloody rebellion by Filipino guerillas. This theme won over some previous opponents, especially "hard money" Germans, former Gold Democrats
National Democratic Party (United States)
The National Democratic Party or Gold Democrats was a short-lived political party of Bourbon Democrats, who opposed the regular party nominee William Jennings Bryan in 1896. Most members were admirers of Grover Cleveland. They considered Bryan a dangerous man and charged that his "free silver"...
, and anti-imperialists such as Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie was a Scottish-American industrialist, businessman, and entrepreneur who led the enormous expansion of the American steel industry in the late 19th century...
.
Both candidates repeated their 1896 campaign techniques, with McKinley again campaigning from the front porch of his home in Canton, Ohio
Canton, Ohio
Canton is the county seat of Stark County in northeastern Ohio, approximately south of Akron and south of Cleveland.The City of Caton is the largest incorporated area within the Canton-Massillon Metropolitan Statistical Area...
; at its peak, he greeted sixteen delegations and 30,000 cheering supporters in one day. Meanwhile Bryan took to the rails again, traveling 18,000 miles to hundreds of rallies across the Midwest and East. This time, he was matched by Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore "Teddy" Roosevelt was the 26th President of the United States . He is noted for his exuberant personality, range of interests and achievements, and his leadership of the Progressive Movement, as well as his "cowboy" persona and robust masculinity...
, McKinley's running mate and the Governor of New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
, who campaigned just as energetically in 24 states, covering 21,000 miles by train.
Philippine–American War claims

However, as one lieutenant explained in a letter to his wife, “It looks good on paper, but there really has been no reduction of the force here. These battalions [being sent home] are made up on men…about to be discharged.”
In addition, Secretary of War Elihu Root
Elihu Root
Elihu Root was an American lawyer and statesman and the 1912 recipient of the Nobel Peace Prize. He was the prototype of the 20th century "wise man", who shuttled between high-level government positions in Washington, D.C...
had a report from MacArthur of September 1900 that he did not release until after the election. General Arthur MacArthur, Jr.
Arthur MacArthur, Jr.
Lieutenant General Arthur MacArthur, Jr. , was a United States Army General. He became the military Governor-General of the American-occupied Philippines in 1900 but his term ended a year later due to clashes with the civilian governor, future President William Howard Taft...
had been in command of the Philippines for four months, warning Washington that the war was not lessening and that the end was not even in sight. MacArthur believed that the guerrilla stage of the war was just beginning and that Filipinos were refining their techniques through experience. Furthermore, Philippine leader Emilio Aguinaldo
Emilio Aguinaldo
Emilio Aguinaldo y Famy was a Filipino general, politician, and independence leader. He played an instrumental role during the Philippines' revolution against Spain, and the subsequent Philippine-American War or War of Philippine Independence that resisted American occupation...
’s strategy had popular support. MacArthur wrote:
The success of this unique system of war depends upon almost complete unity of action of the entire native population. That such unity is a fact is too obvious to admit of discussion; how it is brought about and maintained is not so plain. Intimidation has undoubtedly accomplished much to this end, but fear as the only motive is hardly sufficient to account for the united and apparently spontaneous action of several millions of people. One traitor in each town would eventually destroy such a complex organization. It is more probable that the adhesive principle comes from ethological homogeneity, which induces men to respond for a time to the appeals of consanguineous leadership even when such action is opposed to their interests and convictions of expediency.
Soldier vote

The Election
Despite Bryan's energetic efforts, the renewed prosperity under McKinley, combined with the public's approval of the Spanish–American War, allowed McKinley to gain a comfortable victory. His popular and electoral-vote margins were both larger than in 1896; he even carried Bryan's home state of NebraskaNebraska
Nebraska is a state on the Great Plains of the Midwestern United States. The state's capital is Lincoln and its largest city is Omaha, on the Missouri River....
. As in 1896, Bryan did best in the traditionally Democratic "Solid South" and among farmers in the West. Bryan won New York City
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
, but President McKinley won the state of New York, winning all the state's electoral votes.
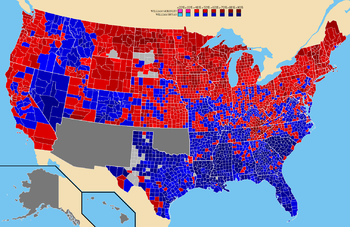
Results
Source (Popular Vote):Source (Electoral Vote):
Primary sources
- Bryan, William Jennings. "The Election of 1900," pp. 788-801 Bryan gives his analysis of why he lost
- Stevenson, Adlai E., et al. "Bryan or McKinley? The Present Duty of American Citizens," The North American Review Vol. 171, No. 527 (Oct., 1900), pp. 433-516 in JSTOR political statements by politicians on all sides, including Adlai E. Stevenson, B. R. Tillman, Edward M. Shepard, Richard Croker, Erving Winslow, Charles Emory Smith, G. F. Hoar, T. C. Platt, W. M. Stewart, Andrew Carnegie, and James H. Eckels
External links
- Opper cartoons for 1900 election ridiculing TR and McKinley as pawns of Trusts and Sen. Hanna
- 1900 popular vote by counties
- 1900 State-by-state Popular vote
- How close was the 1900 election? — Michael Sheppard, Massachusetts Institute of Technology

