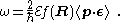Vacuum Rabi oscillation
Encyclopedia
A vacuum Rabi oscillation is a damped oscillation of an initially excited atom coupled to an electromagnetic resonator or cavity in which the atom alternately emits photon
(s) into a single-mode electromagnetic cavity and reabsorbs them. The atom interacts with a single-mode field confined to a limited volume V in an optical cavity.
Spontaneous emission
results as a consequence of coupling between the atom and the vacuum fluctuations of the cavity field. The vacuum Rabi frequency is given by
where R is the location of the atom, f ( R ) = exp ( i k.R) for plane-wave fields, ε is the field polarization,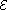 = [ ħ ωk / ( 2 ε0 V )]1/2 is the electric field per photon, and < p.ε > is the dipole matrix element.
= [ ħ ωk / ( 2 ε0 V )]1/2 is the electric field per photon, and < p.ε > is the dipole matrix element.
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
(s) into a single-mode electromagnetic cavity and reabsorbs them. The atom interacts with a single-mode field confined to a limited volume V in an optical cavity.
Spontaneous emission
Spontaneous emission
Spontaneous emission is the process by which a light source such as an atom, molecule, nanocrystal or nucleus in an excited state undergoes a transition to a state with a lower energy, e.g., the ground state and emits a photon...
results as a consequence of coupling between the atom and the vacuum fluctuations of the cavity field. The vacuum Rabi frequency is given by
where R is the location of the atom, f ( R ) = exp ( i k.R) for plane-wave fields, ε is the field polarization,
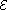 = [ ħ ωk / ( 2 ε0 V )]1/2 is the electric field per photon, and < p.ε > is the dipole matrix element.
= [ ħ ωk / ( 2 ε0 V )]1/2 is the electric field per photon, and < p.ε > is the dipole matrix element.See also
- Spontaneous emissionSpontaneous emissionSpontaneous emission is the process by which a light source such as an atom, molecule, nanocrystal or nucleus in an excited state undergoes a transition to a state with a lower energy, e.g., the ground state and emits a photon...
- Vacuum fluctuations
- Jaynes-Cummings modelJaynes-Cummings modelThe Jaynes–Cummings model is a theoretical model in quantum optics. It describes the system of a two-level atom interacting with a quantized mode of an optical cavity, with or without the presence of light...
- Rabi frequencyRabi frequencyThe Rabi frequency is the frequency of population oscillation for a given atomic transition in a given light field. It is associated with the strength of the coupling between the light and the transition. Rabi flopping between the levels of a 2-level system illuminated with resonant light, will...
- Rabi cycleRabi cycleIn physics, the Rabi cycle is the cyclic behaviour of a two-state quantum system in the presence of an oscillatory driving field. A two-state system has two possible states, and if they are not degenerate energy levels the system can become "excited" when it absorbs a quantum of energy.The effect...
- Rabi problemRabi problemThe Rabi problem concerns the response of an atom to an applied harmonic electric field, with an applied frequency very close to the atom's natural frequency...