
Vegan nutrition
Encyclopedia

Veganism
Veganism is the practice of eliminating the use of animal products. Ethical vegans reject the commodity status of animals and the use of animal products for any purpose, while dietary vegans or strict vegetarians eliminate them from their diet only...
diets. The American Dietetic Association and Dietitians of Canada regard the vegan diet as appropriate for all stages of the life-cycle, though they caution that poorly planned vegan diets can be deficient in Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, vitamin B12 or vitamin B-12, also called cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin with a key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and for the formation of blood. It is one of the eight B vitamins...
, vitamin D
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids. In humans, vitamin D is unique both because it functions as a prohormone and because the body can synthesize it when sun exposure is adequate ....
, calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
, iodine
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The name is pronounced , , or . The name is from the , meaning violet or purple, due to the color of elemental iodine vapor....
, iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
and omega-3 fatty acid
Omega-3 fatty acid
N−3 fatty acids are essential unsaturated fatty acids with a double bond starting after the third carbon atom from the end of the carbon chain....
s.
Benefits of a vegan diet
Doctors Dean OrnishDean Ornish
Dean Michael Ornish, M.D., is president and founder of the nonprofit Preventive Medicine Research Institute in Sausalito, California, as well as Clinical Professor of Medicine at the University of California, San Francisco....
, T. Colin Campbell
T. Colin Campbell
T. Colin Campbell is an American biochemist who specializes in the effects of nutrition on long-term health. He is the Jacob Gould Schurman Professor Emeritus of Nutritional Biochemistry at Cornell University, and the author of over 300 research papers...
, John A. McDougall
John A. McDougall
John A. McDougall, M.D., is an American physician and author whose philosophy is that degenerative disease can be prevented and treated with a plant-based diet of whole, unprocessed, low-fat foods, especially starches such as potatoes, rice, and beans, and which excludes all animal foods and added...
, Caldwell Esselstyn
Caldwell Esselstyn
Caldwell Blakeman Esselstyn Jr., M.D., is an American physician, author, and former Olympic rowing champion.-Biography:...
and Neal D. Barnard
Neal D. Barnard
Neal D. Barnard is an American physician, author, clinical researcher, and founding president of the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine , an international network of physicians, scientists, and laypeople who promote preventive medicine, conduct clinical research, and promote higher...
claim that high animal fat and protein diets, such as the standard American diet, are detrimental to health. They also state that a lifestyle change incorporating a low fat vegan diet could not only prevent various degenerative disease
Degenerative disease
A degenerative disease, also called neurodegenerative disease, is a disease in which the function or structure of the affected tissues or organs will progressively deteriorate over time, whether due to normal bodily wear or lifestyle choices such as exercise or eating habits...
s, such as coronary artery disease, but reverse them.
Nutrition
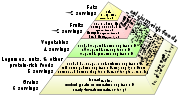
Pregnancy
Pregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
, lactation
Lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process occurs in all female mammals, however it predates mammals. In humans the process of feeding milk is called breastfeeding or nursing...
, infancy
Infant
A newborn or baby is the very young offspring of a human or other mammal. A newborn is an infant who is within hours, days, or up to a few weeks from birth. In medical contexts, newborn or neonate refers to an infant in the first 28 days after birth...
, childhood
Childhood
Childhood is the age span ranging from birth to adolescence. In developmental psychology, childhood is divided up into the developmental stages of toddlerhood , early childhood , middle childhood , and adolescence .- Age ranges of childhood :The term childhood is non-specific and can imply a...
, and adolescence
Adolescence
Adolescence is a transitional stage of physical and mental human development generally occurring between puberty and legal adulthood , but largely characterized as beginning and ending with the teenage stage...
.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, vitamin B12 or vitamin B-12, also called cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin with a key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and for the formation of blood. It is one of the eight B vitamins...
deficiency is potentially extremely serious, leading to megaloblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia is an anemia that results from inhibition of DNA synthesis in red blood cell production. When DNA synthesis is impaired, the cell cycle cannot progress from the G2 growth stage to the mitosis stage...
, nerve degeneration and irreversible neurological damage.
Evidence suggests that vegans who are not taking vitamin B12 supplements do not consume sufficient servings of B12 and often have abnormally low blood concentrations of vitamin B12. This is because, unless fortified, plant foods do not contain reliable amounts of active vitamin B12
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, vitamin B12 or vitamin B-12, also called cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin with a key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and for the formation of blood. It is one of the eight B vitamins...
.
However recent studies (such as the Framingham study) have shown that many omnivores are also deficient in vitamin B12 - in fact around 40% of Americans. This is attributed to various things, including the inability to produce the intrinsic factor which is required to successfully metabolize B12.
Omega-3 fatty acids

Omega-3 fatty acid
N−3 fatty acids are essential unsaturated fatty acids with a double bond starting after the third carbon atom from the end of the carbon chain....
s (O3FA). Major vegan sources of O3FA include algae
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
, hempseeds and hempseed oil
Hemp
Hemp is mostly used as a name for low tetrahydrocannabinol strains of the plant Cannabis sativa, of fiber and/or oilseed varieties. In modern times, hemp has been used for industrial purposes including paper, textiles, biodegradable plastics, construction, health food and fuel with modest...
, walnut
Walnut
Juglans is a plant genus of the family Juglandaceae, the seeds of which are known as walnuts. They are deciduous trees, 10–40 meters tall , with pinnate leaves 200–900 millimetres long , with 5–25 leaflets; the shoots have chambered pith, a character shared with the wingnuts , but not the hickories...
s, flaxseeds and flaxseed oil
Flax
Flax is a member of the genus Linum in the family Linaceae. It is native to the region extending from the eastern Mediterranean to India and was probably first domesticated in the Fertile Crescent...
, olive oil
Olive oil
Olive oil is an oil obtained from the olive , a traditional tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin. It is commonly used in cooking, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and soaps and as a fuel for traditional oil lamps...
, canola
Canola
Canola refers to a cultivar of either Rapeseed or Field Mustard . Its seeds are used to produce edible oil suitable for consumption by humans and livestock. The oil is also suitable for use as biodiesel.Originally, Canola was bred naturally from rapeseed in Canada by Keith Downey and Baldur R...
(rapeseed
Rapeseed
Rapeseed , also known as rape, oilseed rape, rapa, rappi, rapaseed is a bright yellow flowering member of the family Brassicaceae...
) oil, avocado
Avocado
The avocado is a tree native to Central Mexico, classified in the flowering plant family Lauraceae along with cinnamon, camphor and bay laurel...
and chia seeds
Salvia hispanica
Salvia hispanica, commonly known as chia, is a species of flowering plant in the mint family, Lamiaceae, native to central and southern Mexico and Guatemala. The 16th century Codex Mendoza provides evidence that it was cultivated by the Aztec in pre-Columbian times; it has been said that it was an...
. However, diets lacking generous amounts of sea vegetables (seaweed) generally lack a direct source of long-chain O3FA such as eicosapentaenoic acid
Eicosapentaenoic acid
Eicosapentaenoic acid is an omega-3 fatty acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 20:5. It also has the trivial name timnodonic acid...
(EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid
Docosahexaenoic acid
Docosahexaenoic acid is an omega-3 fatty acid that is a primary structural component of the human brain and retina. In chemical structure, DHA is a carboxylic acid with a 22-carbon chain and six cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the third carbon from the omega end...
(DHA). Vegan diets may also have a high ratio of O6FA to O3FA, which inhibits the conversion of short-chain fatty acids such as alpha-Linolenic acid
Alpha-linolenic acid
α-Linolenic acid is an organic compound found in many common vegetable oils. In terms of its structure, it is named all-cis-9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid. In physiological literature, it is given the name 18:3 ....
(ALA), found in most vegan O3FA sources, to EPA and DHA. Short-term supplemental ALA has been shown to increase EPA levels but not DHA levels, suggesting poor conversion of the intermediary EPA to DHA. DHA supplements derived from DHA-rich microalgae are available, and the human body can also convert DHA to EPA.

Scientific consensus
Scientific consensus is the collective judgment, position, and opinion of the community of scientists in a particular field of study. Consensus implies general agreement, though not necessarily unanimity. Scientific consensus is not by itself a scientific argument, and it is not part of the...
on the role of omega-3 fatty acids, they may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease
Heart disease
Heart disease, cardiac disease or cardiopathy is an umbrella term for a variety of diseases affecting the heart. , it is the leading cause of death in the United States, England, Canada and Wales, accounting for 25.4% of the total deaths in the United States.-Types:-Coronary heart disease:Coronary...
, lower triglycerides, stabilize mood and help prevent depression
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
, help reduce symptoms of ADD
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is a developmental disorder. It is primarily characterized by "the co-existence of attentional problems and hyperactivity, with each behavior occurring infrequently alone" and symptoms starting before seven years of age.ADHD is the most commonly studied and...
, reduce joint pain and other rheumatoid
Rheumatism
Rheumatism or rheumatic disorder is a non-specific term for medical problems affecting the joints and connective tissue. The study of, and therapeutic interventions in, such disorders is called rheumatology.-Terminology:...
problems, and reduce the risk of dementia
Dementia
Dementia is a serious loss of cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging...
in older age. While there is little evidence of adverse health or cognitive effects due to DHA deficiency in adult vegetarians or vegans, fetal and breast milk levels remain a concern. EPA and DHA supplementation has been shown to reduce platelet aggregation in vegetarians, but a direct link to cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, which is already lower for vegetarians, has yet to be determined.
Vitamin D
The human body can synthesizeBiosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
vitamin D
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids. In humans, vitamin D is unique both because it functions as a prohormone and because the body can synthesize it when sun exposure is adequate ....
when skin
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
. If vegans cannot obtain enough vitamin D from exposure to sunlight, it is recommended that they eat foods or pills fortified with synthetic vitamin D2 (vitamin D3 supplements are animal-derived, mainly from lanolin
Lanolin
Lanolin , also called Adeps Lanae, wool wax or wool grease, is a yellow waxy substance secreted by the sebaceous glands of wool-bearing animals. Most lanolin used by humans comes from domestic sheep...
). Those who don't expose their extremities for at least 15–30 minutes per day or those living at latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
s close to the pole
Geographical pole
A geographical pole is either of the two points—the north pole and the south pole—on the surface of a rotating planet where the axis of rotation meets the surface of the body...
s) are vulnerable to vitamin D deficiencies.
Vitamin D acts as a hormone
Hormone
A hormone is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. In essence, it is a chemical messenger that transports a signal from one...
, sending a message to the intestine
Intestine
In human anatomy, the intestine is the segment of the alimentary canal extending from the pyloric sphincter of the stomach to the anus and, in humans and other mammals, consists of two segments, the small intestine and the large intestine...
s to increase the absorption of calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
and phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
, which produces strong bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
s. Vitamin D also works in concert with a number of other vitamin
Vitamin
A vitamin is an organic compound required as a nutrient in tiny amounts by an organism. In other words, an organic chemical compound is called a vitamin when it cannot be synthesized in sufficient quantities by an organism, and must be obtained from the diet. Thus, the term is conditional both on...
s, mineral
Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
s, and hormones to promote bone mineralization
Mineralization (biology)
In biology, mineralization refers to the process where an organic substance is converted to an inorganic substance.This may also be a normal biological process which takes place during the life of an organism such as the formation of bone tissue or egg shells, largely with calcium.This term may...
. Research also suggests that vitamin D may help maintain a healthy immune system
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
and help regulate cell growth
Cell growth
The term cell growth is used in the contexts of cell development and cell division . When used in the context of cell division, it refers to growth of cell populations, where one cell grows and divides to produce two "daughter cells"...
and differentiation
Cellular differentiation
In developmental biology, cellular differentiation is the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as the organism changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of...
.
Calcium
It is recommended that vegans eat three servings per day of a high-calciumCalcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
food, such as fortified soy milk, almonds, hazelnuts, and take a calcium supplement as necessary. The EPIC-Oxford
European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition
The European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study is a Europe-wide prospective cohort study of the relationships between diet and cancer, as well as other chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease...
study suggested that vegans have an increased risk of bone fractures over meat eaters and vegetarians, likely because of lower dietary calcium intake, but that vegans consuming more than 525 mg/day had a risk of fractures similar to other groups. A 2009 study of bone density found the bone density of vegans was 94 percent that of omnivores, but deemed the difference clinically insignificant. Another study in 2009 by the same researchers examined over 100 vegan post-menopausal women, and found that their diet had no adverse effect on bone mineral density (BMD) and no alteration in body composition. Biochemist T. Colin Campbell
T. Colin Campbell
T. Colin Campbell is an American biochemist who specializes in the effects of nutrition on long-term health. He is the Jacob Gould Schurman Professor Emeritus of Nutritional Biochemistry at Cornell University, and the author of over 300 research papers...
suggested in The China Study
The China Study
The China Study is a 2005 book by T. Colin Campbell and his son, Thomas M. Campbell II. It examines the relationship between the consumption of animal products and illnesses such as cancers of the breast, prostate, and large bowel, diabetes, coronary heart disease, obesity, autoimmune disease,...
(2005) that osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
is linked to the consumption of animal protein because, unlike plant protein, animal protein increases the acidity of blood and tissues, which is then neutralized by calcium pulled from the bones resulting in hypercalciuria
Hypercalciuria
Hypercalciuria or hypercalcinuria is the condition of elevated calcium in the urine. Chronic hypercalcinuria may lead to impairment of renal function, nephrocalcinosis, and renal insufficiency....
. Cornell wrote that his China-Oxford-Cornell study of nutrition in the 1970s and 1980s found that, in rural China, "where the animal to plant ratio [for protein] was about 10 percent, the fracture rate is only one-fifth that of the U.S."
Iodine
One study reported a "potential danger of iodineIodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The name is pronounced , , or . The name is from the , meaning violet or purple, due to the color of elemental iodine vapor....
deficiency disorders due to strict forms of vegetarian nutrition, especially when fruits and vegetables grown in soils with low [iodine] levels are ingested." Iodine, however, is usually supplied by iodized salt and other sources in first world countries
First World
The concept of the First World first originated during the Cold War, where it was used to describe countries that were aligned with the United States. These countries were democratic and capitalistic. After the fall of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War, the term "First World" took on a...
. Other significant sources of iodine include sea vegetables (seaweed) and bread made with dough conditioner
Dough conditioner
A dough conditioner is any ingredient or chemical added to bread dough to strengthen its texture or otherwise improve it in some way.Examples of dough conditioners include ascorbic acid, monoglycerides and diglycerides, ammonium chloride, enzymes, DATEM, and calcium salts such as calcium...
s.
However, Raw Vegans who eat a high fruit diet and abstain from eating overt salt, can find enough iodine in foods such as bananas, permitting that caloric needs are met.
Iron
It is recommended for vegans to eat iron-rich foods and vitamin C daily. In several studies, vegans were not found to suffer from ironIron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
-deficiency any more than non-vegans.
Choline
It is recommended for vegans to eat food rich in cholineCholine
Choline is a water-soluble essential nutrient. It is usually grouped within the B-complex vitamins. Choline generally refers to the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the N,N,N-trimethylethanolammonium cation....
, as plant based sources of choline are limited. Soy lecithin, cauliflower, spinach, wheat germ, firm tofu, kidney beans, quinoa and amaranth are vegan sources of choline. The Adequate Intake (AI) of choline is 425 mg (milligrams) per day for adult women; higher for pregnant and breastfeeding women. The AI for adult men is 550 mg/day.
See also
- Nutritional medicineOrthomolecular medicineOrthomolecular medicine is a form of complementary and alternative medicine that seeks to maintain health and prevent or treat diseases by optimizing nutritional intake and/or prescribing supplements...
- Raw veganismRaw veganismRaw veganism is a diet that combines veganism and raw foodism. It excludes all food of animal origin, and all food cooked above 48 degrees Celsius . A raw vegan diet includes raw vegetables and fruits, nuts and nut pastes, grain and legume sprouts, seeds, plant oils, sea vegetables, herbs, and...
- The China StudyThe China StudyThe China Study is a 2005 book by T. Colin Campbell and his son, Thomas M. Campbell II. It examines the relationship between the consumption of animal products and illnesses such as cancers of the breast, prostate, and large bowel, diabetes, coronary heart disease, obesity, autoimmune disease,...
- Vegetarian nutritionVegetarian nutritionVegetarian nutrition is the set of health-related challenges and advantages of vegetarian diets.Well-planned vegetarian and vegan diets are nutritionally adequate and are appropriate for all stages of the life cycle, including during pregnancy, lactation, infancy, childhood, and adolescence...
1990s
- Diet for a New America (1992) by John Robbins, featuring Michael KlaperMichael KlaperMichael A. Klaper, M.D., is an American physician, author and vegan.-Early years and education:Klaper spent much of his childhood vacations on his uncle’s dairy farm in Wisconsin....
- A Diet for All Reasons (1993) by Michael KlaperMichael KlaperMichael A. Klaper, M.D., is an American physician, author and vegan.-Early years and education:Klaper spent much of his childhood vacations on his uncle’s dairy farm in Wisconsin....
2000s
- Eating (2002) by Mike Anderson, featuring Caldwell EsselstynCaldwell EsselstynCaldwell Blakeman Esselstyn Jr., M.D., is an American physician, author, and former Olympic rowing champion.-Biography:...
and John A. McDougallJohn A. McDougallJohn A. McDougall, M.D., is an American physician and author whose philosophy is that degenerative disease can be prevented and treated with a plant-based diet of whole, unprocessed, low-fat foods, especially starches such as potatoes, rice, and beans, and which excludes all animal foods and added... - Total Health Solution (2003) by John A. McDougallJohn A. McDougallJohn A. McDougall, M.D., is an American physician and author whose philosophy is that degenerative disease can be prevented and treated with a plant-based diet of whole, unprocessed, low-fat foods, especially starches such as potatoes, rice, and beans, and which excludes all animal foods and added...
- Simply Raw: Reversing Diabetes in 30 Days (2009) by Gabriel Cousens, featuring Joel FuhrmanJoel FuhrmanJoel Fuhrman, MD , is an American board-certified family physician who specializes in nutrition-based treatments for obesity and chronic disease. He is a member of the board of directors of the American College of Lifestyle Medicine, and serves as Research Director of the Nutritional Research...
2010s
- Latest in Clinical Nutrition (2010) by Michael GregerMichael GregerMichael Greger, is an American physician, author, vegan and professional speaker. Dr. Greger is a graduate of the Cornell University School of Agriculture and the Tufts University School of Medicine. He became vegan in 1990. He is currently the Director of Public Health and Animal Agriculture at...
- Forks Over KnivesForks Over KnivesForks Over Knives is a 2011 American documentary film directed by Lee Fulkerson, an American independent filmmaker. The film examines the "profound claim that most, if not all, of the degenerative diseases that afflict us can be controlled, or even reversed, by rejecting our present menu of...
(2011) by Lee Fulkerson, featuring T. Colin CampbellT. Colin CampbellT. Colin Campbell is an American biochemist who specializes in the effects of nutrition on long-term health. He is the Jacob Gould Schurman Professor Emeritus of Nutritional Biochemistry at Cornell University, and the author of over 300 research papers...
, Caldwell EsselstynCaldwell EsselstynCaldwell Blakeman Esselstyn Jr., M.D., is an American physician, author, and former Olympic rowing champion.-Biography:...
and Neal D. BarnardNeal D. BarnardNeal D. Barnard is an American physician, author, clinical researcher, and founding president of the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine , an international network of physicians, scientists, and laypeople who promote preventive medicine, conduct clinical research, and promote higher...
1980s
- John Robbins (1987) Diet for a New America
- Michael KlaperMichael KlaperMichael A. Klaper, M.D., is an American physician, author and vegan.-Early years and education:Klaper spent much of his childhood vacations on his uncle’s dairy farm in Wisconsin....
(1987) Vegan Nutrition
1990s
- William Harris (1993) Scientific Basis of Vegetarianism
- Neal Pinckney (1996) Healthy Heart Handbook
- Dean OrnishDean OrnishDean Michael Ornish, M.D., is president and founder of the nonprofit Preventive Medicine Research Institute in Sausalito, California, as well as Clinical Professor of Medicine at the University of California, San Francisco....
(1996) Dr. Dean Ornish's Programme for Reversing Heart Disease - John A. McDougallJohn A. McDougallJohn A. McDougall, M.D., is an American physician and author whose philosophy is that degenerative disease can be prevented and treated with a plant-based diet of whole, unprocessed, low-fat foods, especially starches such as potatoes, rice, and beans, and which excludes all animal foods and added...
(1996) The McDougall Program for a Healthy Heart - George Eisman (1999) A Basic Course in Vegetarian and Vegan Nutrition
- J. Robert Hatherill (1999) Eat To Beat Cancer
2000s
- Physicians Committee for Responsible MedicinePhysicians Committee for Responsible MedicineThe Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine is a non-profit organization based in Washington, D.C., which promotes a vegan diet, preventive medicine, alternatives to animal research, and encourages what it describes as "higher standards of ethics and effectiveness in research." Its primary...
(2002) Healthy Eating for Life to Prevent and Treat Cancer - Joel FuhrmanJoel FuhrmanJoel Fuhrman, MD , is an American board-certified family physician who specializes in nutrition-based treatments for obesity and chronic disease. He is a member of the board of directors of the American College of Lifestyle Medicine, and serves as Research Director of the Nutritional Research...
(2003) Eat to Live - Kerrie K. Saunders (2003) The Vegan Diet as Chronic Disease Prevention
- Steven Walsh (2003) Plant Based Nutrition and Health
- Mike Anderson (2004) The RAVE Diet & Lifestyle
- T. Colin CampbellT. Colin CampbellT. Colin Campbell is an American biochemist who specializes in the effects of nutrition on long-term health. He is the Jacob Gould Schurman Professor Emeritus of Nutritional Biochemistry at Cornell University, and the author of over 300 research papers...
(2005) The China Study - Michael GregerMichael GregerMichael Greger, is an American physician, author, vegan and professional speaker. Dr. Greger is a graduate of the Cornell University School of Agriculture and the Tufts University School of Medicine. He became vegan in 1990. He is currently the Director of Public Health and Animal Agriculture at...
(2005) Carbophobia! - Ruth Heidreich (2005) A Race for Life
- Will TuttleWill TuttleDr Will Tuttle, PhD, is an award-winning American author, speaker, educator, pianist and composer. He is a former Zen monk and a PhD graduate from the University of California, Berkeley. He has been awarded a Peace Abbey Courage of Conscience award His wife Madeleine is a visual artist...
(2005) World Peace DietWorld Peace Diet- Reviews and reception :The World Peace Diet has been reviewed in VegNews, in which Tuttle was said to "...lift the discussion of veganism to a higher level. He argues cogently for a spiritual component, one where the consequence of using and consuming animals, so ubiquitous in human society,... - Douglas N. Graham (2006) The 80/10/10 Diet
- Neal D. BarnardNeal D. BarnardNeal D. Barnard is an American physician, author, clinical researcher, and founding president of the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine , an international network of physicians, scientists, and laypeople who promote preventive medicine, conduct clinical research, and promote higher...
(2007) Dr. Neal Barnard's Program for Reversing Diabetes - Caldwell EsselstynCaldwell EsselstynCaldwell Blakeman Esselstyn Jr., M.D., is an American physician, author, and former Olympic rowing champion.-Biography:...
(2008) Prevent and Reverse Heart Disease
External links
- Nutritional guidelines by the Vegan Society
- Shattering The Meat Myth: Humans Are Natural Vegetarians by Kathy Freston, The Huffington Post, June 11, 2009

