
Urdu alphabet
Encyclopedia

Right-to-left
A language is described as right-to-left if writing starts from the right of the page, and continues to the left. Right to left scripts are:* Arabic alphabet - used for Arabic, Persian, Urdu and many other languages....
alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
used for the Urdu language
Urdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
. It is a modification of the Persian alphabet, which is itself a derivative of the Arabic alphabet
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
. With 38 letters, the Urdu alphabet is typically written in the calligraphic Nasta'liq script
Nasta'liq script
' is one of the main script styles used in writing the Perso-Arabic script, and traditionally the predominant style in Persian calligraphy. It was developed in Iran in the 8th and 9th centuries...
, whereas Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
is more commonly in the Naskh
Naskh (script)
Naskh is a specific calligraphic style for writing in the Arabic alphabet, thought to be invented by the Iranian calligrapher Ibn Muqlah Shirazi . The root of this Arabic term means "to copy". It either refers to the fact that it replaced its predecessor, Kufic script, or that this style allows...
style.
Usually, bare transliterations of into Roman letters omit many phonemic
Phoneme
In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances....
elements that have no equivalent in English or other languages commonly written in the Roman alphabet. The National Language Authority
National Language Authority
The National Language Authority is an autonomous regulatory institution established in 1979 to support the advancement and promotion of Urdu which is the national language of Pakistan. Initially it was aimed at creating a synergy between national and provincial governments and institutions for...
of Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
has developed a number of systems with specific notations to signify non-English sounds, but these can only be properly read by someone already familiar with , Persian, or Arabic for letters such as or and Hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
for letters such as .
History
The language developed during the Mughal EmpireMughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
under the influence of Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
and, to a lesser extent, of Arabic and Turkic languages
Turkic languages
The Turkic languages constitute a language family of at least thirty five languages, spoken by Turkic peoples across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean to Siberia and Western China, and are considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family.Turkic languages are spoken...
on the Hindi dialects
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
of North-central India. A modification of the Persian alphabet was developed to suit this language. Despite the invention of the Urdu typewriter
Urdu keyboard
The Urdu keyboardاردو is any keyboard layout for an Urdu computer and typewriter keyboards. Since the first Urdu typewriter was made available in 1911, the layout has gone through various phases of evolution. With time, the variety of layouts introduced in the 1950s for mechanised compositions have...
in 1911, newspapers continued to be published from handwritten scripts by masters (called katibs or khush-navees) until the late 1980s. The Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
i national newspaper Daily Jang
Daily Jang
The Daily Jang is an Urdu newspaper based in Pakistan. It is the oldest newspaper of Pakistan in continuous publication since its foundation in 1939. Its current Group Chief Executive & Editor-in-Chief is Mir Shakil-ur-Rahman....
was the first newspaper
Newspaper
A newspaper is a scheduled publication containing news of current events, informative articles, diverse features and advertising. It usually is printed on relatively inexpensive, low-grade paper such as newsprint. By 2007, there were 6580 daily newspapers in the world selling 395 million copies a...
to use Nasta’liq computer-based composition. There are efforts under way to develop more sophisticated and user-friendly support on computers and the internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
. Nowadays, nearly all newspapers, magazines, journals, and periodicals are composed on computers via various software programs.
Nasta'liq
The Nasta'liq calligraphic writing style began as a Persian mixture of scripts NaskhNaskh (script)
Naskh is a specific calligraphic style for writing in the Arabic alphabet, thought to be invented by the Iranian calligrapher Ibn Muqlah Shirazi . The root of this Arabic term means "to copy". It either refers to the fact that it replaced its predecessor, Kufic script, or that this style allows...
and Ta'liq. After the Mughal conquest
Muslim conquest in the Indian subcontinent
Muslim conquest in South Asia mainly took place from the 13th to the 16th centuries, though earlier Muslim conquests made limited inroads into the region, beginning during the period of the ascendancy of the Rajput Kingdoms in North India, from the 7th century onwards.However, the Himalayan...
, Nasta'liq became the preferred writing style for Urdu. It is the dominant style in Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, and many Urdu writers elsewhere in the world use it. Nasta'liq is more cursive and flowing than its Naskh
Naskh (script)
Naskh is a specific calligraphic style for writing in the Arabic alphabet, thought to be invented by the Iranian calligrapher Ibn Muqlah Shirazi . The root of this Arabic term means "to copy". It either refers to the fact that it replaced its predecessor, Kufic script, or that this style allows...
counterpart.
Alphabet
A list of the letters of the alphabet and their pronunciation is given below. contains many historical spellings from Arabic and Persian, and therefore has many irregularities. The Arabic letters yaa and haa both have two variants in : one of the yaa variants is used at the ends of words for the sound [i], and one of the haa variants is used to indicate the aspiratedAspiration (phonetics)
In phonetics, aspiration is the strong burst of air that accompanies either the release or, in the case of preaspiration, the closure of some obstruents. To feel or see the difference between aspirated and unaspirated sounds, one can put a hand or a lit candle in front of one's mouth, and say pin ...
consonants. The retroflex consonant
Retroflex consonant
A retroflex consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the hard palate. They are sometimes referred to as cerebral consonants, especially in Indology...
s needed to be added as well; this was accomplished by placing a superscript ط (to'e) above the corresponding dental consonants. Several letters which represent distinct consonants in Arabic are conflated in Persian, and this has carried over to . Some of the original Arabic letters are not used in Urdu.
This is the list of the Urdu letters, giving the consonant pronunciation. Many of these letters also represent vowel sounds.

| Letter | Name of letter | Transcription | IPA International Phonetic Alphabet The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic... |
|---|---|---|---|
| alif | – | – | |
| be | b | /b/ | |
| pe | p | /p/ | |
| te | t | /t̪/ | |
| /ʈ/ | |||
| se | s | /s/ | |
| jīm | j | /d͡ʒ/ | |
| che | ch | /t͡ʃ/ | |
| h | /h/ | ||
| khe | kh | /x/ | |
| dāl | d | /d̪/ | |
| /ɖ/ | |||
| zāl | dh | /z/ | |
| re | r | /r/ | |
| /ɽ/ | |||
| ze | z | /z/ | |
| zhe | zh | /ʒ/ | |
| sīn | s | /s/ | |
| shīn | sh | /ʃ/ | |
| su'ād | ṣ | /s/ | |
| zu'ād | z̤ | /z/ | |
| to'e | t | /t/ | |
| zo'e | ẓ | /z/ | |
| ‘ain | ' | - | |
| ghain | gh | /ɣ/ | |
| fe | f | /f/ | |
| qāf | q | /q/ | |
| kāf | k | /k/ | |
| gāf | g | /ɡ/ | |
| lām | l | /l/ | |
| mīm | m | /m/ | |
| nūn | n | /n/ | |
| vā'o | v, o, or ū | /ʋ/, /oː/, /ɔ/ or /uː/ | |
| h | /h/ | ||
| do chashmī he | h | /ʰ/ | |
| hamza | ' | /ʔ/ | |
| ye | y, i | /j/ or /iː/ | |
| bari ye | ai or e | /ɛː/, or /eː/ |
Vowels
VowelVowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
s in Urdu are represented by letters that are also considered consonant
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
s. Many vowel sounds can be represented by one letter. Confusion can arise, but context is usually enough to figure out the correct sound.
Vowel chart
This is a list of Urdu vowels found in the initial, medial, and final positions.| Romanization | Pronunciation International Phonetic Alphabet The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic... |
Final | Medial | Initial |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | /ə/ |  |
 |
 |
| ā | /ɑː/ | 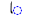 |
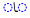 |
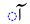 |
| i | /ɪ/ |  |
 |
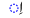 |
| ī | /iː/ |  |
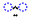 |
 |
| u | /ʊ/ | 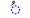 |
 |
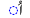 |
| ū | /uː/ | 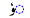 |
 |
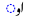 |
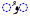
| e | /eː/ | 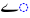 |
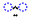 |
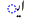 |
| ai | /ɛ/ |  |
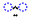 |
 |
| o | /oː/ | 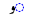 |
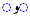 |
 |
| au | /ɔ/ | 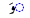 |
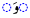 |
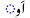 |
Short vowels
Short vowels ("a", "i", "u") are represented by marks above and below a consonant.| Vowel | Name | Transcription | IPA International Phonetic Alphabet The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic... |
| بَ | zabar | ba | /ə/ |
| بِ | zer | bi | /ɪ/ |
| بُ | pesh | bu | /ʊ/ |
Alif
Alif (ا) is the first letter of the Urdu alphabet, and it is used exclusively as a vowel. At the beginning of a word, alif can be used to represent any of the short vowels, e.g. اب ab, اسم ism, اردو urdū. Also at the beginning, an alif (ا) followed by either wā'o (و) or ye (ی) represents a long vowel sound. However, wā'o (و) or ye (ی) alone at the beginning represents a consonant.Alif also has a variant, call alif madd (آ). It is used to represent a long "ā" at the beginning of a word, e.g. آپ āp, آدمی ādmi. At the middle or end of a word, long ā is represented simply by alif (ا), e.g. بات bāt, آرام ārām.
Wā'o
Wā'o is used to render the vowels "ū", "o", and "au". It also renders the consonant "w" , but many people get confused between (W and V)sounds.(Wā'o ) sound is not closer to the consonant (V) sound because V has vibrating sound. Many Urdu linguists believe that there is no (V) sound in Urdu.
Ye
Ye is divided into two variants: and .(ی) is written in all forms exactly as in Persian. It is used for the long vowel "ī" and the consonant "y".
(ے) is used to render the vowels "e" and "ai" (/eː/ and /æː/ respectively). is distinguished in writing from choṭī ye only when it comes at the end of a word.
Retroflex letters
Retroflex consonantRetroflex consonant
A retroflex consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the hard palate. They are sometimes referred to as cerebral consonants, especially in Indology...
s were not present in the Persian alphabet, and therefore had to be created specifically for . This was accomplished by placing a superscript ط (to'e) above the corresponding dental consonants.
| Letter | Name | IPA |
| ٹ | [ʈ] | |
| ڈ | [ɖ] | |
| ڑ | [ɽ] |
Do chashmī he
The letter do chashmī he (ھ) is used in native Hindustānī words, for aspiration of certain consonants. The aspirated consonants are sometimes classified as separate letters, although it takes two characters to represent them.| Transcription | IPA | |
| بھا | bhā | [bʱɑː] |
| پھا | phā | [pʰɑː] |
| تھا | thā | [t̪ʰɑː] |
| ٹھا | [ʈʰɑː] | |
| جھا | jhā | [d͡ʒʱɑː] |
| چھا | chā | [t͡ʃʰɑː] |
| دھا | dhā | [dʱɑː] |
| ڈھا | [ɖʱɑː] | |
| ڑھا | [ɽʱɑː] | |
| کھا | khā | [kʰɑː] |
| گھا | ghā | [ɡʱɑː] |
See also
- Nasta'liq scriptNasta'liq script' is one of the main script styles used in writing the Perso-Arabic script, and traditionally the predominant style in Persian calligraphy. It was developed in Iran in the 8th and 9th centuries...
- Persian alphabet
- Urdu WikipediaUrdu WikipediaUrdu Wikipedia , started in January 2004, is the Urdu language edition of Wikipedia, a free, open-content encyclopedia. As of November 2009, it had more than 11,500 articles.- History :...
- Urdu keyboardUrdu keyboardThe Urdu keyboardاردو is any keyboard layout for an Urdu computer and typewriter keyboards. Since the first Urdu typewriter was made available in 1911, the layout has gone through various phases of evolution. With time, the variety of layouts introduced in the 1950s for mechanised compositions have...

