Urinary tract infection
Encyclopedia
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a bacterial infection
that affects any part of the urinary tract
. Symptoms include frequent feeling and/or need to urinate, pain during urination
, and cloudy urine. The main causal agent is Escherichia coli
. Although urine
contains a variety of fluids, salts, and waste products, it does not usually have bacteria in it, but when bacteria get into the bladder
or kidney
and multiply in the urine, they may cause a UTI.
The most common type of UTI is acute cystitis
often referred to as a bladder infection. An infection of the upper urinary tract or kidney is known as pyelonephritis
, and is potentially more serious. Although they cause discomfort, urinary tract infections can usually be easily treated with a short course of antibiotics with no significant difference between the classes of antibiotics commonly used.
), frequency of urination, an urge to urinate, no vaginal discharge
, and no significant pain. An upper urinary tract infection or pyelonephritis may also present with flank (abdominal) pain
and a fever
. Healthy women have an average of 5 days of symptoms.
The symptoms of urinary tract infections may vary with age and the part of the urinary system that was affected. In young children, urinary tract infection symptoms may include diarrhea
, loss of appetite
, nausea
and vomiting
, fever, and excessive crying that cannot be resolved by typical measures. Older children on the other hand may experience abdominal pain
, or incontinence. Lower urinary tract infections in adults may manifest with symptoms including hematuria
(blood in the urine), inability to urinate despite the urge, and malaise
.
Other signs of urinary tract infections include foul-smelling urine and urine that appears cloudy.
Depending on the site of infection, urinary tract infections may cause different symptoms. Urethritis, meaning only the urethra
has been affected, does not usually cause any other symptoms besides dysuria. However, if the bladder is affected (cystitis), the patient is likely to experience more symptoms, including lower abdomen discomfort, low-grade fever, pelvic pressure, and frequent urination, all together with dysuria.
Whereas in infant
s the condition may cause jaundice
and hypothermia
, in the elderly
, symptoms of urinary tract infections may include lethargy and a change in mental status
, signs that are otherwise nonspecific.
women, sexual activity does not affect the risk of developing a UTI. Spermicide
use, independent of sexual frequency, increases the risk of UTIs.
is much closer to the anus
and is shorter than in males; furthermore, women lack the bacteriostatic properties of prostatic
secretions. Among the elderly, UTI frequency is roughly equal in women and men. This is due, in part, to an enlarged prostate
in older men. As the gland grows, it obstructs the urethra, leading to increased frequency of urinary retention
.
is a risk factor for urinary tract infections. The risk of an associated infection can be decreased by catheter
izing only when necessary, using aseptic technique
for insertion, and maintaining unobstructed closed drainage of the catheter.
Infections can also be reduced by reducing the number of medically unnecessary catheters placed each year. In 2009, nearly 9.8m indwelling catheters were placed in hospitals with up to 38% considered medically unnecessary. Utilizing alternatives to indwelling catheters such as external collection devices, may significantly reduce catheter associated urinary tract infection (CAUTI).
. While ascending infections are, in general, the rule for lower urinary tract infections, the same is not necessarily true for upper urinary tract infections like pyelonephritis, which may originate from a blood-borne infection
.
Complicating factors of UTIs are rather vague and includes predisposing anatomic, functional, or metabolic abnormalities. A complicated UTI is more difficult to treat and usually requires more aggressive evaluation, treatment and follow-up.
, while Staphylococcus saprophyticus
is the cause in 5–10%.
The bladder wall, in common with most epithelia is coated with a variety of cationic antimicrobial peptides such as the defensin
s and cathelicidin
which disrupt the integrity of bacterial cell walls. In addition, there are also mannosylated proteins present, such as Tamm-Horsfall proteins (THP), which interfere with the binding of bacteria to the uroepithelium. As binding is an important factor in establishing pathogenicity for these organisms, its disruption results in reduced capacity for invasion of the tissues. Moreover, the unbound bacteria are more easily removed when voiding. The use of urinary catheters (or other physical trauma) may physically disturb this protective lining, thereby allowing bacteria to invade the exposed epithelium.
During cystitis, uropathogenic Escherichia coli
(UPEC) subvert innate defenses by invading superficial umbrella cells and rapidly increasing in numbers to form intracellular bacterial communities (IBCs). By working together, bacteria in biofilms build themselves into structures that are more firmly anchored in infected cells and are more resistant to immune-system assaults and antibiotic treatments. This is often the cause of chronic urinary tract infections.
In complicated UTIs, the most common pathogens are E.coli, Enterococci, Klebsiella
, Proteus and P.aeruginosa.
of urinary tract infections.
A number of measures have not been confirmed to affect UTI frequency including: the use of birth control pills or condoms, voiding after sex, the type of underwear used, personal hygiene methods used after voiding or defecating, and whether one takes a bath instead of a shower.
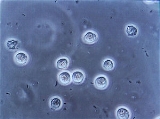
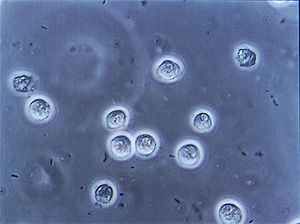 In straight-forward cases, a diagnosis may be made and treatment given based on symptoms alone without further laboratory confirmation. In complicated or questionable cases, it may be useful to confirm via urinalysis
In straight-forward cases, a diagnosis may be made and treatment given based on symptoms alone without further laboratory confirmation. In complicated or questionable cases, it may be useful to confirm via urinalysis
, looking for the presence of urinary nitrites, leukocytes, or leukocyte esterase
, or via urine microscopy, looking for the presence of red blood cells, white blood cells, and bacteria
(with presence of bacteria termed bacteriuria
).
Urine culture
showing a quantitative count of greater than or equal to 103 colony-forming units (CFU) per mL of a typical urinary tract organism along with antibiotic sensitives is useful to guide antibiotic choice. However, women with negative cultures may still improve with antibiotic treatment.
Most cases of lower urinary tract infections in females are benign and do not need exhaustive laboratory work-ups. However, UTI in young infants may receive some imaging study, typically a retrograde urethrogram
, to ascertain the presence/absence of congenital urinary tract anomalies.
The presence of bacteria in the urinary tract of older adults, without symptoms or signs of infection, is a well-recognized phenomenon that may not require antibiotics. This is usually referred to as asymptomatic bacteriuria. The overuse of antibiotics in the context of bacteriuria among the elderly is an issue of concern.
s such as trimethoprim
, cephalosporin
s, nitrofurantoin
, or a fluoroquinolone
substantially shorten the time to recovery. All are equally effective for both short and long term cure rates. About 50% of people will recover without treatment within a few days or weeks. The Infectious Diseases Society of America
recommends a combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole as a first-line agent in uncomplicated UTIs rather than fluoroquinolones. Fluoroquinolones are not recommended first line due to their cost and concern that over use will increase resistance
and thus decrease the utility of this class for those with severe infections. Resistance has developed in the community to all of these medications due to their widespread use.
A three-day treatment with trimethoprim, TMP/SMX, or a fluoroquinolone is usually sufficient, whereas nitrofurantoin requires 7 days. Trimethoprim is often recommended to be taken at night to ensure maximal urinary concentrations to increase its effectiveness. While trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole was previously internationally used (and continues to be used in the U.S. and Canada), the addition of the sulfonamide
gives little additional benefit compared to the trimethoprim component alone. However, it is responsible for a high incidence of mild allergic reactions and rare but potentially serious complications. For simple UTIs, children often respond well to a three-day course of antibiotics.
) is treated more aggressively than a simple bladder infection using either a longer course of oral antibiotics or intravenous antibiotics. Regimens vary, and include SMX/TMP and fluoroquinolones. In the past, they have included aminoglycosides (such as gentamicin) used in combination with a beta-lactam (such as ampicillin or ceftriaxone). These are continued for 48 hours after fever subsides.
If there is a poor response to IV antibiotics (marked by persistent fever, worsening renal function), then imaging is indicated to rule out formation of an abscess
either within or around the kidney, or the presence of an obstructing lesion such as a kidney stone
or tumor.
The prevalence of urinary tract infections in pre-school and school girls is 1% to 3%, nearly 30-fold higher than that in boys. Approximately 5% of girls will develop at least one urinary tract infection during their school years.
Bacteriuria appears to increase in prevalence with age in women, still being 50 times greater than the one in males. It is estimated that bacteriuria will be experienced by 20 to 50% of older women and 5 to 20% of older men. In non-institutionalized elderly populations, urinary tract infections are the second-most-common form of infection, accounting for nearly 25% of all infections. The condition rarely occurs in men who are younger than 50 years old and who did not undergo any genitourinary procedure. However, the incidence of urinary tract infections in men tends to rise after the age of 50.
According to a 1997 survey, urinary tract infection accounted for nearly 7 million office visits and 1 million emergency department visits, resulting in 100,000 hospitalizations in the United States.
. If urine testing shows signs of infection even in the absence of symptoms (known as asymptomatic bacteriuria) women are treated. Treatment is typically with cephalexin or nitrofurantoin
as while there are no adequate studies of these antibiotics in pregnant women, many women have safely used them during pregnancy. On the other hand, research has shown that pregnancy does not increase risk of asymptomatic bacteriuria. However, if the bacteriuria is not properly treated, it can significantly increase the risk of kidney infection in pregnant women. Pregnancy makes a woman particularly vulnerable to these infections. A pregnant woman may have high levels of progesterone in the blood, which decreases the muscle tone of the ureters and bladder. This leads to a greater likelihood of reflux, where urine flows back up the ureters and towards the kidneys. In addition, the growing uterus may compress the ureters, making it harder for urine to flow through. This, coupled with the urine reflux, gives bacteria more time to replicate and may aid in infecting the kidneys.
Furthermore, during pregnancy the urine may become less acidic and may contain glucose, two factors that can increase the risk of bacterial growth and increase a woman’s risk for a UTI and kidney infection.
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
that affects any part of the urinary tract
Urinary system
The urinary system is the organ system that produces, stores, and eliminates urine. In humans it includes two kidneys, two ureters, the bladder and the urethra.-Kidney:...
. Symptoms include frequent feeling and/or need to urinate, pain during urination
Urination
Urination, also known as micturition, voiding, peeing, weeing, pissing, and more rarely, emiction, is the ejection of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. In healthy humans the process of urination is under voluntary control...
, and cloudy urine. The main causal agent is Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms . Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes can cause serious food poisoning in humans, and are occasionally responsible for product recalls...
. Although urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
contains a variety of fluids, salts, and waste products, it does not usually have bacteria in it, but when bacteria get into the bladder
Urinary bladder
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor...
or kidney
Kidney
The kidneys, organs with several functions, serve essential regulatory roles in most animals, including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and...
and multiply in the urine, they may cause a UTI.
The most common type of UTI is acute cystitis
Cystitis
Cystitis is a term that refers to urinary bladder inflammation that results from any one of a number of distinct syndromes. It is most commonly caused by a bacterial infection in which case it is referred to as a urinary tract infection.-Signs and symptoms:...
often referred to as a bladder infection. An infection of the upper urinary tract or kidney is known as pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is an ascending urinary tract infection that has reached the pyelum or pelvis of the kidney. It is a form of nephritis that is also referred to as pyelitis...
, and is potentially more serious. Although they cause discomfort, urinary tract infections can usually be easily treated with a short course of antibiotics with no significant difference between the classes of antibiotics commonly used.
Signs and symptoms
The most common symptoms of a bladder infection are burning with urination (dysuriaDysuria
In medicine, specifically urology, dysuria refers to painful urination.Difficult urination is also sometimes described as dysuria.It is one of a constellation of irritative bladder symptoms, which includes urinary frequency and haematuria....
), frequency of urination, an urge to urinate, no vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge is term given to biological fluids contained within or expelled from the vagina.While most discharge is normal and can reflect the various stages of a woman's cycle, some discharge can be a result of an infection, such as a sexually transmitted disease.The term blennorrhea is...
, and no significant pain. An upper urinary tract infection or pyelonephritis may also present with flank (abdominal) pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain can be one of the symptoms associated with transient disorders or serious disease. Making a definitive diagnosis of the cause of abdominal pain can be difficult, because many diseases can result in this symptom. Abdominal pain is a common problem...
and a fever
Fever
Fever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
. Healthy women have an average of 5 days of symptoms.
The symptoms of urinary tract infections may vary with age and the part of the urinary system that was affected. In young children, urinary tract infection symptoms may include diarrhea
Diarrhea
Diarrhea , also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having three or more loose or liquid bowel movements per day. It is a common cause of death in developing countries and the second most common cause of infant deaths worldwide. The loss of fluids through diarrhea can cause dehydration and...
, loss of appetite
Anorexia (symptom)
Anorexia is the decreased sensation of appetite...
, nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
and vomiting
Vomiting
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
, fever, and excessive crying that cannot be resolved by typical measures. Older children on the other hand may experience abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain can be one of the symptoms associated with transient disorders or serious disease. Making a definitive diagnosis of the cause of abdominal pain can be difficult, because many diseases can result in this symptom. Abdominal pain is a common problem...
, or incontinence. Lower urinary tract infections in adults may manifest with symptoms including hematuria
Hematuria
In medicine, hematuria, or haematuria, is the presence of red blood cells in the urine. It may be idiopathic and/or benign, or it can be a sign that there is a kidney stone or a tumor in the urinary tract , ranging from trivial to lethal...
(blood in the urine), inability to urinate despite the urge, and malaise
Malaise
Malaise is a feeling of general discomfort or uneasiness, of being "out of sorts", often the first indication of an infection or other disease. Malaise is often defined in medicinal research as a "general feeling of being unwell"...
.
Other signs of urinary tract infections include foul-smelling urine and urine that appears cloudy.
Depending on the site of infection, urinary tract infections may cause different symptoms. Urethritis, meaning only the urethra
Urethra
In anatomy, the urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of fluids out of the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine...
has been affected, does not usually cause any other symptoms besides dysuria. However, if the bladder is affected (cystitis), the patient is likely to experience more symptoms, including lower abdomen discomfort, low-grade fever, pelvic pressure, and frequent urination, all together with dysuria.
Whereas in infant
Infant
A newborn or baby is the very young offspring of a human or other mammal. A newborn is an infant who is within hours, days, or up to a few weeks from birth. In medical contexts, newborn or neonate refers to an infant in the first 28 days after birth...
s the condition may cause jaundice
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellowish pigmentation of the skin, the conjunctival membranes over the sclerae , and other mucous membranes caused by hyperbilirubinemia . This hyperbilirubinemia subsequently causes increased levels of bilirubin in the extracellular fluid...
and hypothermia
Hypothermia
Hypothermia is a condition in which core temperature drops below the required temperature for normal metabolism and body functions which is defined as . Body temperature is usually maintained near a constant level of through biologic homeostasis or thermoregulation...
, in the elderly
Old age
Old age consists of ages nearing or surpassing the average life span of human beings, and thus the end of the human life cycle...
, symptoms of urinary tract infections may include lethargy and a change in mental status
Altered level of consciousness
An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal. Level of consciousness is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment. A mildly depressed level of consciousness may be classed as lethargy; someone in this state can be...
, signs that are otherwise nonspecific.
Intercourse
In young sexually active women, sex is the cause of 75–90% of bladder infections, with the risk of infection related to the frequency of sex. The term "honeymoon cystitis" has been applied to this phenomenon of frequent UTIs during early marriage. In post-menopausalMenopause
Menopause is a term used to describe the permanent cessation of the primary functions of the human ovaries: the ripening and release of ova and the release of hormones that cause both the creation of the uterine lining and the subsequent shedding of the uterine lining...
women, sexual activity does not affect the risk of developing a UTI. Spermicide
Spermicide
Spermicide is a contraceptive substance that eradicates sperm, inserted vaginally prior to intercourse to prevent pregnancy. As a contraceptive, spermicide may be used alone. However, the pregnancy rate experienced by couples using only spermicide is higher than that of couples using other methods...
use, independent of sexual frequency, increases the risk of UTIs.
Gender
Women are more prone to UTIs than men because, in females, the urethraUrethra
In anatomy, the urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of fluids out of the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine...
is much closer to the anus
Anus
The anus is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, unwanted semi-solid matter produced during digestion, which, depending on the type of animal, may be one or more of: matter which the animal cannot digest,...
and is shorter than in males; furthermore, women lack the bacteriostatic properties of prostatic
Prostate
The prostate is a compound tubuloalveolar exocrine gland of the male reproductive system in most mammals....
secretions. Among the elderly, UTI frequency is roughly equal in women and men. This is due, in part, to an enlarged prostate
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia also known as benign prostatic hypertrophy , benign enlargement of the prostate , and adenofibromyomatous hyperplasia, refers to the increase in size of the prostate....
in older men. As the gland grows, it obstructs the urethra, leading to increased frequency of urinary retention
Urinary retention
Urinary retention, also known as ischuria, is a lack of ability to urinate. It is a common complication of benign prostatic hyperplasia , although it can also be caused by nerve dysfunction, constipation, infection, or medications...
.
Urinary catheters
Urinary catheterizationUrinary catheterization
In urinary catheterization , a latex, polyurethane or silicone tube known as a urinary catheter is inserted into a patient's bladder via his or her urethra. Catheterization allows the patient's urine to drain freely from the bladder for collection. It may be used to inject liquids used for...
is a risk factor for urinary tract infections. The risk of an associated infection can be decreased by catheter
Catheter
In medicine, a catheter is a tube that can be inserted into a body cavity, duct, or vessel. Catheters thereby allow drainage, administration of fluids or gases, or access by surgical instruments. The process of inserting a catheter is catheterization...
izing only when necessary, using aseptic technique
Aseptic technique
Aseptic technique refers to a procedure that is performed under sterile conditions. This includes medical and laboratory techniques, such as with microbiological cultures. It includes techniques like flame sterilization...
for insertion, and maintaining unobstructed closed drainage of the catheter.
Infections can also be reduced by reducing the number of medically unnecessary catheters placed each year. In 2009, nearly 9.8m indwelling catheters were placed in hospitals with up to 38% considered medically unnecessary. Utilizing alternatives to indwelling catheters such as external collection devices, may significantly reduce catheter associated urinary tract infection (CAUTI).
Others
A predisposition for bladder infections may run in families. Other risk factors include diabetesDiabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced...
. While ascending infections are, in general, the rule for lower urinary tract infections, the same is not necessarily true for upper urinary tract infections like pyelonephritis, which may originate from a blood-borne infection
Bacteremia
Bacteremia is the presence of bacteria in the blood. The blood is normally a sterile environment, so the detection of bacteria in the blood is always abnormal....
.
Complicating factors of UTIs are rather vague and includes predisposing anatomic, functional, or metabolic abnormalities. A complicated UTI is more difficult to treat and usually requires more aggressive evaluation, treatment and follow-up.
Pathogenesis
The most common organism implicated in UTIs (80–85%) is E. coliEscherichia coli
Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms . Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes can cause serious food poisoning in humans, and are occasionally responsible for product recalls...
, while Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Staphylococcus saprophyticus is a coagulase-negative species of Staphylococcus bacteria. S. saprophyticus is often implicated in urinary tract infections. S. saprophyticus is resistant to the antibiotic novobiocin, a characteristic that is used in laboratory identification to distinguish it from S...
is the cause in 5–10%.
The bladder wall, in common with most epithelia is coated with a variety of cationic antimicrobial peptides such as the defensin
Defensin
Defensins are small cysteine-rich cationic proteins found in both vertebrates and invertebrates. They have also been reported in plants. They are, and function as, host defense peptides. They are active against bacteria, fungi and many enveloped and nonenveloped viruses. They consist of 18-45 amino...
s and cathelicidin
Cathelicidin
Members of the cathelicidin family of antimicrobial polypeptides are characterized by a highly conserved region and a highly variable cathelicidin peptide domain.Cathelicidin peptides have been isolated from many different species of mammals...
which disrupt the integrity of bacterial cell walls. In addition, there are also mannosylated proteins present, such as Tamm-Horsfall proteins (THP), which interfere with the binding of bacteria to the uroepithelium. As binding is an important factor in establishing pathogenicity for these organisms, its disruption results in reduced capacity for invasion of the tissues. Moreover, the unbound bacteria are more easily removed when voiding. The use of urinary catheters (or other physical trauma) may physically disturb this protective lining, thereby allowing bacteria to invade the exposed epithelium.
During cystitis, uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms . Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes can cause serious food poisoning in humans, and are occasionally responsible for product recalls...
(UPEC) subvert innate defenses by invading superficial umbrella cells and rapidly increasing in numbers to form intracellular bacterial communities (IBCs). By working together, bacteria in biofilms build themselves into structures that are more firmly anchored in infected cells and are more resistant to immune-system assaults and antibiotic treatments. This is often the cause of chronic urinary tract infections.
In complicated UTIs, the most common pathogens are E.coli, Enterococci, Klebsiella
Klebsiella
Klebsiella is a genus of non-motile, Gram-negative, oxidase-negative, rod-shaped bacteria with a prominent polysaccharide-based capsule. It is named after the German microbiologist Edwin Klebs...
, Proteus and P.aeruginosa.
Prevention
The following are measures that studies suggest may reduce the incidenceIncidence (epidemiology)
Incidence is a measure of the risk of developing some new condition within a specified period of time. Although sometimes loosely expressed simply as the number of new cases during some time period, it is better expressed as a proportion or a rate with a denominator.Incidence proportion is the...
of urinary tract infections.
- A prolonged course (six months to a year) of low-dose antibiotics (usually nitrofurantoin or TMP/SMX) is effective in reducing the frequency of UTIs in those with recurrent UTIs.
- CranberryCranberryCranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus Oxycoccus of the genus Vaccinium. In some methods of classification, Oxycoccus is regarded as a genus in its own right...
(juice or capsules) may decrease the incidence of UTI in those with frequent infections. Long-term tolerance, however, is an issue. Subsequent research has questioned these findings. - For post-menopausal women intravaginal application of topical estrogens was found to greatly reduce or prevent recurrent cystitis. As opposed to topical creams, the use of vaginal estrogen pessariesPessaryA pessary is a small plastic or silicone medical device which is inserted into the vagina or rectum and held in place by the pelvic floor musculature. - Therapeutic pessaries :...
was not as useful as low dose antibiotics. E. coli continues to evolve multi-drug resistance, which bears on the evaluation of appropriate empiric therapy. - Studies have shown that breastfeeding can reduce the risk of UTIs in infants.
A number of measures have not been confirmed to affect UTI frequency including: the use of birth control pills or condoms, voiding after sex, the type of underwear used, personal hygiene methods used after voiding or defecating, and whether one takes a bath instead of a shower.
Diagnosis

Urinalysis
A urinalysis , also known as Routine and Microscopy , is an array of tests performed on urine, and one of the most common methods of medical diagnosis...
, looking for the presence of urinary nitrites, leukocytes, or leukocyte esterase
Leukocyte esterase
Leukocyte esterase is a urine test for the presence of white blood cells and other abnormalities associated with infection.White blood cells in the urine usually indicate a urinary tract infection. The leukocyte esterase test detects esterase, an enzyme released by white blood cells. Positive...
, or via urine microscopy, looking for the presence of red blood cells, white blood cells, and bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
(with presence of bacteria termed bacteriuria
Bacteriuria
In medicine, bacteriuria denotes the presence of bacteria in urine not due to contamination from urine sample collection.Urine is normally a sterile bodily fluid when inside the bladder, but can pick up commensals and pathogens when exiting through the urethra...
).
Urine culture
Microbiological culture
A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture media under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are used to determine the type of organism, its abundance in the sample being tested,...
showing a quantitative count of greater than or equal to 103 colony-forming units (CFU) per mL of a typical urinary tract organism along with antibiotic sensitives is useful to guide antibiotic choice. However, women with negative cultures may still improve with antibiotic treatment.
Most cases of lower urinary tract infections in females are benign and do not need exhaustive laboratory work-ups. However, UTI in young infants may receive some imaging study, typically a retrograde urethrogram
Retrograde urethrogram
A retrograde urethrogram is a routine radiologic procedure used to image the integrity of the urethra.Hence a retrograde urethrogram is essential for diagnosis of urethral injury, or urethral stricture.-Process:...
, to ascertain the presence/absence of congenital urinary tract anomalies.
Differential diagnosis
If the urine culture is negative:- Symptoms of urethritis may point at Chlamydia trachomatisChlamydia trachomatisChlamydia trachomatis, an obligate intracellular human pathogen, is one of three bacterial species in the genus Chlamydia. C. trachomatis is a Gram-negative bacteria, therefore its cell wall components retain the counter-stain safranin and appear pink under a light microscope.The inclusion bodies...
or Neisseria gonorrheae infection. - Symptoms of cystitis may point at interstitial cystitisInterstitial cystitisInterstitial cystitis or bladder pain syndrome is a chronic, oftentimes severely debilitating disease of the urinary bladder...
. - In men, prostatitisProstatitisProstatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland, in men. A prostatitis diagnosis is assigned at 8% of all urologist and 1% of all primary care physician visits in the United States.-Classification:...
may present with dysuria.
The presence of bacteria in the urinary tract of older adults, without symptoms or signs of infection, is a well-recognized phenomenon that may not require antibiotics. This is usually referred to as asymptomatic bacteriuria. The overuse of antibiotics in the context of bacteriuria among the elderly is an issue of concern.
Uncomplicated
Uncomplicated UTIs can be diagnosed and treated based on symptoms alone. Oral antibioticAntibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s such as trimethoprim
Trimethoprim
Trimethoprim is a bacteriostatic antibiotic mainly used in the prophylaxis and treatment of urinary tract infections.It belongs to the class of chemotherapeutic agents known as dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors...
, cephalosporin
Cephalosporin
The cephalosporins are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from Acremonium, which was previously known as "Cephalosporium".Together with cephamycins they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems.-Medical use:...
s, nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin is an antibiotic which is marketed under the following brand names; Furadantin, Macrobid, Macrodantin, Nitrofur Mac, Nitro Macro, Nifty-SR, Martifur-MR, Martifur-100 , Urantoin, and Uvamin . It is usually used in treating urinary tract infection...
, or a fluoroquinolone
Quinolone
The quinolones are a family of synthetic broad-spectrum antibiotics. The term quinolone refers to potent synthetic chemotherapeutic antibacterials....
substantially shorten the time to recovery. All are equally effective for both short and long term cure rates. About 50% of people will recover without treatment within a few days or weeks. The Infectious Diseases Society of America
Infectious Diseases Society of America
The Infectious Diseases Society of America is a medical association representing physicians, scientists and other health care professionals who specialize in infectious diseases. As of 2010, IDSA had approximately 9,000 members...
recommends a combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole as a first-line agent in uncomplicated UTIs rather than fluoroquinolones. Fluoroquinolones are not recommended first line due to their cost and concern that over use will increase resistance
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a type of drug resistance where a microorganism is able to survive exposure to an antibiotic. While a spontaneous or induced genetic mutation in bacteria may confer resistance to antimicrobial drugs, genes that confer resistance can be transferred between bacteria in a...
and thus decrease the utility of this class for those with severe infections. Resistance has developed in the community to all of these medications due to their widespread use.
A three-day treatment with trimethoprim, TMP/SMX, or a fluoroquinolone is usually sufficient, whereas nitrofurantoin requires 7 days. Trimethoprim is often recommended to be taken at night to ensure maximal urinary concentrations to increase its effectiveness. While trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole was previously internationally used (and continues to be used in the U.S. and Canada), the addition of the sulfonamide
Sulfonamide (medicine)
Sulfonamide or sulphonamide is the basis of several groups of drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame...
gives little additional benefit compared to the trimethoprim component alone. However, it is responsible for a high incidence of mild allergic reactions and rare but potentially serious complications. For simple UTIs, children often respond well to a three-day course of antibiotics.
Pyelonephritis
A urinary tract infection that has reached the kidney (pyelonephritisPyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is an ascending urinary tract infection that has reached the pyelum or pelvis of the kidney. It is a form of nephritis that is also referred to as pyelitis...
) is treated more aggressively than a simple bladder infection using either a longer course of oral antibiotics or intravenous antibiotics. Regimens vary, and include SMX/TMP and fluoroquinolones. In the past, they have included aminoglycosides (such as gentamicin) used in combination with a beta-lactam (such as ampicillin or ceftriaxone). These are continued for 48 hours after fever subsides.
If there is a poor response to IV antibiotics (marked by persistent fever, worsening renal function), then imaging is indicated to rule out formation of an abscess
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has accumulated in a cavity formed by the tissue in which the pus resides due to an infectious process or other foreign materials...
either within or around the kidney, or the presence of an obstructing lesion such as a kidney stone
Kidney stone
A kidney stone, also known as a renal calculus is a solid concretion or crystal aggregation formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals in the urine...
or tumor.
Recurrent
Women with recurrent simple UTIs may benefit from self-treatment upon occurrence of symptoms with medical follow-up only if the initial treatment fails. A prescription for an effective emprical treatment can be delivered to a pharmacist by phone.Epidemiology
Bladder infections are most common in young women, with 10% of women getting an infection yearly and 60% having an infection at some point in their life. Pyelonephritis occurs between 18–29 times less frequently. Nearly 1 in 3 women will have had at least 1 episode of urinary tract infections requiring antimicrobial therapy by the age of 24 years.The prevalence of urinary tract infections in pre-school and school girls is 1% to 3%, nearly 30-fold higher than that in boys. Approximately 5% of girls will develop at least one urinary tract infection during their school years.
Bacteriuria appears to increase in prevalence with age in women, still being 50 times greater than the one in males. It is estimated that bacteriuria will be experienced by 20 to 50% of older women and 5 to 20% of older men. In non-institutionalized elderly populations, urinary tract infections are the second-most-common form of infection, accounting for nearly 25% of all infections. The condition rarely occurs in men who are younger than 50 years old and who did not undergo any genitourinary procedure. However, the incidence of urinary tract infections in men tends to rise after the age of 50.
According to a 1997 survey, urinary tract infection accounted for nearly 7 million office visits and 1 million emergency department visits, resulting in 100,000 hospitalizations in the United States.
In children
Children with recurrent UTIs may be treated with preventative antibiotics that decrease the rate of microbiological recurrence but not symptomatic recurrence. These conclusion must be viewed in light of the poor quality of evidence available.In pregnancy
Urinary tract infections are more concerning in pregnancyPregnancy
Pregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
. If urine testing shows signs of infection even in the absence of symptoms (known as asymptomatic bacteriuria) women are treated. Treatment is typically with cephalexin or nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin is an antibiotic which is marketed under the following brand names; Furadantin, Macrobid, Macrodantin, Nitrofur Mac, Nitro Macro, Nifty-SR, Martifur-MR, Martifur-100 , Urantoin, and Uvamin . It is usually used in treating urinary tract infection...
as while there are no adequate studies of these antibiotics in pregnant women, many women have safely used them during pregnancy. On the other hand, research has shown that pregnancy does not increase risk of asymptomatic bacteriuria. However, if the bacteriuria is not properly treated, it can significantly increase the risk of kidney infection in pregnant women. Pregnancy makes a woman particularly vulnerable to these infections. A pregnant woman may have high levels of progesterone in the blood, which decreases the muscle tone of the ureters and bladder. This leads to a greater likelihood of reflux, where urine flows back up the ureters and towards the kidneys. In addition, the growing uterus may compress the ureters, making it harder for urine to flow through. This, coupled with the urine reflux, gives bacteria more time to replicate and may aid in infecting the kidneys.
Furthermore, during pregnancy the urine may become less acidic and may contain glucose, two factors that can increase the risk of bacterial growth and increase a woman’s risk for a UTI and kidney infection.
External links
- NIH articles on Urinary Tract Infections in Adults and in Children
- SOGC Clinical Practice Guideline. Recurrent urinary tract infection
- Urinary Tract Infection Video
- Emedicine: Urinary Tract Infections in Pregnancy

