
Victorian Railways C class
Encyclopedia
The C class was a mainline goods locomotive of the 2-8-0
'Consolidation' type that ran on the Victorian Railways
between 1918 and 1962. Although its original design had some key shortcomings, a number of improvements were made over the class' long career on the VR, many of which were subsequently applied to other locomotive classes on the system.
and A2 class
passenger locomotives. When introduced in 1918, they were the heaviest and most powerful steam locomotives in Australia.
In an attempt to rectify these problems, locomotive C 5 was fitted in 1933 with a new front end, based on the Association of American Railroads
(AAR) design of self-cleaning smokebox
, to improve steaming qualities. The results were very promising and led to further experimental work, using A2 class locomotive A2 998 as a test bed and conducted under the direction of VR Rolling Stock branch engineer Edgar Brownbill, in streamlining the steam passages and other changes to reduce back pressure on the exhaust side and increase efficiency. These changes, referred to as 'Modified Front End', were such an improvement that the rest of the A2 and C classes were progressively modified, as well as all of the K
, N
, S
and X
classes.
In 1929, C 5 also became the first VR locomotive to be fitted with a cross-compound air compressor, which was also subsequently adopted across other VR locomotive classes. The C class was also the first goods locomotive to be fitted with Automatic Staff Exchange apparatus, given their frequent used on express goods and fruit services.
As the poor quality of coal available after World War II
exacerbated the problems of firing the C class and industrial action in the mines threatened supply, the entire class was converted to oil firing from 1946 onwards following an initial conversion of C 15 in 1946. Despite the success of the conversion, C class locomotives were still prone to running out of steam when pushed on long rising gradients.
Whereas other VR locomotives to receive Modified Front End treatment had been equipped with smoke deflectors
in the 1930s, it was not until 1947 that the VR finally developed a successful design of smoke deflector for the C class, based on the German "Witte" pattern. This design was then adopted for the final Newport-built N class
locomotives as well as the last two steam locomotive classes on the VR, the R
and J
classes.
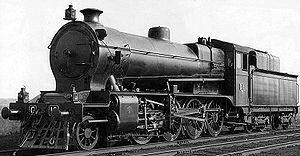 In 1923, C 16 was modified with Fuller-Lehigh equipment to run on Pulverised Brown Coal (PBC), a potentially abundant fuel in Victoria given the large brown coal reserves in the Latrobe Valley
In 1923, C 16 was modified with Fuller-Lehigh equipment to run on Pulverised Brown Coal (PBC), a potentially abundant fuel in Victoria given the large brown coal reserves in the Latrobe Valley
. Unlike the later conversion of X class
locomotive X 32 to PBC firing in 1949, this early experiment was not considered a success and C 16 was returned to black coal operation.
, increasingly heavy passenger trains and a shortage of suitable motive power saw the C class used as mainline passenger locomotives, a somewhat unusual assignment for a 2-8-0. To facilitate passenger working, their maximum allowable speed was raised from 50 mph (80 km/h) to 60 mph (96 km/h) on the key North Eastern, Ballarat, Bendigo and Geelong lines.
s.
With these new locomotives entering service, the ageing C class locomotives were progressively withdrawn from service, commencing with C 20 in June 1954. The last C class in service, C 7, was withdrawn in April 1962.
 C 10 was set aside for preservation on 18 May 1962, after having run 1160856 miles (1,868,212 km) during its career on the VR. It is today preserved at the ARHS
C 10 was set aside for preservation on 18 May 1962, after having run 1160856 miles (1,868,212 km) during its career on the VR. It is today preserved at the ARHS
North Williamstown Railway Museum.
2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels...
'Consolidation' type that ran on the Victorian Railways
Victorian Railways
The Victorian Railways operated railways in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1983. The first railways in Victoria were private companies, but when these companies failed or defaulted, the Victorian Railways was established to take over their operations...
between 1918 and 1962. Although its original design had some key shortcomings, a number of improvements were made over the class' long career on the VR, many of which were subsequently applied to other locomotive classes on the system.
History
Designed by Chief Mechanical Engineer W. M. Shannon, the C class was the first goods locomotive designed and built entirely in-house by the Victorian Railways Newport Workshops, following on from the successful DdVictorian Railways Dd class
The Dd class was a passenger and mixed traffic steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1902 to 1974...
and A2 class
Victorian Railways A2 class
The A2 class was an express passenger locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1907 to 1963. A highly successful design entirely the work of Victorian Railways' own design office, its long service life was repeatedly extended as economic depression and war delayed the introduction of more...
passenger locomotives. When introduced in 1918, they were the heaviest and most powerful steam locomotives in Australia.
Production
The prototype locomotive C 1 was the last locomotive to be painted in the Victorian Railways 'Canadian Red' scheme. Locomotive C 2 was the first new locomotive finished in the new VR livery of plain, unrelieved black. It was the first of a further 25 C class members also built at Newport Workshops between 1921 and 1926.Design improvements
In practice, the C class was initially a somewhat less successful design than the A2. Key shortcomings included a very long, 9 in 7 in (2.92 m) manually stoked firebox that was difficult to fire and prone to clinkering, and an undersized boiler. The locomotives tended to run out of steam when worked hard.In an attempt to rectify these problems, locomotive C 5 was fitted in 1933 with a new front end, based on the Association of American Railroads
Association of American Railroads
The Association of American Railroads is an industry trade group representing primarily the major freight railroads of North America . Amtrak and some regional commuter railroads are also members...
(AAR) design of self-cleaning smokebox
Smokebox
A smokebox is one of the major basic parts of a Steam locomotive exhaust system. Smoke and hot gases pass from the firebox through tubes where they pass heat to the surrounding water in the boiler. The smoke then enters the smokebox, and is exhausted to the atmosphere through the chimney .To assist...
, to improve steaming qualities. The results were very promising and led to further experimental work, using A2 class locomotive A2 998 as a test bed and conducted under the direction of VR Rolling Stock branch engineer Edgar Brownbill, in streamlining the steam passages and other changes to reduce back pressure on the exhaust side and increase efficiency. These changes, referred to as 'Modified Front End', were such an improvement that the rest of the A2 and C classes were progressively modified, as well as all of the K
Victorian Railways K class
The K class was a branch line steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1922 to 1979. Although its design was entirely conventional and its specifications unremarkable, the K class was in practice a remarkably versatile and dependable locomotive...
, N
Victorian Railways N class
The N class was a branch line steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1925 to 1966. A development of the successful K class 2-8-0, it was the first VR locomotive class designed for possible conversion from 5 ft 3 in broad gauge to 4 ft 8½ in standard gauge.-History:In 1923, in...
, S
Victorian Railways S class
The S class was an express passenger steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1928 to 1954. Built when the VR was at its zenith and assigned to haul premier interstate express passenger services, the S class remained the VR's most prestigious locomotive class until the advent of diesel...
and X
Victorian Railways X class
The X class was a mainline goods locomotive of the 2-8-2 'Mikado' type that ran on the Victorian Railways between 1929 and 1961. They were the most powerful goods locomotive on the VR until the advent of diesel-electric traction, and operated over the key Bendigo, Wodonga, and Gippsland...
classes.
In 1929, C 5 also became the first VR locomotive to be fitted with a cross-compound air compressor, which was also subsequently adopted across other VR locomotive classes. The C class was also the first goods locomotive to be fitted with Automatic Staff Exchange apparatus, given their frequent used on express goods and fruit services.
As the poor quality of coal available after World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
exacerbated the problems of firing the C class and industrial action in the mines threatened supply, the entire class was converted to oil firing from 1946 onwards following an initial conversion of C 15 in 1946. Despite the success of the conversion, C class locomotives were still prone to running out of steam when pushed on long rising gradients.
Whereas other VR locomotives to receive Modified Front End treatment had been equipped with smoke deflectors
Smoke deflectors
Smoke deflectors are vertical plates attached to the front of a steam locomotive on each side of the smokebox. They are designed to lift smoke away from the locomotive at speed so that the driver has better visibility unimpaired by drifting smoke....
in the 1930s, it was not until 1947 that the VR finally developed a successful design of smoke deflector for the C class, based on the German "Witte" pattern. This design was then adopted for the final Newport-built N class
Victorian Railways N class
The N class was a branch line steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1925 to 1966. A development of the successful K class 2-8-0, it was the first VR locomotive class designed for possible conversion from 5 ft 3 in broad gauge to 4 ft 8½ in standard gauge.-History:In 1923, in...
locomotives as well as the last two steam locomotive classes on the VR, the R
Victorian Railways R class
The R class was an express passenger steam locomotive that ran on Australia's Victorian Railways from 1951 to 1974. A long overdue replacement for the 1907-era A2 class 4-6-0, their development and construction was repeatedly delayed due to financial constraints caused by the Great Depression and...
and J
Victorian Railways J class
The J class was a branch line steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1954 to 1972. A development of the successful Victorian Railways K class 2-8-0, it was the last new class of steam locomotive introduced on the VR...
classes.
Experimental use of pulverised brown coal

Latrobe Valley
The Latrobe Valley is an inland geographical region and urban area of Gippsland in the state of Victoria, Australia. It is east of the City Of Melbourne and nestled between the Strzelecki Ranges to the south and the Great Dividing Range to the north – with the highest peak to the north of the...
. Unlike the later conversion of X class
Victorian Railways X class
The X class was a mainline goods locomotive of the 2-8-2 'Mikado' type that ran on the Victorian Railways between 1929 and 1961. They were the most powerful goods locomotive on the VR until the advent of diesel-electric traction, and operated over the key Bendigo, Wodonga, and Gippsland...
locomotive X 32 to PBC firing in 1949, this early experiment was not considered a success and C 16 was returned to black coal operation.
Passenger use
During World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, increasingly heavy passenger trains and a shortage of suitable motive power saw the C class used as mainline passenger locomotives, a somewhat unusual assignment for a 2-8-0. To facilitate passenger working, their maximum allowable speed was raised from 50 mph (80 km/h) to 60 mph (96 km/h) on the key North Eastern, Ballarat, Bendigo and Geelong lines.
Withdrawal
The postwar rebuilding of Victorian Railways in the late 1940s and early 1950s saw the order of hundreds of new locomotives of superior design to the C class, culminating in the delivery of B class mainline diesel electric and L class mainline electric locomotiveElectric locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or an on-board energy storage device...
s.
With these new locomotives entering service, the ageing C class locomotives were progressively withdrawn from service, commencing with C 20 in June 1954. The last C class in service, C 7, was withdrawn in April 1962.
Preservation

Australian Railway Historical Society
The Australian Railway Historical Society was founded in Sydney in 1933 as The Australasian Railway and Locomotive Historical Society. It aims to foster an interest in the railways, and record and preserve many facets of railway operations. Membership now exceeds 2,500, with Divisions in every...
North Williamstown Railway Museum.

