
Victorian Railways A2 class
Encyclopedia
The A2 class was an express passenger locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways
from 1907 to 1963. A highly successful design entirely the work of Victorian Railways' own design office, its long service life was repeatedly extended as economic depression and war delayed the introduction of more modern and powerful replacement locomotives.
A2 locomotives were built between 1907 and 1915. The design was then altered to incorporate larger diameter cylinders, a higher pressure boiler and Walschaerts valve gear, and a further 60 locomotives of this design were produced between 1915 and 1922.
and Geelong from 90 minutes to 63 and finally 55 minutes, a time not significantly improved upon until the introduction of 160 km/h Regional Fast Rail
services in 2006.
A2s were also used to haul a number of special services, such as the Royal Trains
for the Prince of Wales
' and the Duke of York
's Australian tours in 1920 and 1927 respectively. Towards the end of their lives, A2 995 and 996 also had the distinction of hauling the last broad gauge
Spirit of Progress
service into Melbourne on 16 April 1962.
With their comparatively high tractive effort
(the Walschaerts A2 had a higher nominal tractive effort than any other VR locomotive, regardless of type, until the introduction of the C class
2-8-0
of 1918) they also saw widespread use as a fast goods locomotive, particularly in their later life.
Although initially limited to principle mainlines due to their comparatively heavy axle load
, gradual upgrades to secondary lines saw the route availability of the class expand, together with the range of services they hauled.
In 1928, the A2 was replaced on the principal North-eastern line Sydney Limited and Albury Express services by the considerably more powerful three-cylinder S class
Pacifics
. However, new locomotive development ground to a halt during the 1930s as the Great Depression
severely affected both VR traffic volumes and operating revenues, and the A2 continued as the main express passenger power on all other VR mainlines.
s, and to differentiate between the two variants the saturated steam locomotives were renumbered as A1 class, each being reclassified as A2 class again when fitted with a superheater. The last of the A1 class, No. 808, was converted in October 1949.
Experiments were conducted in 1923-4 with A2 800 using Pulverised Brown Coal
(PBC) burning equipment, however the experiment was discontinued and the locomotive returned to black coal operation.
The A2 class, along with other post-1900 VR steam locomotive designs, was equipped with electric lighting from 1926 onwards. Automatic Staff Exchange equipment to allow non-stop high-speed running between track sections was also fitted from 1926 onwards.
heavy goods locomotive C 5 was equipped with a new front end, based on the Association of American Railroads
(AAR) design of self-cleaning smokebox
, to improve steaming qualities. The results were very promising, and in 1934 A2 998 was selected for a series of further tests aimed at further front end improvement, conducted under the direction of VR Rolling Stock branch engineer, Edgar Brownbill.
 Experiments based on the work of Dr Wagner of the Deutsche Reichsbahn
Experiments based on the work of Dr Wagner of the Deutsche Reichsbahn
and E. C. Young of the University of Illinois were conducted, with final modifications to the A2 locomotive including:
The sum result of these changes was a significant improvement in power and available tractive effort. Maximum drawbar horsepower increased some 40% from 860 HP at 26 mi/h to 1230 HP at 32 mi/h. The improvement was such that the VR was able to further accelerate services hauled by the A2, with the steeply graded 100+3/4 mi Melbourne to Bendigo express running time being cut from 162 to 145 minutes, and literally hours being cut from the schedule of the Melbourne to Adelaide Overland express.
Modified Front End was an extremely cost effective improvement given that it allowed the VR to defer new locomotive construction through improvements to existing locomotives that at the time cost just £
140 ($
280) per locomotive. It was so successful that not only was the entire A2 fleet converted during 1936-39, but also the C, K
, N
, S
and X class
locomotive fleets, and its principles were also incorporated into the design of all subsequent steam locomotives built for VR.
was fitted to A2 973. However, there was not sufficient improvement in efficiency for the equipment to be fitted to other locomotives and it was removed twelve years later.
With the reduced exhaust blast resulting from the revised smokebox, smoke deflectors were fitted to prevent drifting smoke from obscuring visibility.
In the years following World War II
, problems with the quality and availability of coal supplies caused VR to order the conversion of all 60 Walschaerts A2s to oil firing.
Late in their life, some of the A2s also received Boxpok
driving wheels as their conventional spoked wheels began to suffer fatigue cracks with age and mileage.
broke out. The massive increase in traffic on the VR the war effort brought saw these ageing locomotives subjected to a punishing regime of heavy utilisation and minimal maintenance.
 With VR's locomotive workshops switched to production of armaments and all available manpower given to the war effort, plans to eliminate the double-headed A2 operations on Melbourne-Adelaide passenger services with the introduction of more powerful H class
With VR's locomotive workshops switched to production of armaments and all available manpower given to the war effort, plans to eliminate the double-headed A2 operations on Melbourne-Adelaide passenger services with the introduction of more powerful H class
4-8-4
locomotives and additional S class locomotives did not come to fruition. The extra S class locomotives were never built and the line to Adelaide did not receive the necessary upgrades to take the weight of the H class.
The A2's principal express passenger role continued into the postwar years as the VR, struggling with a backlog of repairs and limited capital expenditure, deferred new passenger locomotive construction. It was not until March 1946 when the first of the class, A2 878, was withdrawn from service.
In 1951, when the first of 70 new R class
4-6-4
express passenger locomotives were introduced, the A2 was finally superseded. In 1953, no fewer than 53 A2s went to scrap, followed by 36 more in 1954. However, many of the class (particularly the later Walschaerts variants) continued on in secondary roles such as branch-line passenger and goods services and a number lasted into the 1960s. Their last regular mainline duty was hauling services between Flinders Street Station
and Leongatha
, on the South Gippsland line. The last in service, A2 986, was withdrawn on 2 December 1963, exactly 56 years after the original A2 572 entered service.
 Only one of the original batch of 125 Stephenson A2 locomotives survives; 1913-built A2 884 is today preserved at the ARHS
Only one of the original batch of 125 Stephenson A2 locomotives survives; 1913-built A2 884 is today preserved at the ARHS
North Williamstown Railway Museum, along with (Walschaerts) A2 995. The museum notes that A2 884 ran a total 1002624 miles (1,613,562.9 km) and A2 995 a total 1270404 miles (2,044,512 km) during their service lives.
A2 996 is preserved in Victorian regional city of Echuca and A2 964 is preserved in the Melbourne
suburb of Reservoir
.
A2 986 is currently being restored to full working order by Steamrail Victoria
.
Victorian Railways
The Victorian Railways operated railways in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1983. The first railways in Victoria were private companies, but when these companies failed or defaulted, the Victorian Railways was established to take over their operations...
from 1907 to 1963. A highly successful design entirely the work of Victorian Railways' own design office, its long service life was repeatedly extended as economic depression and war delayed the introduction of more modern and powerful replacement locomotives.
History
The introduction of the A2 class marked a turning point in Victorian Railways locomotive design, as it was entirely designed by VR engineers of the newly established Locomotive Design Section and the entire class built in-house at Victorian Railways workshops.Production
Based on the success of the prototype A2 572, a total of 125 Stephenson valve gearStephenson valve gear
The Stephenson valve gear or Stephenson link or shifting link is a simple design of valve gear that was widely used throughout the world for all kinds of steam engine. It is named after Robert Stephenson but was actually invented by his employees....
A2 locomotives were built between 1907 and 1915. The design was then altered to incorporate larger diameter cylinders, a higher pressure boiler and Walschaerts valve gear, and a further 60 locomotives of this design were produced between 1915 and 1922.
Regular service
For over forty years, the A2 was the main express passenger locomotive on the VR, hauling intrastate and interstate services. With a maximum permitted speed of 70 miles per hour (112.7 km/h) the A2 was instrumental in the acceleration of timetables on many lines in the years following its introduction. They famously ran the Geelong Flier service (the first "named" train in Victoria) slashing journey times between MelbourneMelbourne
Melbourne is the capital and most populous city in the state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia. The Melbourne City Centre is the hub of the greater metropolitan area and the Census statistical division—of which "Melbourne" is the common name. As of June 2009, the greater...
and Geelong from 90 minutes to 63 and finally 55 minutes, a time not significantly improved upon until the introduction of 160 km/h Regional Fast Rail
Regional Fast Rail project
The Regional Fast Rail project was a rail transport project of the State Government of Victoria, Australia undertaken between 2000 and 2006 aimed at improving the passenger services on the Victorian regional railway network , specifically to reduce travel times, enhance service frequency and...
services in 2006.
A2s were also used to haul a number of special services, such as the Royal Trains
Victorian Railways Royal Train
The Victorian Railways operated Royal Trains to transport members of the Monarchy of Australia on their Royal visits to Australia. The same carriages were also used for a number of vice-regal trains for the Governor-General of Australia and the Governor of Victoria...
for the Prince of Wales
Edward VIII of the United Kingdom
Edward VIII was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth, and Emperor of India, from 20 January to 11 December 1936.Before his accession to the throne, Edward was Prince of Wales and Duke of Cornwall and Rothesay...
' and the Duke of York
George VI of the United Kingdom
George VI was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until his death...
's Australian tours in 1920 and 1927 respectively. Towards the end of their lives, A2 995 and 996 also had the distinction of hauling the last broad gauge
Broad gauge
Broad-gauge railways use a track gauge greater than the standard gauge of .- List :For list see: List of broad gauges, by gauge and country- History :...
Spirit of Progress
Spirit of Progress
The Spirit of Progress was the premier express train passenger service on the Victorian Railways in Australia, running from Melbourne to the Victorian border, and later through to Sydney.-Route:...
service into Melbourne on 16 April 1962.
With their comparatively high tractive effort
Tractive effort
As used in mechanical engineering, the term tractive force is the pulling or pushing force exerted by a vehicle on another vehicle or object. The term tractive effort is synonymous with tractive force, and is often used in railway engineering to describe the pulling or pushing capability of a...
(the Walschaerts A2 had a higher nominal tractive effort than any other VR locomotive, regardless of type, until the introduction of the C class
Victorian Railways C class
The C class was a mainline goods locomotive of the 2-8-0 'Consolidation' type that ran on the Victorian Railways between 1918 and 1962. Although its original design had some key shortcomings, a number of improvements were made over the class' long career on the VR, many of which were subsequently...
2-8-0
2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels...
of 1918) they also saw widespread use as a fast goods locomotive, particularly in their later life.
Although initially limited to principle mainlines due to their comparatively heavy axle load
Axle load
The axle load of a wheeled vehicle is the total weight felt by the roadway for all wheels connected to a given axle. Viewed another way, it is the fraction of total vehicle weight resting on a given axle...
, gradual upgrades to secondary lines saw the route availability of the class expand, together with the range of services they hauled.
In 1928, the A2 was replaced on the principal North-eastern line Sydney Limited and Albury Express services by the considerably more powerful three-cylinder S class
Victorian Railways S class
The S class was an express passenger steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1928 to 1954. Built when the VR was at its zenith and assigned to haul premier interstate express passenger services, the S class remained the VR's most prestigious locomotive class until the advent of diesel...
Pacifics
4-6-2
4-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .These locomotives are also known as Pacifics...
. However, new locomotive development ground to a halt during the 1930s as the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
severely affected both VR traffic volumes and operating revenues, and the A2 continued as the main express passenger power on all other VR mainlines.
Design Improvements
The majority of A2 locomotives were originally built with saturated steam boilers. The class were gradually fitted with superheaterSuperheater
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam or wet steam into dry steam used for power generation or processes. There are three types of superheaters namely: radiant, convection, and separately fired...
s, and to differentiate between the two variants the saturated steam locomotives were renumbered as A1 class, each being reclassified as A2 class again when fitted with a superheater. The last of the A1 class, No. 808, was converted in October 1949.
Experiments were conducted in 1923-4 with A2 800 using Pulverised Brown Coal
Lignite
Lignite, often referred to as brown coal, or Rosebud coal by Northern Pacific Railroad,is a soft brown fuel with characteristics that put it somewhere between coal and peat...
(PBC) burning equipment, however the experiment was discontinued and the locomotive returned to black coal operation.
The A2 class, along with other post-1900 VR steam locomotive designs, was equipped with electric lighting from 1926 onwards. Automatic Staff Exchange equipment to allow non-stop high-speed running between track sections was also fitted from 1926 onwards.
Modified front end
In 1933, C classVictorian Railways C class
The C class was a mainline goods locomotive of the 2-8-0 'Consolidation' type that ran on the Victorian Railways between 1918 and 1962. Although its original design had some key shortcomings, a number of improvements were made over the class' long career on the VR, many of which were subsequently...
heavy goods locomotive C 5 was equipped with a new front end, based on the Association of American Railroads
Association of American Railroads
The Association of American Railroads is an industry trade group representing primarily the major freight railroads of North America . Amtrak and some regional commuter railroads are also members...
(AAR) design of self-cleaning smokebox
Smokebox
A smokebox is one of the major basic parts of a Steam locomotive exhaust system. Smoke and hot gases pass from the firebox through tubes where they pass heat to the surrounding water in the boiler. The smoke then enters the smokebox, and is exhausted to the atmosphere through the chimney .To assist...
, to improve steaming qualities. The results were very promising, and in 1934 A2 998 was selected for a series of further tests aimed at further front end improvement, conducted under the direction of VR Rolling Stock branch engineer, Edgar Brownbill.

Deutsche Reichsbahn
Deutsche Reichsbahn was the name of the following two companies:* Deutsche Reichsbahn, the German Imperial Railways during the Weimar Republic, the Third Reich and the immediate aftermath...
and E. C. Young of the University of Illinois were conducted, with final modifications to the A2 locomotive including:
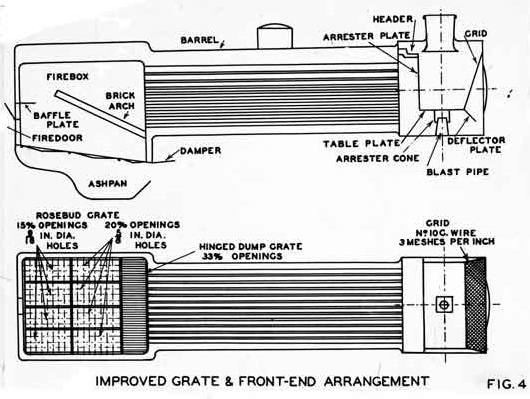
- Revision of exhaust nozzle and chimney position and diameter using Wagner's recommended ratios, with a larger 23 in (584.2 mm) diameter funnel and 6 in (152.4 mm) diameter, low exhaust nozzle replacing the original 18+1/2 in diameter narrow flanged chimney and 5+1/2 in diameter, high exhaust nozzle
- Revision to the firebox grate with fitting of a "rosebud" type grate with reduced air openings to improve fire stability under heavy load and give better firing qualities
- Replacement of full length 1+3/8 in return bend superheater elements with 8 in 6 in (2.59 m) long 1+1/2 in elements
The sum result of these changes was a significant improvement in power and available tractive effort. Maximum drawbar horsepower increased some 40% from 860 HP at 26 mi/h to 1230 HP at 32 mi/h. The improvement was such that the VR was able to further accelerate services hauled by the A2, with the steeply graded 100+3/4 mi Melbourne to Bendigo express running time being cut from 162 to 145 minutes, and literally hours being cut from the schedule of the Melbourne to Adelaide Overland express.
Modified Front End was an extremely cost effective improvement given that it allowed the VR to defer new locomotive construction through improvements to existing locomotives that at the time cost just £
Australian pound
The pound was the currency of Australia from 1910 until 13 February 1966, when it was replaced by the Australian dollar. It was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence.- Earlier Australian currencies :...
140 ($
Australian dollar
The Australian dollar is the currency of the Commonwealth of Australia, including Christmas Island, Cocos Islands, and Norfolk Island, as well as the independent Pacific Island states of Kiribati, Nauru and Tuvalu...
280) per locomotive. It was so successful that not only was the entire A2 fleet converted during 1936-39, but also the C, K
Victorian Railways K class
The K class was a branch line steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1922 to 1979. Although its design was entirely conventional and its specifications unremarkable, the K class was in practice a remarkably versatile and dependable locomotive...
, N
Victorian Railways N class
The N class was a branch line steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1925 to 1966. A development of the successful K class 2-8-0, it was the first VR locomotive class designed for possible conversion from 5 ft 3 in broad gauge to 4 ft 8½ in standard gauge.-History:In 1923, in...
, S
Victorian Railways S class
The S class was an express passenger steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1928 to 1954. Built when the VR was at its zenith and assigned to haul premier interstate express passenger services, the S class remained the VR's most prestigious locomotive class until the advent of diesel...
and X class
Victorian Railways X class
The X class was a mainline goods locomotive of the 2-8-2 'Mikado' type that ran on the Victorian Railways between 1929 and 1961. They were the most powerful goods locomotive on the VR until the advent of diesel-electric traction, and operated over the key Bendigo, Wodonga, and Gippsland...
locomotive fleets, and its principles were also incorporated into the design of all subsequent steam locomotives built for VR.
Other changes
In 1935 an experimental A.C.F.I. (Accessoires pour les Chemins de Fer et l'Industrie) feedwater heaterFeedwater heater
A feedwater heater is a power plant component used to pre-heat water delivered to a steam generating boiler. Preheating the feedwater reduces the irreversibilities involved in steam generation and therefore improves the thermodynamic efficiency of the system...
was fitted to A2 973. However, there was not sufficient improvement in efficiency for the equipment to be fitted to other locomotives and it was removed twelve years later.
With the reduced exhaust blast resulting from the revised smokebox, smoke deflectors were fitted to prevent drifting smoke from obscuring visibility.
In the years following World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, problems with the quality and availability of coal supplies caused VR to order the conversion of all 60 Walschaerts A2s to oil firing.
Late in their life, some of the A2s also received Boxpok
Boxpok
A Boxpok is a steam locomotive wheel that gains its strength through being made of a number of box sections rather than having traditional solid spokes . Being hollow, they allow better counterbalancing than conventional drivers, which is important for fast locomotives...
driving wheels as their conventional spoked wheels began to suffer fatigue cracks with age and mileage.
Later Years
In 1939, by which time most of the class was already over twenty-five years old, World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
broke out. The massive increase in traffic on the VR the war effort brought saw these ageing locomotives subjected to a punishing regime of heavy utilisation and minimal maintenance.

Victorian Railways H class
The H class was an express passenger steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1941 to 1958. Intended to eliminate the use of double heading A2 class locomotives on Overland services on the steeply graded Western line to Adelaide, wartime restrictions led to only one locomotive being built...
4-8-4
4-8-4
Under the Whyte notation classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles .Other equivalent classifications are:UIC classification: 2D2...
locomotives and additional S class locomotives did not come to fruition. The extra S class locomotives were never built and the line to Adelaide did not receive the necessary upgrades to take the weight of the H class.
The A2's principal express passenger role continued into the postwar years as the VR, struggling with a backlog of repairs and limited capital expenditure, deferred new passenger locomotive construction. It was not until March 1946 when the first of the class, A2 878, was withdrawn from service.
In 1951, when the first of 70 new R class
Victorian Railways R class
The R class was an express passenger steam locomotive that ran on Australia's Victorian Railways from 1951 to 1974. A long overdue replacement for the 1907-era A2 class 4-6-0, their development and construction was repeatedly delayed due to financial constraints caused by the Great Depression and...
4-6-4
4-6-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles .Other equivalent classifications are:UIC classification:...
express passenger locomotives were introduced, the A2 was finally superseded. In 1953, no fewer than 53 A2s went to scrap, followed by 36 more in 1954. However, many of the class (particularly the later Walschaerts variants) continued on in secondary roles such as branch-line passenger and goods services and a number lasted into the 1960s. Their last regular mainline duty was hauling services between Flinders Street Station
Flinders Street Station
Flinders Street Station is the central railway station of the suburban railway network of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. It is on the corner of Flinders and Swanston Streets next to the Yarra River in the heart of the city, stretching from Swanston Street to Queen Street and covering two city...
and Leongatha
Leongatha railway station, Victoria
Leongatha is a railway station in the town of Leongatha, Victoria on the former South Gippsland railway line in South Gippsland, Victoria, Australia.The station opened in 1891 as a terminus, the line being extended to Welshpool the next year...
, on the South Gippsland line. The last in service, A2 986, was withdrawn on 2 December 1963, exactly 56 years after the original A2 572 entered service.
Accidents
Some A2 locomotives were unfortunate enough to be involved in major accidents:- At 2:58am on 7 September 1951, the westbound and eastbound Overland expresses, both hauled by double-headingDouble-headingIn railroad terminology, double-heading or double heading indicates the use of two locomotives at the front of a train, each operated individually by its own crew. The practice of triple-heading involves the use of three locomotives....
A2s, collided head-on at Serviceton. All four locomotives were written off; three were so badly damaged they were scrapped on site.
- Australia's worst level crossingLevel crossingA level crossing occurs where a railway line is intersected by a road or path onone level, without recourse to a bridge or tunnel. It is a type of at-grade intersection. The term also applies when a light rail line with separate right-of-way or reserved track crosses a road in the same fashion...
accident occurred on 8 May 1943, when A2 863 collided with a bus carrying troops at Wodonga. 25 people were killed.
Preservation

Australian Railway Historical Society
The Australian Railway Historical Society was founded in Sydney in 1933 as The Australasian Railway and Locomotive Historical Society. It aims to foster an interest in the railways, and record and preserve many facets of railway operations. Membership now exceeds 2,500, with Divisions in every...
North Williamstown Railway Museum, along with (Walschaerts) A2 995. The museum notes that A2 884 ran a total 1002624 miles (1,613,562.9 km) and A2 995 a total 1270404 miles (2,044,512 km) during their service lives.
A2 996 is preserved in Victorian regional city of Echuca and A2 964 is preserved in the Melbourne
Melbourne
Melbourne is the capital and most populous city in the state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia. The Melbourne City Centre is the hub of the greater metropolitan area and the Census statistical division—of which "Melbourne" is the common name. As of June 2009, the greater...
suburb of Reservoir
Reservoir, Victoria
Reservoir is a suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 12 km north from Melbourne's central business district. Its Local Government Area is the City of Darebin. At the 2006 Census, Reservoir had a population of 45,970....
.
A2 986 is currently being restored to full working order by Steamrail Victoria
Steamrail Victoria
Steamrail Victoria is a not-for-profit volunteer group established in 1965 to the restore and operate historic locomotives and rolling stock used on the railways in Victoria, Australia. The main depot of the group is at the Newport Railway Workshops in suburban Melbourne...
.
External links
- Dee et al., Power Parade, VicRail Public Relations Division, Melbourne, 1981, ISBN 0-7241-3323-2
- Pearce et al., North Williamstown Railway Museum, ARHS, Melbourne, 1980, ISBN 0-85849-018-8
- The Recorder, ARHS, Adelaide, November 1985, ISSN 0158-1856
- AHRS Railway Museum History 1900 - 1950 retrieved on 6 September 2006
- National Library of Australia Photograph of prototype A2 572, December 1907
- victorianrailways.net Stephenson A2 936 hauling a goods train, 11 June 1930.
- victorianrailways.net Walschaerts A2 973 leads a Stephenson A2 on The Overland, circa 1930
- Public Record Office Victoria Classic VR photograph of A2-hauled passenger train with E type carriageE type carriageThe E type carriages were wooden express passenger carriage used on the railways of Victoria, Australia. Introduced by Victorian Railways Chairman of Commissioners Thomas James Tait and based on Canadian carriage design, the class remained in regular service for 85 years.-Design:Carriages on...
s crossing the MalmsburyMalmsbury, VictoriaMalmsbury is a town in central Victoria, Australia. It lies on the Old Calder Highway , 96 km north west of the state capital, Melbourne and 11 km north west of Kyneton. Situated close by the Coliban River, Malmsbury has a population of 587...
viaduct, 1945 - Public Record Office Victoria The end of the line - A2 856 is cut up for scrap.
- victorianrailways.net A2 986, seen around 1962 near the end of its service life. Various modifications over the years have significantly altered its appearance from when photographed in 1916 (see top of this page)
- Steamrail A2 986 page Photos detailing the progress of current restoration work on A2 986

