
Utility maximization problem
Encyclopedia
In microeconomics
, the utility maximization problem is the problem consumers
face: "how should I spend my money
in order to maximize my utility
?" It is a type of optimal decision problem
.
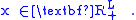
Suppose also that the prices (p) of the L commodities are positive
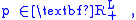
and that the consumer's wealth is w, then the set of all affordable packages, the budget set
, is
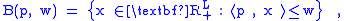
where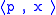 is the inner product of p and x, or the total cost of consuming x of the products at price level p:
is the inner product of p and x, or the total cost of consuming x of the products at price level p: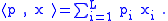
The consumer would like to buy the best package of commodities it can afford. Suppose that the consumer's utility function (u) is a real valued function with domain of the commodity bundles, or
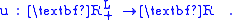
Then the consumer's optimal choices x(p, w) are the utility maximizing bundle that is in the budget set, or
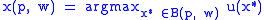 .
.
Finding x(p, w) is the utility maximization problem. If u is continuous and no commodities are free of charge, then x(p, w) exists. If there is always a unique maximizer, then it is called the Marshallian demand function
. The relationship between the utility function and Marshallian demand in the Utility Maximization Problem mirrors the relationship between the expenditure function
and Hicksian demand in the Expenditure Minimization Problem
.
In practice, a consumer may not always pick an optimal package. For example, it may require too much thought. Bounded rationality
is a theory that explains this behaviour with satisficing
- picking packages that are suboptimal but good enough.
Microeconomics
Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of how the individual modern household and firms make decisions to allocate limited resources. Typically, it applies to markets where goods or services are being bought and sold...
, the utility maximization problem is the problem consumers
Consumer
Consumer is a broad label for any individuals or households that use goods generated within the economy. The concept of a consumer occurs in different contexts, so that the usage and significance of the term may vary.-Economics and marketing:...
face: "how should I spend my money
Money
Money is any object or record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts in a given country or socio-economic context. The main functions of money are distinguished as: a medium of exchange; a unit of account; a store of value; and, occasionally in the past,...
in order to maximize my utility
Utility
In economics, utility is a measure of customer satisfaction, referring to the total satisfaction received by a consumer from consuming a good or service....
?" It is a type of optimal decision problem
Optimal decision
An optimal decision is a decision such that no other available decision options will lead to a better outcome. It is an important concept in decision theory. In order to compare the different decision outcomes, one commonly assigns a relative utility to each of them...
.
Basic setup
Suppose their consumption set, or the enumeration of all possible consumption bundles that could be selected if there are no budget constraints, has L commodities and is limited to positive amounts of consumption of each commodity. Let x be the vector x={xi;i=1,...L} containing the amounts of each commodity, then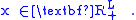
Suppose also that the prices (p) of the L commodities are positive
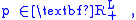
and that the consumer's wealth is w, then the set of all affordable packages, the budget set
Budget set
A budget set or opportunity set includes all possible consumption bundles that someone can afford given the prices of goods and the person's income level...
, is
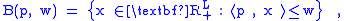
where
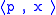 is the inner product of p and x, or the total cost of consuming x of the products at price level p:
is the inner product of p and x, or the total cost of consuming x of the products at price level p: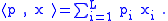
The consumer would like to buy the best package of commodities it can afford. Suppose that the consumer's utility function (u) is a real valued function with domain of the commodity bundles, or
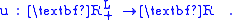
Then the consumer's optimal choices x(p, w) are the utility maximizing bundle that is in the budget set, or
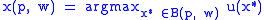 .
.Finding x(p, w) is the utility maximization problem. If u is continuous and no commodities are free of charge, then x(p, w) exists. If there is always a unique maximizer, then it is called the Marshallian demand function
Marshallian demand function
In microeconomics, a consumer's Marshallian demand function specifies what the consumer would buy in each price and wealth situation, assuming it perfectly solves the utility maximization problem...
. The relationship between the utility function and Marshallian demand in the Utility Maximization Problem mirrors the relationship between the expenditure function
Expenditure function
In microeconomics, the expenditure function describes the minimum amount of money an individual needs to achieve some level of utility, given a utility function and prices....
and Hicksian demand in the Expenditure Minimization Problem
Expenditure minimization problem
In microeconomics, the expenditure minimization problem is another perspective on the utility maximization problem: "how much money do I need to reach a certain level of happiness?". This question comes in two parts...
.
In practice, a consumer may not always pick an optimal package. For example, it may require too much thought. Bounded rationality
Bounded rationality
Bounded rationality is the idea that in decision making, rationality of individuals is limited by the information they have, the cognitive limitations of their minds, and the finite amount of time they have to make a decision...
is a theory that explains this behaviour with satisficing
Satisficing
Satisficing, a portmanteau "combining satisfy with suffice", is a decision-making strategy that attempts to meet criteria for adequacy, rather than to identify an optimal solution...
- picking packages that are suboptimal but good enough.
non unique solution
The solution x(p, w) need not be unique. If a consumer always picks an optimal package as defined above, then x(p, w) is called the Marshallian demand correspondence.See also
- Optimal decisionOptimal decisionAn optimal decision is a decision such that no other available decision options will lead to a better outcome. It is an important concept in decision theory. In order to compare the different decision outcomes, one commonly assigns a relative utility to each of them...
- Choice ModellingChoice ModellingChoice modelling attempts to model the decision process of an individual or segment in a particular context. Choice modelling may also be used to estimate non-market environmental benefits and costs....
- Utility function
- Expenditure minimization problemExpenditure minimization problemIn microeconomics, the expenditure minimization problem is another perspective on the utility maximization problem: "how much money do I need to reach a certain level of happiness?". This question comes in two parts...
- Profit maximization formulaeLinear programmingLinear programming is a mathematical method for determining a way to achieve the best outcome in a given mathematical model for some list of requirements represented as linear relationships...

